The future of EV charging is being shaped by powerful forces. Three key drivers—technological innovation, strategic infrastructure growth, and evolving government policy—are making EV charging faster and smarter across the UK. The current landscape of EV charging stations reflects this rapid evolution. The UK’s charging infrastructure saw a 26% increase in total charge points compared to the previous year, with a notable 29% growth in faster chargers. This highlights the accelerating trends in electric vehicle charging.

This progress in technology and charging infrastructure transforms the charging experience. It creates a more efficient and user-friendly energy ecosystem for all EV owners. Elektrikli araç şarj cihazı üreticileri, including technologically advanced electric vehicle charging solution providers like TPSON, are at the forefront of these EV charging trends, defining the future of EV charging stations. This ensures every new EV şarj cihazı meets the demands of a growing electric fleet.
Driver 1: Technological Innovations Shaping the Future of EV Charging Stations

The innovations shaping the future of EV charging are transforming the user experience. Technology is the engine driving progress, making EV charging faster, more convenient, and seamlessly integrated into our energy systems. These advancements are pivotal for the future of EV charging stations in the UK.
The Leap to Ultra-Fast and Wireless Charging
Long charging times are becoming a relic of the past. New technology trends focus on speed and convenience, directly addressing two of the biggest hurdles to EV adoption.
High-Power Charging (HPC) Technology
High-Power Charging (HPC) represents a significant leap forward. These systems deliver power outputs greater than 150 kW, with some modern units reaching up to 400 kW. This technology is essential for long-distance travel.
Drastically Reducing Charging Times
HPC drastically reduces time spent at charging stations. An EV can now gain a significant charge, often from 10% to 80%, in as little as 20 ila 40 dakika. This makes the EV charging experience much closer to a traditional refueling stop.
Inductive Charging for Ultimate Convenience
Wireless charging eliminates the need for physical cables. Using electromagnetic induction, an EV begins charging simply by parking over a ground-based pad. Major automotive companies are investing heavily in this innovation, with Toyota Motor leading in patent filings.
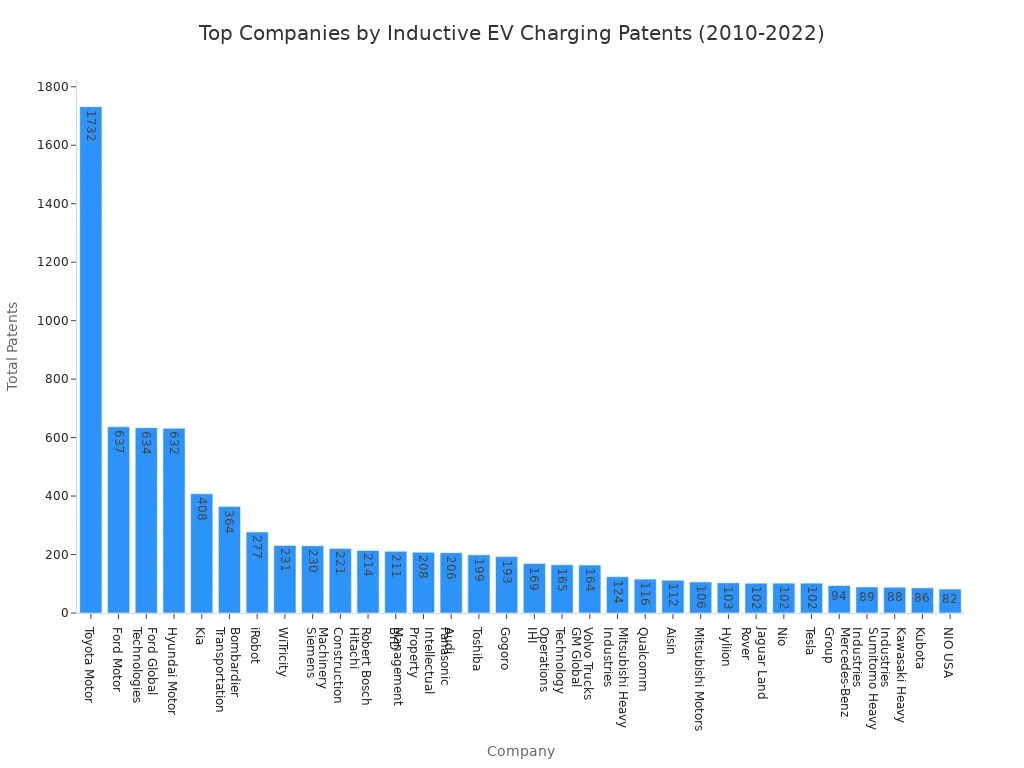
Static vs. Dynamic Wireless Systems
Current wireless systems are primarily static, meaning the EV must be parked. However, development is underway for dynamic systems. This technology would allow an EV to charge while driving over roads embedded with charging infrastructure.
Smart Charging and Bidirectional Power Flow
Beyond speed, the future of EV charging is intelligent. Smart charging and bidirectional power flow create a symbiotic relationship between electric vehicles and the power grid, enhancing sustainability.
What is Smart Charging?
Smart charging technology optimizes the charging process. It automatically schedules an EV to charge during off-peak hours when electricity demand is low and prices are cheaper. This reduces strain on the grid and lowers costs for EV owners.
