
The Philippines stands poised for an electric vehicle transformation in 2025. Strategic Carregador de veículos eléctricos policies and rapid infrastructure development have fueled growth, resulting in over 960 public charging stations nationwide.
| Policy Element | Descrição | Impacto na infraestrutura de carregamento |
|---|---|---|
| EVIDA (2022) | National framework with fleet mandates and incentives. | Drives demand for public and private stations, supporting scalable DC networks. |
| CREVI | Targets 7,300 stations by 2028; annual updates. | Guides strategic deployment, emphasizing AC solutions for residential growth. |
| PDP 2023-2050 | 35% renewables by 2030; grid resilience focus. | Enables hybrid solar-charging hubs, reducing loads via smart management. |
| CIDP | Integration into distribution plans. | Ensures regulatory compliance for high-power installations with safety features. |
| Zero-Tariff Extensions | Exemptions on EVs and components until 2028. | Lowers barriers, boosting adoption and need for robust, compatible chargers. |
Consumers and businesses now experience greater accessibility to electric vehicle charging, lower operating costs, and new opportunities for innovation. Collaboration between the government and Fabricantes de carregadores para veículos eléctricos, along with upgrades from utilities like MERALCO, has accelerated the electric vehicle market. Prompt implementation of Executive Order 12 and expanded tax incentives for two- and three-wheeled electric vehicles further support the EV Charger rollout.
Key EV Charger Policies Shaping the Future
National EV Roadmap (CREVI)
Policy objectives
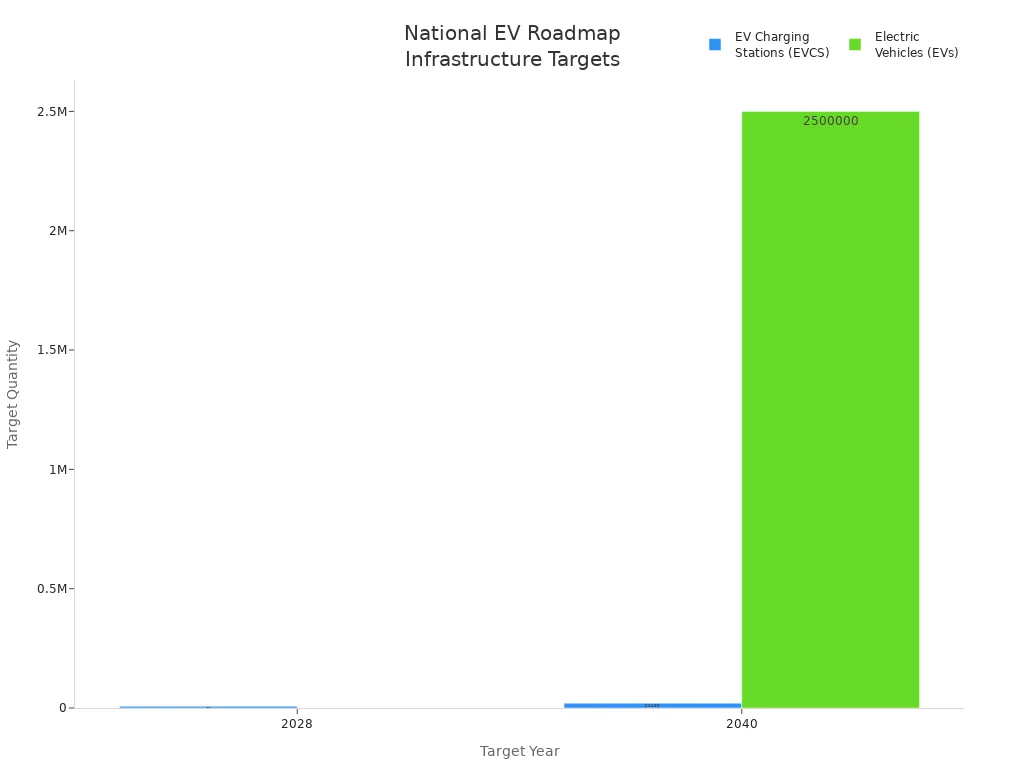
The National EV Roadmap, known as CREVI, sets ambitious targets for the expansion of EV charging infrastructure in the Philippines. The roadmap aims to create a robust network of charging stations and support the adoption of electric vehicles nationwide. The government uses CREVI to guide the deployment of both AC and DC charging solutions, focusing on accessibility and scalability. The roadmap also aligns with broader energy and transportation goals, ensuring that EV charger policies support sustainable growth.
| Objective | Target Quantity | Ano Objetivo |
|---|---|---|
| EV Charging Stations (EVCS) | 7,300 | 2028 |
| EV Charging Stations (EVCS) | 20,400 | 2040 |
| Electric Vehicles (EVs) nationwide | 2.5 million | 2040 |
CREVI’s objectives reflect the government’s commitment to building a future-ready charging network. The roadmap emphasizes the need for both public and private sector participation to meet these targets.
