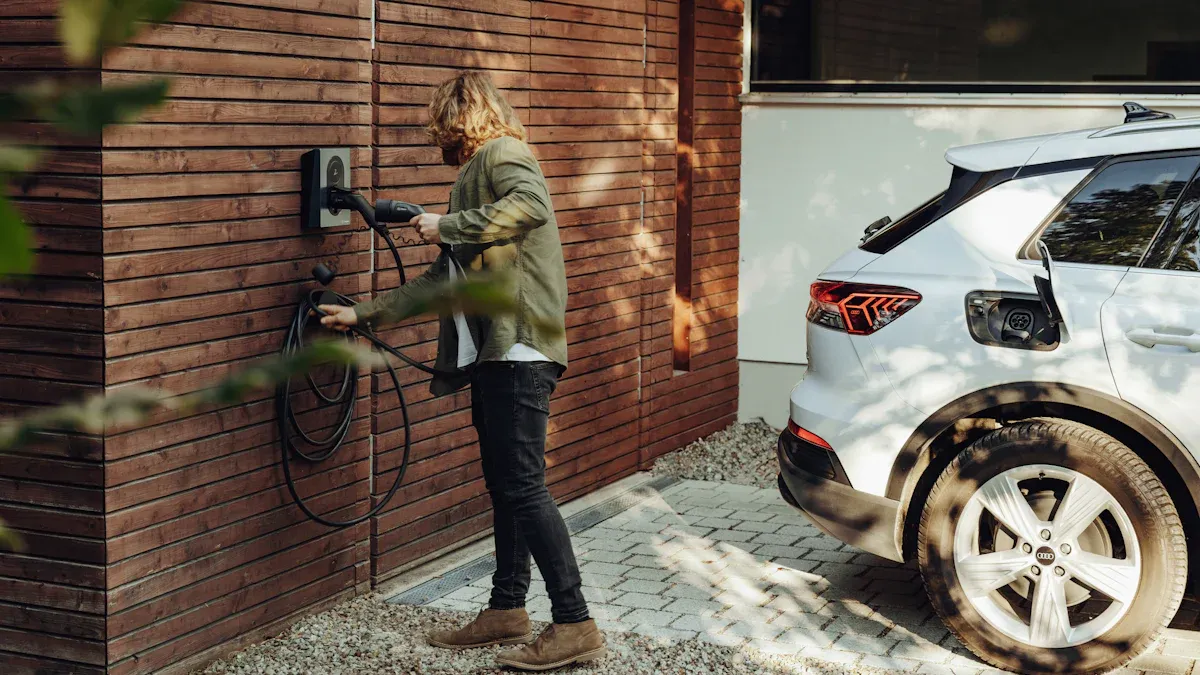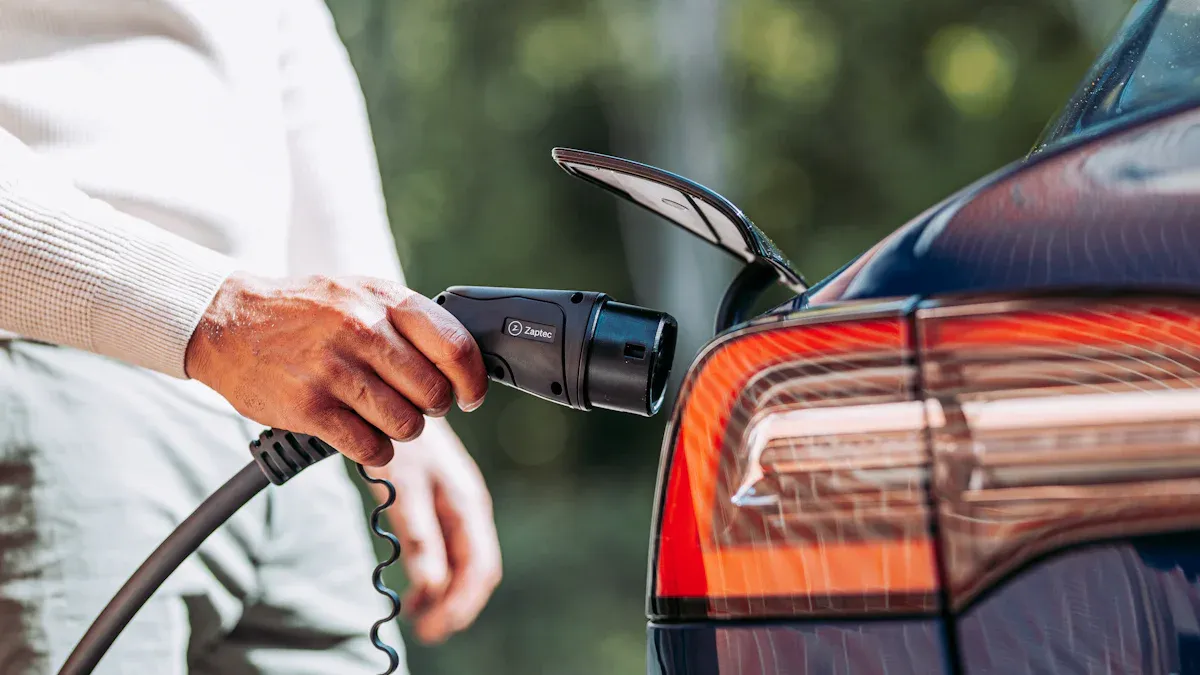
An electric vehicle owner can plug an EV into a standard 120V household outlet. This method is the slowest for charging an electric vehicle. It has important limitations. This process, known as Level 1 charging, serves as a backup or occasional option. It is not a primary solution for daily driving needs. Understanding its slow speed, safety requirements, and practical uses is crucial before using a regular outlet.
As the electric vehicle market grows, with EV sales reaching 13% of new sales in September, more drivers encounter this charging question.
| Period | EV Share of New Sales |
|---|---|
| September (New EV Sales) | 13% |
| Q3 Average | 10.5% |
| Q2 Average | 7% |
Not: Using a regular outlet for charging an EV requires careful consideration. This Level 1 charging method offers convenience but lacks the speed of dedicated EV şarj cihazı installations from various Elektrikli araç şarj cihazı üreticileri. For most EV owners, taşınabilir elektrikli araç şarj cihazları and regular outlet charging are best reserved for emergencies, not routine use. The right Elektrikli araç şarj çözümleri depend on driving habits and access to faster options.
What is Level 1 Charging with a Regular Outlet?
Seviye 1 şarj is the most basic method for powering an electric vehicle. It utilizes standard home electricity without any special equipment installation. This approach involves plugging the vehicle directly into a common wall outlet, the same kind used for lamps and laptops. Understanding the components and power limitations is key to using this charging method effectively.