Implementation timeline
The implementation timeline for CREVI follows a phased approach. By 2028, the government expects to reach 7,300 charging stations across the country. This milestone will lay the foundation for further expansion, with a target of 20,400 stations by 2040. The roadmap also projects 2.5 million electric vehicles on Philippine roads by 2040. The government updates the roadmap annually, adjusting strategies to address emerging challenges and opportunities in EV charger policies.
Electric Vehicle Industry Development Act (EVIDA)
Mandates for charging infrastructure
The Electric Vehicle Industry Development Act, or EVIDA, establishes clear mandates for EV charging infrastructure. The law requires the government to accredit charging station service providers and maintain an annual inventory of all accredited providers and commercial charging stations. Distribution utilities must submit their charging infrastructure development plans every year by August 30. EVIDA enforces compliance with the installation of charging stations, as outlined in Sections 18 and 19 of the Act. The law also requires commercial charging stations to unbundle their fees, promoting transparency for consumers. The government consolidates data from various agencies to provide public access to information about EVs and charging stations.
| Mandate | Descrição |
|---|---|
| (f) | Accredit charging stations service providers and publish an annual inventory of all accredited providers and commercial charging stations. |
| (g) | Require Distribution Utilities (DUs) to submit their charging infrastructure development plans annually by August 30. |
| (h) | Enforce compliance with the installation of charging stations as mandated by Sections 18 and 19 of the Act. |
| (i) | Enforce compliance with the unbundling of charging fees by commercial charging stations. |
| (k) | Consolidate data from various agencies regarding EVs and charging stations for public access. |
Incentives for stakeholders
EVIDA offers a range of incentives to encourage investment in EV charging infrastructure. The government provides tax breaks and other financial benefits to accredited charging providers. These incentives lower the barriers for businesses to enter the market and help accelerate the rollout of new charging stations. The law also supports research and development, encouraging innovation in charging technology. By offering these incentives, the government ensures that EV charger policies remain attractive to both local and international investors.
Iniciativas da administração local
City-level charging station requirements
Local governments play a crucial role in the success of EV charger policies. Several cities in the Philippines have introduced their own requirements for charging station installations. For example, Quezon City has deployed electric buses under the Libreng Sakay program and distributed electric tricycles, supported by solar-powered charging stations. Pasig City launched a solar-powered Electric Vehicle Charging Station (EVCS) with three charging terminals, capable of supporting six EVs at once. These city-level actions demonstrate how local policies can drive the adoption of EV charging infrastructure.
Regional pilot programs
Regional pilot programs further support the expansion of charging networks. Mandaue City is preparing to launch Cebu’s first EV charging station and is advocating for the integration of electric buses into the public transport system. Collaboration between government, private sector, and auto manufacturers remains essential for expanding the EV charging station network, especially in urban areas. These pilot programs serve as models for other regions, showing how targeted initiatives can accelerate the adoption of EV charger policies across the Philippines.
DOE EVCS Policy Guidelines
Subsidies and tax breaks for EV charging stations
The Department of Energy (DOE) has introduced comprehensive policy guidelines to accelerate the deployment of electric vehicle charging stations (EVCS) across the Philippines. These guidelines focus on making EV charging infrastructure more affordable for both homeowners and businesses. The DOE offers a range of tax credits and financial incentives that reduce the initial investment required for installing charging stations.
Homeowners who install EV charging ports can claim a tax credit of 30% of the total cost, including components and installation labor, with a cap of $1,000. Businesses benefit from a 6% tax credit on the cost of depreciable property, up to $100,000 per item. Projects that meet prevailing wage and apprenticeship standards qualify for an even higher tax credit of 30% on depreciable property. These incentives lower the financial barriers for early adopters and encourage broader participation in the EV ecosystem.
| Provision | Descrição |
|---|---|
| Tax Credit for Home Charging Stations | 30% of the cost of the EV charging port, components, and installation labor, up to $1,000. |
| Tax Credit for Business Charging Stations | 6% of the cost of property subject to depreciation, with a maximum credit of $100,000 per item. |
| Prevailing Wage Projects | Eligible for a tax credit equal to 30% of the cost of property subject to depreciation if they meet specific wage and apprenticeship requirements. |
💡 Sugestão: These tax credits can significantly reduce the payback period for both residential and commercial EV charging investments, making the transition to electric mobility more attractive.
The DOE’s approach ensures that both individuals and organizations have strong financial reasons to invest in EV charging infrastructure. By lowering upfront costs, the government paves the way for faster adoption and a more robust charging network nationwide.
Import regulations for EV equipment
Import regulations play a crucial role in shaping the availability and affordability of EV charging stations in the Philippines. The DOE, in coordination with other government agencies, has implemented policies that streamline the importation process for EV equipment. These policies include tax incentives and tariff reductions, which directly impact the cost structure for charging station providers and end-users.