The Basics of Your Standard Household Outlet
Understanding 120-Volt Power
The standard household outlet in North America delivers 120-volt (120V) alternating current (AC) power. This level of voltage is sufficient for most small electronics and appliances. For an EV, it provides a slow but steady trickle of energy. This method of charging is convenient because these outlets are ubiquitous. However, the low power output makes Level 1 charging a time-intensive process, best suited for specific situations rather than daily use. Using a regular outlet for charging an EV requires patience.
The NEMA 5-15 Plug Explained
The plug and outlet combination for this type of charging is officially known as NEMA 5-15. An owner can identify this standard outlet by its distinct three-prong configuration.
- One taller, neutral slot
- One shorter, “hot” slot
- One round ground pin below the two slots
This design is the most common electrical outlet found in homes across the United States and Canada. Its universal presence is what makes Level 1 charging so accessible.
The Equipment You Need to Plug an EV In
The Mobile Connector Cord
To plug an EV into a regular outlet, the owner needs a specific piece of equipment called a mobile connector. Most electric vehicle manufacturers include this cord with a new vehicle purchase. This portable charger has a standard NEMA 5-15 plug on one end to connect to the wall outlet. The other end has a J1772 connector, which plugs into the vehicle’s charging port. The cord’s internal electronics manage the flow of electricity safely.