A reduction in import tariffs lowers the price of EV charging equipment, making it more accessible to a wider market. Tax incentives further decrease the overall cost, encouraging more businesses to establish charging stations. Infrastructure development support from the government increases the reach and density of charging networks, especially in underserved areas.
| Tipo de regulamento | Impacto nas estações de carregamento de veículos eléctricos |
|---|---|
| Tax incentives | Lower costs for consumers due to reduced import costs |
| Import tariff reductions | Encourages establishment of more charging stations |
| Infrastructure development support | Increases accessibility and availability of charging stations |
The combination of tax breaks and streamlined import regulations creates a favorable environment for EV infrastructure growth. As a result, more Filipinos can access reliable charging options, and the country moves closer to its clean energy and transportation goals.
The DOE’s policy guidelines demonstrate a clear commitment to building a sustainable EV charging ecosystem. By addressing both financial and regulatory barriers, the government empowers stakeholders to invest confidently in the future of electric mobility.
Current State of EV Charging Stations

Number and Distribution
Metro Manila coverage
Metro Manila, also known as the national capital region, leads the country in the deployment of EV charging stations. The region has experienced rapid growth in the number of installations over the past year. Most charging stations nationwide are concentrated in Metro Manila, providing convenient access for urban EV owners. The dense network supports both residential and commercial users, making it easier for drivers to find reliable charging options.
- Metro Manila has seen significant expansion in EV charging stations.
- The majority of charging stations nationwide are located in this region.
- Urban centers benefit from increased accessibility and shorter wait times.
Expansion in provincial areas
Provincial areas in the Philippines continue to lag behind Metro Manila in terms of infrastructure development. While some cities have made progress, the overall distribution remains uneven. Cebu City has established 14 public charging stations, and Davao has 7. Individual stations operate in Legazpi, Naga, and Sorsogon, but many provinces still lack sufficient coverage. The government and private sector aim to address these gaps by prioritizing new installations outside the national capital region.
Note: The expansion of charging stations in provincial areas is crucial for supporting long-distance travel and encouraging EV adoption beyond urban centers.
Tipos de carregadores disponíveis
Fast chargers (DC)
Fast chargers, also known as DC charging stations, provide rapid energy transfer for electric vehicles. These stations are ideal for commercial locations and high-traffic areas. The EMobility DC Fast Charger can deliver up to 80% charge in just 30 minutes, reducing downtime for drivers and supporting fleet operations.
Standard chargers (AC)
Standard chargers use alternating current (AC) and are suitable for home and workplace environments. Wallbox and AC Mini Plus models offer compact designs and easy installation. Wallbox chargers deliver 7.4 kW, while AC Mini Plus units provide 7.2 kW, allowing most vehicles to reach full charge within a few hours.
| Tipo de carregador | Descrição | Potência de carregamento | Tempo de carregamento |
|---|---|---|---|
| Caixa de parede | Level 2 AC charger for home/workplace, compact | 7,4 kW | Few hours |
| AC Mini Plus | Portable Level 2 AC charger for home use | 7,2 kW | 3-4 hours |
| EMobility DC Fast Charger | DC station for quick charging, commercial use | Up to 80% in 30 mins | 30 minutos |
Battery swapping units
Battery swapping units represent an emerging solution for quick energy replenishment. These stations allow drivers to exchange depleted batteries for fully charged ones, minimizing wait times. Although adoption remains limited, battery swapping technology offers potential for future growth, especially in fleet and public transport applications.
Adoption Rates and Market Growth
EV sales trends
EV sales in the Philippines continue to rise, reflecting growing consumer interest and improved infrastructure. Projections indicate that sales will reach 20,000 units by 2025. The increase in EV sales correlates with the expansion of charging stations nationwide, supporting the government’s goal of achieving 50% EV sales penetration by 2040.
Consumer awareness and interest
The expansion of EV charging stations has influenced consumer behavior. Drivers increasingly rely on public charging options, especially in urban areas. Many consumers show a willingness to pay for convenience, with regional differences in pricing sensitivity. Key factors influencing charging point selection include high charging speed, easy access, and the availability of multiple charging stations. As EV ownership grows, public and workplace charging usage is expected to rise, shaping the next generation of electric mobility in the Philippines.
- Projected EV sales will reach 20,000 units by 2025.
- By mid-2025, there are 962 public charging stations, including 421 AC and 59 DC stations.
- The growth in charging stations responds to increasing EV adoption.
- Consumers prioritize charging speed, access, and station availability.
- Public charging usage will increase as more drivers transition to electric vehicles.
Private Sector Participation
Investments by energy companies
Private energy companies have played a pivotal role in expanding the EV charging infrastructure in the Philippines. These organizations have invested in both urban and suburban locations, accelerating the deployment of charging stations and supporting the government’s clean energy goals.
- Ayala Corporation has led the way by establishing charging stations in Metro Manila and Cavite.
- The first integrated EV charging station launched at Ayala 30th Mall in Pasig City, marking a significant milestone for the industry.
- The Philippines currently hosts an estimated 9,000 EVs and 300 charging stations, with electric motorcycles dominating the market.
“The government cannot do it alone. We need private partnerships that employ commercially viable and efficient solutions that will address our country’s need to hasten and move towards carbon neutrality.”
Energy companies have recognized the commercial potential of EV charging networks. They have adopted innovative business models and leveraged existing assets, such as shopping malls and commercial complexes, to maximize accessibility. These investments have not only increased the number of charging stations but also improved the quality and reliability of services offered to EV owners.
Partnerships with automakers
Automakers have shifted their strategies to prioritize electric mobility. They now collaborate with charging providers to create seamless experiences for drivers and accelerate the growth of the charging network. These partnerships have introduced advanced technologies and enhanced user convenience.
Traditional automakers once hesitated to invest in charging infrastructure. Today, they view EV adoption as essential to their long-term success. Seven major automakers have joined forces to build a network of 30,000 charging stations across North America. This initiative demonstrates the scale and ambition possible when industry leaders work together.
| Automakers Involved | Número de postos de carregamento | Caraterísticas principais |
|---|---|---|
| BMW Group | 30,000 | High-powered DC chargers, renewable energy |
| General Motors | Amenities like restrooms and foodservice | |
| Honda | Seamless integration with in-vehicle experiences | |
| Hyundai | Accessibility for all EVs with CCS or NACS | |
| Kia | Focus on convenience and compatibility | |
| Mercedes-Benz Group | Premier charging experience | |
| Stellantis NV | Support for long-distance travel |
Automakers and charging providers have prioritized compatibility with all-electric and plug-in hybrid vehicles. They have also focused on powering stations with renewable energy and offering amenities such as restrooms and foodservice. These features enhance the overall charging experience and encourage more drivers to switch to electric vehicles.
Accredited charging providers
Accredited charging providers ensure the safety, reliability, and efficiency of EV charging stations. The government requires these providers to meet strict standards and maintain transparent operations. Accreditation builds consumer trust and supports the growth of the EV market.
Charging providers must comply with technical requirements and regularly update their service offerings. They collaborate with energy companies and automakers to deliver integrated solutions. Accredited providers also participate in data sharing initiatives, helping the government track infrastructure development and monitor usage trends.
- Accredited providers maintain high safety standards.
- They offer transparent pricing and reliable service.
- Collaboration with industry partners drives innovation and expansion.
Accreditation has become a key factor in the success of the EV charging ecosystem. It encourages healthy competition, attracts investment, and ensures that consumers receive consistent and high-quality service across the country.
Opportunities Created by EV Charger Policies
For Consumers
Improved accessibility and convenience
EV charger policies in the Philippines have transformed the consumer experience. Shoppers now find charging stations in malls, allowing them to power their vehicles while they shop. This convenience reduces range anxiety and encourages more drivers to consider electric vehicles. The visibility of charging stations in public spaces normalizes EV ownership and educates the public about sustainable transport. Many establishments offer free or discounted parking for EVs, making the switch to electric mobility more attractive.
| Tipo de prova | Descrição |
|---|---|
| Legislation | The EVIDA Law encourages EV adoption by making vehicles cheaper to import and own. |
| Incentivos | Tax incentives are provided to promote EV ownership. |
| Infra-estruturas | Mandates for charging stations reduce range anxiety for consumers. |
| Traffic Policy | EVs are exempt from the number coding scheme, encouraging their use. |
| Postos de carregamento | Mandated installation of charging stations in establishments. |
Consumers benefit from increased accessibility, reduced waiting times, and a growing network of charging stations across urban and provincial areas.
Lower operating costs
Drivers in the Philippines experience lower operating costs due to recent EV charger policies. Tax incentives and reduced import duties make electric vehicles more affordable. Owners save on fuel expenses and maintenance compared to traditional vehicles. The government’s push for fleet conversion in both public and private sectors further supports cost savings. Increased awareness of the environmental and financial benefits motivates more consumers to transition to electric mobility.