Yerleşik Şarj Cihazının Rolü
The mobile connector cord itself is not the only charger involved. Every EV has an onboard charger built into the vehicle. This essential component converts the 120V AC power from a regular outlet into direct current (DC) power, which the vehicle’s battery can store.
Not: This conversion process is not 100% efficient. The onboard charger in an EV typically operates with an efficiency between 75% and 95%. This means some energy is lost as heat during the AC-to-DC conversion, so not all the power from the outlet makes it into the battery.
The Reality of Level 1 Charging Speed
The primary drawback of using a regular outlet for an electric vehicle is its extremely slow charging speed. While convenient, Level 1 charging provides only a trickle of power to the vehicle’s battery. This method is often insufficient for the daily needs of an average EV driver. Understanding the exact rate of charge and what that means in practical terms is essential.
How Slow Is It, Really?
The speed of Level 1 charging can be surprising to new electric vehicle owners. The low power output from a standard 120V outlet limits how quickly the onboard charger can replenish the battery. This slow pace makes it a method best suited for patience and specific use cases.
Miles of Range Gained Per Hour
Using a regular outlet, an EV owner can typically expect to add between 3 to 5 miles of range for every hour of charging. This rate can vary slightly based on the vehicle’s efficiency and the ambient temperature.
- Araç Verimliliği: Larger, less efficient models may gain closer to 3 miles per hour.
- Temperature: Colder weather can reduce charging efficiency, resulting in slower range addition.
This slow replenishment rate highlights why Seviye 1 şarj is not a practical solution for drivers who need to add significant range quickly.
Calculating Your Total Charge Time
An owner can estimate the total charging time with a simple calculation. The formula provides a clear picture of the time commitment required when using a standard outlet.
Formula for Estimating Charge Time:
(Miles of Range Needed) / (Average Miles Gained Per Hour) = Total Charging Hours
For example, to add 100 miles of range at a rate of 4 miles per hour, the calculation would be 100 / 4 = 25 hours. A full charge for an EV with a 250-mile battery could take more than two full days.
Real-World Charging Scenarios
While slow, Level 1 charging has a place in certain situations. Its effectiveness depends entirely on the driver’s daily mileage and how long the vehicle remains parked.
The Overnight “Top-Up”
For drivers with short commutes, an overnight charge using a regular outlet can be sufficient. A typical daily commute of 40 miles requires approximately 8 to 10 hours of Level 1 charging to replenish the used range. An owner can plug their ev in when they get home from work and have it ready for the next day’s commute. This scenario works well for those who consistently drive less than 40-50 miles per day and can dedicate a long, uninterrupted charging session each night.
The Weekend “Full Charge”
Another practical scenario is using the weekend to perform a deep charge. If an ev is parked on a Friday evening and left plugged into an outlet until Monday morning, it can gain a substantial amount of range. This long-duration charging session is ideal for catching up on a weekly range deficit.
| Charging Duration | Average Range Gained (at 4 mph) |
|---|---|
| 24 Hours (1 Day) | ~96 Miles |
| 48 Hours (2 Days) | ~192 Miles |
This table shows that while a full charge from empty is difficult, a weekend can restore a significant portion of the battery’s capacity, making the car ready for the week ahead without needing a faster charger.
Is Charging an Electric Car with a Regular Outlet Safe?
Charging an electric car with a regular outlet can be safe, but it demands careful attention to the home’s electrical infrastructure. An electric vehicle draws a significant amount of power continuously for many hours. This sustained load places much more stress on a circuit than a typical appliance. An owner must verify that the wiring, outlet, and circuit are in excellent condition to ensure safety and prevent potential hazards like electrical fires.
Essential Safety Checks for Your Home
Before an owner plugs their ev in, performing a few essential safety checks is non-negotiable. These steps help mitigate the risks associated with the long, continuous power draw required for charging. Ignoring these checks can compromise the safety of the home and the vehicle.
Why You Need a Dedicated Circuit
The most critical safety measure is using a özel devre. An EV charger is classified by the National Electrical Code (NEC) as a “continuous load,” meaning it can operate for three or more hours at maximum current. This classification comes with strict safety requirements.