For Businesses
New market segments
Businesses in the Philippines have identified new market segments through the expansion of charging infrastructure. The development of electric taxi services in Metro Manila and other cities creates opportunities for operators and drivers. Companies invest in public charging station networks and solar-powered solutions to attract environmentally conscious customers. Workforce training initiatives prepare employees for careers in EV technologies, supporting a comprehensive ecosystem.
| Business Opportunity | Descrição |
|---|---|
| Electric Taxi Services | Development of electric taxi services in major cities. |
| Public Charging Station Networks | Rollout of a network of public charging stations to support EV users. |
| Solar-Powered Charging Solutions | Exploration of solar-powered charging options to enhance sustainability. |
| Workforce Training | Initiatives for training the workforce in EV technologies. |
| Comprehensive EV Ecosystem | Building a complete ecosystem covering distribution, charging infrastructure, and e-mobility services. |
Potential for innovation
Companies leverage innovation to enhance the charging experience and capture new business opportunities. Plug & Charge technology streamlines the process, while intelligent software enables predictive maintenance and reliability. Businesses integrate charging solutions into commercial properties, attracting tenants and customers. Fee-based models generate income, and no-cost charging options increase foot traffic and satisfaction. Battery swapping stations and vehicle-to-grid technologies offer quick turnaround and new revenue streams for commercial operators.
- Integration of charging solutions into commercial properties attracts customers.
- Battery swapping stations reduce range anxiety for fleet operators.
- Electrification of delivery vehicles and public transport enhances operational efficiency.
For the Country
Environmental benefits
The widespread adoption of EV charging infrastructure in the Philippines delivers significant environmental benefits. Electric vehicles produce no tailpipe emissions, reducing air pollution in urban centers. Transportation accounts for 56% of outdoor air pollution in Metro Manila, and EVs help lower these levels. The lifetime carbon emissions of EVs are 54% lower than those of internal combustion vehicles. In 2022, the transportation sector produced over 35 million tonnes of carbon dioxide, representing more than 20% of the country’s total emissions. The transition to electric mobility supports national goals for reducing greenhouse gases.
- EVs reduce greenhouse gas emissions and air pollutants.
- The shift to electric vehicles helps the Philippines meet its Nationally Determined Contributions (NDCs) for emissions reduction.
Energy independence
Expanded EV charging infrastructure strengthens energy independence in the Philippines. The country reduces reliance on imported fossil fuels and promotes local energy production. The government’s elimination of tariffs on EVs and components encourages local assembly and infrastructure development. Economic growth follows, with job creation in the renewable energy sector and increased self-sufficiency.
- The Electric Vehicle Industry Development Act (EVIDA) supports sustainability in transport.
- An executive order modified import duties on electric vehicles and components.
- Tariff elimination for five years encourages local assembly and infrastructure growth.
The Philippines moves closer to energy independence and a cleaner future through strategic EV charger policies.
Emerging Technologies in EV Charging Stations
Soluções de carregamento inteligentes
Smart charging solutions represent a major leap forward for the Philippine EV ecosystem. These systems use advanced software and communication technologies to optimize charging times, manage energy loads, and enhance user convenience. Charging stations equipped with smart features can automatically adjust charging speed based on grid demand or electricity prices. This flexibility helps prevent power surges and reduces strain on the local grid.
Key features of smart charging include:
- Remote Monitoring and Control: Operators can track station performance, schedule maintenance, and troubleshoot issues from a central dashboard.
- Gestão dinâmica da carga: Charging stations distribute available power efficiently among multiple vehicles, ensuring fair access and preventing overloads.
- User Authentication and Payment Integration: Drivers can use mobile apps or RFID cards to start charging sessions and pay securely.
⚡ Sugestão: Smart charging stations often support real-time notifications, so drivers receive alerts when their vehicles finish charging or if issues arise.
Smart charging also enables demand response programs. Utilities can incentivize EV owners to charge during off-peak hours, balancing electricity supply and demand. This approach supports grid stability and can lower electricity costs for consumers.
Integration with renewable energy
The integration of renewable energy with EV charging stations aligns with the Philippines’ sustainability goals. Many new charging hubs now feature solar panels or connect to local renewable energy sources. This setup reduces reliance on fossil fuels and cuts greenhouse gas emissions.
Charging stations powered by renewables offer several advantages:
| Benefício | Descrição |
|---|---|
| Menor pegada de carbono | Solar or wind-powered stations produce fewer emissions. |
| Energy Cost Savings | On-site generation reduces dependence on grid electricity. |
| Resiliência da rede | Distributed energy sources help maintain power during outages. |
Some stations use battery storage systems to store excess solar energy during the day. These batteries supply power for EV charging at night or during cloudy weather. This technology ensures a steady supply of clean energy and maximizes the use of renewables.
🌞 Nota: Solar-powered charging stations in cities like Pasig and Quezon City demonstrate the practical benefits of integrating renewables with EV infrastructure.
Emerging technologies such as vehicle-to-grid (V2G) systems also show promise. V2G allows EVs to return electricity to the grid during peak demand, turning parked vehicles into valuable energy resources. As these innovations mature, the Philippines will move closer to a cleaner, more resilient transportation network.