- 125% Sizing Rule: The NEC mandates that circuits and breakers for continuous loads must be rated for 125% of the charger’s maximum current. This rule prevents components from overheating during long charging sessions.
- Özel Devre: The outlet used for charging must be on its own circuit. No other appliances or lights should share this circuit. This isolation prevents overloading and ensures the electric vehicle receives stable power.
These requirements are in place to handle the unique demands of charging an electric car safely.
How to Inspect Your Outlet’s Condition
The physical condition of the wall outlet is another crucial safety factor. A worn or damaged outlet cannot safely handle the sustained load from charging. An owner should inspect the regular outlet for any signs of wear or damage.
- Loose Contacts: The plug from the mobile connector should fit snugly into the outlet. A loose connection can cause arcing and dangerous heat buildup.
- Discoloration: Brown or black marks around the outlet slots are clear indicators of overheating and heat damage.
- Cracks or Damage: Any visible cracks on the faceplate suggest the outlet’s structural integrity is compromised and it should be replaced.
Profesyonel İpucu: Electrical installations degrade over time. Experts recommend that owner-occupied homes have their electrical systems inspected every 10 years. Using a newer, high-quality branded outlet can also ensure a better connection and reduce overheating risks.
The Dangers of Standard Extension Cords
Official electrical safety organizations explicitly advise against using a standard, household extension cord for charging. These cords are not designed for the high, continuous power flow needed for an EV. Using one creates a significant fire hazard due to several risks, including overheating and voltage drops. An owner should invest in a longer, type-approved charging cable or reposition the vehicle closer to the regular outlet.
When to Call a Professional Electrician
Some warning signs indicate that a home’s electrical system is not equipped for the demands of charging. In these cases, an owner must contact a qualified electrician immediately to assess the situation and perform necessary upgrades.
Signs of an Overloaded Circuit
An overloaded circuit is a serious danger. During a charging session, an owner should be aware of any of the following warning signs:
- Frequently tripping circuit breakers
- Flickering or dimming lights elsewhere in the house
- A buzzing sound from the outlet or electrical panel
- A burning smell near the outlet or panel
These symptoms indicate the circuit cannot handle the load, and continuing to use it for charging is unsafe.
Assessing Old or Faulty Wiring
Older homes, particularly those built before modern wiring standards, may have electrical systems incapable of supporting EV charging from a regular outlet. The wiring gauge might be too small, or the insulation may have degraded over time. A professional electrician can assess the wiring’s condition, identify any deficiencies, and determine what upgrades are necessary to meet current safety requirements for charging.
What About Extension Cords for EV Charging?
An owner might be tempted to grab a standard extension cord to bridge the gap between their electric vehicle and a distant outlet. However, this common household tool is not suitable for the demands of EV charging and can introduce serious risks. Using the correct type of cord and following strict safety protocols is essential.
Standart Kordonlar Neden Yangın Tehlikesi Oluşturur?
Most extension cords found in a garage or home are designed for temporary, low-power tasks like running a leaf blower or holiday lights. They cannot handle the sustained, high-current load required for elektrikli bir aracın şarj edilmesi.
Understanding Wire Gauge and Amperage
The primary danger lies in the cord’s construction. Wire thickness is measured by its gauge, where a lower number indicates a thicker wire capable of carrying more electrical current (amperage).
- Standard Cords: Often use thin, high-gauge wires (e.g., 16-gauge) designed for low amperage.
- EV Charging: Bir EV şarj cihazı pulls a high, continuous current (around 12 amps) for many hours.
Pushing this much current through a thin wire is like forcing a river through a garden hose. The wire simply cannot handle the flow.
The Risk of Overheating
This mismatch between the charger’s power draw and the cord’s capacity leads to a dangerous outcome: overheating. The cord can become hot to the touch, causing its plastic insulation to melt. This exposes the live wires, creating a significant risk of electrical shock and fire. For this reason, using a standard extension cord for EV charging is strongly discouraged by safety experts. An owner should never use a regular household cord for this purpose.