Challenges and Barriers to EV Charging Stations Expansion

Lacunas nas infra-estruturas
Rural and remote area coverage
The expansion of EV charging stations in the Philippines faces significant infrastructure gaps, especially in rural and remote regions. Many provinces lack adequate charging facilities, which restricts the adoption of electric vehicles outside major cities. Local governments and private developers encounter obstacles such as limited access to reliable electricity and logistical challenges in transporting equipment. Skilled workforce shortages, particularly among electrical engineers and maintenance technicians, further complicate installation and upkeep in these areas.
| Infrastructure Gap | Descrição |
|---|---|
| Cumbersome Administrative Processes | Lengthy approval processes involving multiple agencies delay the rollout of charging infrastructure. |
| Skilled Workforce Shortages | A lack of qualified personnel, particularly electrical engineers and maintenance technicians, hampers installation and upkeep. |
| Consumer Behavior Issues | Range anxiety and perceptions of inconvenience deter potential EV buyers, despite existing infrastructure. |
Many Filipinos in rural communities remain hesitant to switch to EVs due to concerns about charging availability and convenience.
Grid capacity issues
Grid capacity presents another major barrier to the deployment of EV charging stations. Seventy-five percent of developers report that electric grid limitations hinder the rollout of commercial charging infrastructure. Developers often struggle to secure adequate electricity for new projects, sometimes resorting to fossil fuel-powered generators. The growing interest in distributed energy resources, such as solar and battery storage, reflects a shift toward overcoming these grid constraints. In 2023, the percentage of developers who believe distributed energy can help increased from 74% to 89%.
- Grid limitations restrict the number and reliability of charging stations.
- Developers face challenges in securing sufficient power for their sites.
- Some projects rely on backup generators, which undermines sustainability goals.
Financial and Investment Hurdles
Custos iniciais elevados
Custos iniciais elevados remain a critical challenge for businesses and municipalities investing in EV charging infrastructure. The initial investment for hardware and installation can deter stakeholders, especially when return on investment appears uncertain. Owners often face limited monetization opportunities in the short term due to high costs and low usage rates.
| Tipo de prova | Descrição |
|---|---|
| Custos iniciais | High initial investment can deter businesses from investing in charging infrastructure. |
| Custos elevados | High hardware and installation costs can limit monetization opportunities for owners. |
| ROI Concerns | Low return on investment in the short term due to high costs and low usage. |
| Investment Justification | High upfront costs may benefit relatively few employees, complicating investment decisions. |
Businesses must carefully evaluate the financial viability of installing charging stations, especially in areas with low EV adoption.
Limited funding sources
Limited funding sources further slow the pace of EV charging station expansion. Financial incentives and subsidies remain scarce, making it difficult for developers to justify investments. Burdensome application processes for funding, such as those required for Low-Income Housing Tax Credits, often discourage developers from pursuing installations in affordable housing projects. Streamlined procedures and bundled incentives could make funding opportunities more accessible.
| Hurdle Type | Descrição |
|---|---|
| Funding Challenges | Burdensome application processes for funding deter developers from installing EV chargers in affordable housing. |
| Limited Monetization | High costs can lead to limited monetization opportunities in the short term. |
- Existing infrastructure challenges hinder deployment despite federal investments.
- Site upgrades for adequate power capacity are complicated by slow municipal permitting.
- Supply chain constraints for essential components lead to significant delays.
Regulatory and Policy Delays
Slow permit processes
Slow permit processes create bottlenecks in the establishment of EV charging stations. Developers must navigate lengthy approval procedures involving multiple government agencies. These administrative hurdles delay construction and increase project costs. Municipalities often require extensive documentation and compliance checks, which can stall progress for months.
Inconsistent enforcement
Inconsistent enforcement of policies and regulations adds another layer of complexity. Some regions implement EV charger mandates rigorously, while others lack clear guidelines or fail to monitor compliance. This uneven approach undermines investor confidence and slows the overall growth of the charging network.
Streamlining administrative procedures and ensuring consistent policy enforcement will be essential for accelerating EV charging station deployment across the Philippines.
Preocupações dos consumidores
Range anxiety
Range anxiety remains a significant barrier for many potential electric vehicle (EV) owners in the Philippines. This concern refers to the fear that an EV will run out of battery power before reaching a charging station. Many drivers hesitate to switch from gasoline vehicles because they worry about getting stranded, especially outside Metro Manila where charging infrastructure remains sparse.
Several factors contribute to range anxiety:
- Limited charging station coverage: Most stations cluster in urban centers. Provincial and rural areas often lack reliable access.
- Uncertainty about charging speed: Not all stations offer fast charging. Drivers may need to wait several hours for a full charge at standard AC units.
- Inconsistent station availability: Some charging points may be out of service or reserved for specific users.
⚠️ Nota: Range anxiety can discourage EV adoption, even when vehicles offer sufficient range for daily commutes.
Automakers and policymakers recognize this challenge. They continue to expand the charging network and promote fast-charging solutions. Public awareness campaigns highlight the actual range capabilities of modern EVs, which often exceed 300 kilometers per charge. However, until the charging network achieves broader coverage, range anxiety will likely persist among Filipino consumers.