Using Heavy-Duty, EV-Rated Cords Safely
For situations where reaching a regular outlet is impossible without an extension, only a heavy-duty, EV-rated cord is acceptable. These are specialty products engineered specifically for the high demands of charging.
What Makes an Extension Cord EV-Rated
An EV-rated cord is built to much higher standards than a regular one. These cords meet specific technical requirements for performance and safety. They feature robust construction designed for harsh environments and sustained high-current use.
| Şartname | Detail |
|---|---|
| Tel Ölçer | 1.5mmsq or 3x6mm² (Thick wire for high current) |
| Rated Current | Up to 32 Amps |
| Hava koşullarına dayanıklı | IP66 Rated (Dust-tight and protected from powerful jets of water) |
| Cable Type | H07RN-F Rubber Cable (Resistant to chemicals, impacts, and abrasion) |
| Sertifikalar | TUV, CE, UL94V-0 (Independently tested for safety) |
These features ensure the cord can safely manage the continuous load from an EV charger without overheating.
Best Practices for Occasional Use
Even with a proper EV-rated cord, an owner should treat its use as a temporary solution, not a permanent installation. Following best practices is crucial for safe operation.
Important: An EV-rated extension cord should only be used occasionally when no other option is available.
- Never plug an extension cord into another extension cord.
- Always plug directly into a wall outlet.
- Ensure the cord is fully unwound during charging to help dissipate heat.
- Use a dedicated regular outlet with no other appliances connected.
- Regularly inspect the plug and outlet for signs of warmth or discoloration.
- Consider using a plug-in socket tester to verify the outlet is wired correctly before the first charging session.
Adhering to these guidelines helps mitigate risks when using an extension cord for temporary charging needs.
When Does It Make Sense to Use a Regular Outlet?

Despite its slow speed, Level 1 charging has specific scenarios where it is a practical and logical choice. An owner must weigh the benefits of convenience against the significant time commitment. For some drivers and vehicle types, using a regular outlet for charging an electric car is a perfectly viable solution.
The Pros: When It’s a Good Option
Using a standard wall outlet offers distinct advantages, primarily centered around cost and accessibility. These benefits make it an attractive option for certain users.
No Installation Costs
The most significant advantage is the complete avoidance of installation costs. An owner can plug an ev directly into an existing outlet without needing to hire an electrician or purchase expensive hardware. This makes the initial transition to an electric vehicle more affordable.
Ultimate Convenience and Portability
Bu mobile connector that comes with most EVs provides ultimate convenience and portability. An owner can charge their electric vehicle anywhere a standard outlet is available, such as at a friend’s house, a vacation rental, or a workplace. This flexibility ensures a charging option is almost always nearby.
Ideal for Low-Mileage Drivers and PHEVs
Using a regular outlet is an excellent match for Plug-in Hybrid Electric Vehicles (PHEVs) and drivers with short daily commutes.
- PHEVs have smaller batteries, often providing up to 50 miles of electric range.
- A full charging session for a PHEV can take just 2-4 hours with a standard outlet.
- An eight-hour overnight charging session provides about 30-40 miles of range, which is more than enough to replenish the battery of a PHEV or cover the daily driving needs of a low-mileage EV driver.
This makes slow charging a common and effective method for these specific use cases.
The Cons: The Major Drawbacks
The limitations of using a regular outlet are significant. These drawbacks often make it an impractical primary charging solution for the average battery-electric vehicle owner.
Impractically Slow for Most Drivers
The slow charging speed is the primary disadvantage. For drivers who commute long distances or need to add substantial range quickly, waiting hours for a minimal gain is not feasible. A full charge for a typical EV can take several days, making this method unsuitable for daily use.
Potential Strain on Your Home’s Electrical System
The continuous, high-power draw of charging places considerable strain on a home’s electrical system. Even if an outlet appears to be in good condition, older wiring or a shared circuit can overheat during long charging sessions. This sustained load increases the risk of electrical faults and potential fire hazards over time.
The Better Alternative: Level 2 Home Charging

For most electric vehicle owners, Level 1 charging is a temporary fix. The superior solution for daily charging at home is a Level 2 home charger. This method provides a faster, more reliable, and more convenient experience, transforming EV ownership from manageable to effortless. It represents a true investment in an electric lifestyle.
Seviye 2 Şarj Nedir?
Level 2 charging uses a more powerful electrical circuit than a standard wall outlet. It is the most common and recommended method for home charging. This upgrade requires a dedicated installation but offers significant benefits in speed and efficiency.
240 Volt Gücü Anlama
Level 2 systems operate on 240-volt power, the same voltage used by large appliances like electric ovens and clothes dryers. This higher voltage allows for a much greater power output compared to the 120-volt regular outlet. The difference in charging capability is substantial.
| Şarj Cihazı Tipi | Güç Çıkışı (kW) |
|---|---|
| Seviye 1 | 1.2 – 1.9 |
| Seviye 2 | 7.4 – 11 |
This increased power flow dramatically reduces the time needed for charging an electric vehicle.
The Dryer Outlet Analogy
A simple way to understand 240-volt power is to think of a clothes dryer outlet. These large, robust outlets are designed to handle the high power demands of such appliances. A Level 2 home charging point functions similarly, using a dedicated 240-volt circuit to deliver energy safely and quickly to the EV.
The Speed and Convenience Upgrade
The primary advantage of a Level 2 charger is its speed. This upgrade eliminates the range anxiety associated with slow charging from a regular outlet and makes the vehicle ready for any trip on short notice.
Fully Charging an EV Overnight
With a Level 2 home charger, an owner can fully charge their electric vehicle overnight, every night. A vehicle with a low battery can be plugged in at bedtime and be at 100% by morning. This capability ensures the car’s maximum range is always available.
Comparing Miles Gained Per Hour
The rate of range replenishment is where a Level 2 charger truly excels. While a standard outlet adds only a few miles per hour, a Level 2 unit adds significant range, making it practical for daily drivers.
| Şarj Cihazı Tipi | Miles of Range Per Hour |
|---|---|
| Seviye 1 | 2-5 |
| Seviye 2 | 10-75 |
This rapid charging speed means even a short, one-hour session can add substantial mileage.
Kurulum ve Maliyet Değerlendirmeleri
Upgrading to a Level 2 system involves upfront costs for both the equipment and professional installation. However, many owners find the investment worthwhile for the long-term convenience.
The Price of a Wall Connector
The central piece of equipment is the electric vehicle home charger, often called a wall connector. Technologically advanced providers like TPSON offer a range of solutions. Prices for a charger vary by brand and features.
| Marka | Model | Fiyat |
|---|---|---|
| Tesla | Wall Connector | ~$500 |
| JuiceBox | 40 | ~$600 |
| ChargePoint | Home Flex | ~$700 |
These units provide faster charging and often include smart features like scheduling and energy monitoring.
Nitelikli Bir Elektrikçi Bulma
Important: The installation of a 240-volt outlet and a Level 2 charger is not a DIY project. An owner must hire a qualified electrician.
An electrician will ensure the new circuit is installed safely, meets all local codes, and can handle the continuous power load required for charging. This professional installation guarantees the safety and reliability of the home charging setup.
Comparing Your Home Charging Options
Choosing the right method for charging at home depends on a driver’s needs, budget, and vehicle. A direct comparison of Level 1 and Level 2 charging reveals significant differences in performance and cost. Understanding these options helps an owner make an informed decision for their electric vehicle.
Level 1 vs. Level 2 at a Glance
The two primary home charging methods offer vastly different experiences. One provides convenience with major limitations, while the other requires an investment for superior speed.
Speed and Power Output
The most significant distinction between the two levels is their power output, which directly impacts charging speed. Level 1 charging from a standard outlet provides only a trickle of power. A Level 2 charger delivers a much faster and more substantial flow of energy.
| Şarj Seviyesi | Güç Çıkışı (kW) |
|---|---|
| Seviye 1 | 1,4-2,3 kW |
| Seviye 2 | 3.7–22 kW (typically 7–11 kW for residential) |
This difference means a Level 2 charger can replenish an EV’s battery many times faster than a regular outlet.