Lack of information
A lack of accessible, accurate information about EVs and charging infrastructure also hinders adoption. Many consumers do not understand how EVs work, what charging options exist, or how to access incentives. This information gap creates confusion and slows the transition to electric mobility.
Key information gaps include:
- Charging station locations: Drivers struggle to find up-to-date maps or apps that show available charging points.
- Cost and payment systems: Many do not know how much charging costs or what payment methods stations accept.
- Incentivos governamentais: Some consumers remain unaware of tax breaks, import duty exemptions, or other benefits for EV owners.
- Technical compatibility: Uncertainty about which chargers fit specific vehicle models can cause hesitation.
| Information Gap | Impact on Consumers |
|---|---|
| Station locations | Difficulty planning trips |
| Charging costs | Uncertainty about operating expenses |
| Incentivos | Missed opportunities for savings |
| Compatibilidade | Risk of purchasing incompatible equipment |
📢 Sugestão: Industry stakeholders can address these gaps by providing clear, updated resources online and at point-of-sale locations.
Education and outreach play a crucial role in building consumer confidence. As more Filipinos gain access to reliable information, they can make informed decisions about EV ownership and charging options.
Implications of EV Charger Policies for Stakeholders
Impact on Everyday Drivers
Changes in commuting habits
EV charger policies have started to reshape how Filipinos approach daily travel. Many drivers now plan routes based on charging station locations. Urban commuters often choose electric vehicles for city driving, knowing they can recharge at malls, offices, or public parking areas. Some families have begun to use EVs for weekend trips, relying on the growing network of provincial charging stations. As charging infrastructure expands, drivers feel more confident about longer journeys and less dependent on traditional fuel stations.
🚗 Sugestão: Drivers can use mobile apps to locate nearby charging stations and monitor availability in real time.
Cost savings potential
Electric vehicle ownership brings significant cost advantages. Drivers save on fuel because electricity costs less than gasoline or diesel. Maintenance expenses also decrease, as EVs have fewer moving parts and require less frequent servicing. Government incentives, such as tax breaks and exemptions from number coding, further reduce the total cost of ownership. Over time, these savings can offset the higher upfront price of an EV.
| Tipo de despesa | Traditional Vehicle | Veículo elétrico |
|---|---|---|
| Fuel/Energy | Elevado | Baixa |
| Manutenção | Moderado | Baixa |
| Taxes/Fees | Padrão | Reduced |
Effects on Businesses and Investors
New business models
Businesses have responded to EV charger policies by developing innovative services. Some companies operate charging stations as standalone businesses, while others integrate charging into retail, hospitality, or real estate offerings. Fleet operators invest in dedicated charging hubs to support electric taxis, delivery vans, or buses. Startups create software platforms for payment, station management, and user analytics. These new models open revenue streams and attract investment from both local and international players.
Competitive landscape
The competitive landscape continues to evolve as more companies enter the EV charging market. Energy firms, automakers, and technology providers compete to offer the fastest, most reliable, and user-friendly charging solutions. Accreditation requirements and government incentives encourage high standards and transparency. Businesses that adapt quickly to policy changes and consumer needs gain a competitive edge.
📈 Nota: Early movers in the EV charging sector often secure prime locations and build strong brand recognition.
National Economic and Environmental Outcomes
Job creation
The expansion of EV charging infrastructure creates new jobs across multiple sectors. Construction workers, electricians, and engineers find opportunities in station installation and maintenance. Technology specialists develop software for smart charging and network management. Training programs prepare workers for roles in the growing EV industry. As the market matures, related fields such as battery recycling and renewable energy integration also generate employment.
Carbon emissions reduction
Widespread adoption of electric vehicles and charging stations supports the Philippines’ environmental goals. EVs produce zero tailpipe emissions, which helps reduce air pollution in cities. The use of renewable energy in charging stations further lowers the carbon footprint. As more drivers switch to electric vehicles, the country moves closer to its targets for greenhouse gas reduction and cleaner air.
🌱 EV charger policies play a vital role in building a sustainable and resilient future for the Philippines.
The Road Ahead for EV Charging Stations in 2025
Predicted Milestones
Infrastructure targets (7,300 stations by 2028)
The Philippines continues to pursue ambitious infrastructure goals for EV charging stations. By 2028, the government aims to reach 7,300 public charging stations nationwide. Recent developments highlight steady progress toward this target. Several landmark projects have launched in the past year, signaling strong momentum in the sector.
| Data | Milestone Description |
|---|---|
| April 2025 | Okada Manila introduced the first EV charging station in Entertainment City, promoting sustainable innovation. |
| March 2025 | Mober launched the largest commercial EV Charging hub, Central Charge, with a 56-port capacity. |
| December 2024 | Tesla Philippines opened its first Supercharging station, enhancing sustainable mobility in the region. |
| September 2023 | Shell launched its second Shell Recharge site, contributing to the establishment of an EV highway. |
| May 2024 | NEDA approved the extension of zero-tariff rates on additional battery EVs and components to support EV adoption. |
| June 2024 | Wardwizard Innovations received a USD 1.29 billion order for transforming public transport with EVs. |
| July 2022 | Shell launched the first Nature-based Solutions Carbon Credit Service and Shell Recharge EV charging service. |
| March 2025 | WIML partnered with Beulah International for testing electric three-wheelers in the Philippines. |
These milestones reflect the growing commitment of both public and private sectors to expand the charging network and support the transition to electric mobility.
Policy updates and enforcement
Policy updates and enforcement play a crucial role in shaping the EV charging landscape. Federal policies set long-term market conditions and encourage industry growth. The Inflation Reduction Act (IRA) introduces financial incentives for consumers and businesses, making EVs more affordable. Key provisions include consumer tax credits and commercial clean vehicle tax credits, which lower the cost of ownership and operation.
- Seventeen states sued the former Trump administration for blocking $3.3 billion in federal funding for EV charging stations.
- This legal challenge highlights the importance of government support in expanding infrastructure.
- The halted funds were intended to accelerate the installation of EV stations, which is essential for building consumer confidence and reducing range anxiety.
Potential Game Changers
Technological breakthroughs
Technological advancements promise to transform the EV charging experience in the Philippines. Fast-charging solutions, battery swapping technology, and smart grid integration will increase efficiency and convenience. Companies continue to invest in research and development, aiming to reduce charging times and improve reliability. Innovations such as wireless charging and vehicle-to-grid systems may soon become mainstream, further enhancing the value proposition for EV owners.
International partnerships
International partnerships drive growth and knowledge transfer in the EV sector. Collaborations with global automakers and technology providers introduce best practices and advanced solutions. Joint ventures with foreign companies help local firms access cutting-edge equipment and expertise. These partnerships accelerate the deployment of high-quality charging stations and support the Philippines in meeting its infrastructure targets.
Risks and Uncertainties
Global market influences
Global market trends influence the pace of EV adoption and infrastructure development. Fluctuations in supply chains, raw material costs, and international regulations can affect project timelines and investment decisions. The Philippines must remain agile and responsive to changes in global demand for electric vehicles and charging equipment.
Political shifts
Political changes present uncertainties for the EV charging sector. Shifts in leadership or policy priorities may impact funding, regulatory enforcement, and long-term planning. Stakeholders must monitor the political landscape and adapt strategies to ensure continued progress toward national goals.
The road ahead for EV charging stations in the Philippines features both promise and complexity. Strategic planning, technological innovation, and strong policy enforcement will determine the success of the country’s electric mobility revolution in 2025 and beyond.
The Philippines stands ready for a major shift in EV charging by 2025. Strong government policies and rapid infrastructure growth create new opportunities for consumers, businesses, and the nation. Challenges in implementation and adoption persist, but ongoing investment and technological innovation promise continued progress.
- Stakeholders should monitor policy updates and market trends.
- Active participation will help shape a sustainable EV charging landscape.
The future of electric mobility in the Philippines depends on collaboration, enforcement, and innovation.
FAQ
What is the current number of public EV charging stations in the Philippines?
The Philippines has over 960 estações públicas de carregamento de veículos eléctricos. Metro Manila leads in coverage, while provincial areas continue to expand their networks.
Which government policies support EV charging infrastructure?
Key policies include the Electric Vehicle Industry Development Act (EVIDA), the National EV Roadmap (CREVI), and Department of Energy guidelines. These policies provide mandates, incentives, and regulatory support for charging station deployment.
Are there incentives for installing EV charging stations?
The government offers tax credits and import tariff reductions for both residential and commercial charging station installations. These incentives lower upfront costs and encourage broader participation.
What types of EV chargers are available?
Drivers can access fast DC chargers, standard AC chargers, and emerging battery swapping units. Each type serves different needs, from quick commercial charging to convenient home use.
How do EV charging stations benefit businesses?
Businesses gain new market opportunities, attract environmentally conscious customers, and can innovate with smart charging solutions. Charging stations also increase property value and support workforce development.
What challenges hinder EV charging station expansion?
Infrastructure gaps, high upfront costs, slow permit processes, and grid capacity issues present significant challenges. Range anxiety and lack of information also affect consumer adoption.
Can EV charging stations use renewable energy?
Many new charging stations integrate solar panels or connect to local renewable sources. This approach reduces carbon emissions and supports the country’s sustainability goals.
How does EV adoption impact the environment?
Electric vehicles produce zero tailpipe emissions. Widespread EV use helps reduce air pollution and supports national targets for lowering greenhouse gas emissions.