Upfront Cost and Installation
Cost is a major factor in choosing a charging solution. Level 1 charging has almost no upfront cost, as it uses the mobile connector included with the electric vehicle and a standard wall outlet.
In contrast, a Seviye 2 ev tipi şarj cihazı is an investment. The equipment cost for a standard home charger can range from several hundred to over a thousand dollars, depending on the brand and features. Professional installation adds to this expense, with costs varying based on the complexity of the home’s wiring.
Best Use Case for Each
Each charging level has an ideal scenario.
- Level 1: Best for PHEV owners, low-mileage drivers, or as a portable, emergency charging option when away from home.
- Level 2: The recommended standard for most BEV owners. It provides fast, reliable overnight charging at home, ensuring the car is always ready with maximum range.
What About Level 3 (DC Fast Charging)?
Level 3 charging, also known as DC Fast Charging, represents the quickest way to power an ev. However, it is not a home charging option.
Why It’s Not a Home Charging Option
Important: DC fast chargers are commercial-grade equipment. Their immense power requirements and prohibitive costs make them unsuitable for residential installation.
These systems can have a power output ranging from 50 kW to an incredible 350 kW. A home’s electrical system cannot support this level of power draw. This type of charging requires specialized, high-voltage infrastructure found only at public stations.
Reserved for Road Trips and Quick Stops
DC fast charging is designed for rapid, on-the-go replenishment. Drivers use these stations during long-distance road trips or for a quick power boost while running errands. The goal is to add hundreds of miles of range in under an hour, minimizing travel downtime.
An owner can plug an ev into a regular outlet, but this method of charging is a temporary home charging solution. The slow speed of charging an electric car from a standard outlet makes it impractical for most daily needs. For reliable charging at home, investing in a proper home charger is the clear choice.
Anahtar Paket: To ensure safety and convenience, an owner should not rely on a regular outlet for primary charging. A dedicated electric vehicle home charger is the superior option. An owner can plug an ev into an outlet, but a Level 2 home charger provides faster, safer charging for an electric vehicle. This charger is the best choice for any electric vehicle owner’s outlet.
SSS
Can I charge my Tesla with a regular outlet?
Yes, an owner can charge a Tesla with a standard 120V outlet. Tesla vehicles come with a Mobile Connector and a NEMA 5-15 adapter for this purpose. The charging speed will be very slow, adding only a few miles of range per hour.
Does Level 1 charging damage the EV battery?
No, Seviye 1 şarj is perfectly safe for an EV’s battery. The vehicle’s onboard systems manage the slow power flow, preventing any harm. This gentle charging method does not negatively impact the battery’s long-term health or performance.
How much does it cost to charge an EV with a regular outlet?
The cost depends on local electricity rates, measured in cents per kilowatt-hour (kWh). An owner can find this rate on their utility bill. While Level 1 charging is slow, it is typically the most inexpensive method for replenishing an EV’s range at home.
Is it faster to charge an EV in warmer weather?
Yes, EVs generally charge more efficiently in warmer weather. Cold temperatures can slow the chemical reactions within the battery, slightly reducing the charging speed. The vehicle’s battery management system may also limit charging speed in extreme cold to protect the battery.
Can I leave my EV plugged in all the time?
Yes, an owner can leave their EV plugged in. The vehicle’s Battery Management System (BMS) automatically stops the charging process once the battery reaches its target level. This prevents overcharging and is a recommended practice to keep the battery ready.
What is a J1772 connector?
The J1772 is the industry-standard connector plug for Level 1 and Level 2 AC charging in North America. Most non-Tesla EVs use this port. The mobile charging cord that comes with an EV has a J1772 plug on the end that connects to the car.
Do I need a special adapter for a regular outlet?
No, an owner does not need a special adapter. The mobile charging cord provided by the vehicle manufacturer already has the correct plug (NEMA 5-15) to connect directly to a standard three-prong household outlet. It is an all-in-one solution.