Vehicle-to-Grid (V2G) Explained
Vehicle-to-Grid (V2G) technology enables bidirectional power flow. An EV can not only draw power from the grid but also send stored energy back to it.
“It’s not just about charging; it’s about generating and sharing energy – a game changer not just in the world of cleaner motoring, but in creating cleaner more flexible power.” Dave Butters, Director of E.ON Drive
How V2G Supports the National Grid
V2G helps balance the national grid during periods of high demand. Pilot programs in the UK, such as the Sciurus project, have demonstrated its effectiveness. Technologically advanced providers like TPSON are central to developing this smart charging infrastructure.
Economic Benefits for EV Owners
These EV charging trends offer direct financial benefits. The Sciurus trial found that V2G could save UK customers up to £725 annually compared to unmanaged charging by providing services back to the grid.
Yenilenebilir Enerji Kaynakları ile Entegrasyon
Connecting EV charging with renewable energy is key to achieving true sustainability. This integration creates a cleaner, more resilient energy ecosystem.
Güneş Enerjili Şarj Kanopileri
Many new charging stations now feature canopies covered in solar panels. These structures provide shelter for vehicles and generate clean, renewable electricity on-site to power the chargers.
Wind-Powered Charging Stations
In suitable locations, charging stations can be powered by nearby wind turbines. This approach leverages another powerful renewable resource to support the growing demand for electric vehicle charging.
On-Site Battery Storage Solutions
Battery Energy Storage Systems (BESS) are a critical component. They store excess renewable energy generated during sunny or windy periods. This stored power is then used to charge an EV, ensuring a consistent supply even when the sun isn’t shining.
Creating a Self-Sustaining Ecosystem
Combining renewable generation with on-site storage creates a self-sustaining model for different types of charging stations. This reduces reliance on the grid, lowers operational costs, and minimizes the carbon footprint of every charging session.
Driver 2: Strategic Growth of UK EV Charging Infrastructure
Technological progress requires a robust physical foundation. The strategic growth of the UK EV charging infrastructure is the second major driver shaping the future of EV charging. This expansion focuses on increasing the number of charging points and placing them where drivers need them most, a key trend in charging infrastructure development.
The Rapid Expansion of Public Charging Networks
The public charging network in the UK is growing at an unprecedented rate. This growth is a collaborative effort involving network operators, businesses, and government bodies.
Major Players in the UK Market
A diverse group of companies leads the expansion of the UK network. Major players include dedicated charging providers, energy companies, and automotive manufacturers, all contributing to a more competitive and accessible market.
Investment and Corporate Partnerships
Corporate partnerships are accelerating the rollout of charging stations. Major retailers are integrating EV charging into their customer experience.
- Tesco partnered with Pod Point and Volkswagen to install over 2,400 charging bays.
- Sainsbury's implemented charging points at over 300 locations through its Smart Charge partnership.
- Moto service stations feature hubs from operators like Ionity and Fastned at 58 locations.
Data-Driven Location Planning
Operators use sophisticated data analysis to plan new charging locations. They forecast demand for different vehicle types to identify high-traffic areas, ensuring new infrastructure meets current and future needs.
The Role of Public vs. Private Funding
Both public and private funding are essential for infrastructure growth. The UK government’s ‘Taking Charge’ strategy outlines a national vision for the EV charging infrastructure rollout. This includes a £400 million investment to overcome barriers and ensure the charging network expands ahead of demand.
The Rise of Dedicated EV Charging Hubs
A significant trend is the development of large, dedicated EV charging hubs. These sites offer multiple high-power chargers and driver amenities, improving the charging experience.
Highway and Motorway Superhubs
Superhubs are transforming long-distance electric travel. InstaVolt’s hub at Stroud Park on the M40, with 32 rapid chargers, is a prime example. Looking ahead, Moto plans to open its first superhubs for electric HGVs, with a goal of 300 charging bays across 23 key UK locations by 2030.
Perakende ve Varış Noktası Şarjı
Charging is becoming a common feature at retail parks, supermarkets, and tourist destinations. The Norwich Electric Forecourt offers 36 chargers alongside shops and cafes, making charging a convenient part of a day out.
Urban Charging Hubs for City Dwellers
To serve residents without private driveways, urban charging hubs are emerging. These hubs provide reliable access to charging in densely populated areas, a critical step for equitable EV adoption.
Fleet and Commercial Charging Depots
The electrification of commercial fleets creates a strong demand for specialized charging depots. These facilities support businesses in transitioning their vans and trucks to electric power.
Evolving Business and Payment Models
The way drivers pay for charging is also evolving. New models offer greater flexibility and can reduce the overall cost of EV ownership.
The Shift to Subscription Services
Many networks now offer subscription services. For a monthly fee, EV drivers can access lower per-kWh charging rates, making frequent public charging more affordable.
Pay-As-You-Go vs. Membership Models
Drivers can choose between pay-as-you-go (PAYG) or membership models. While PAYG offers flexibility, memberships typically provide a lower cost per charge. For example, a BP Pulse subscription can significantly reduce the cost compared to its PAYG rate. The future of EV charging stations will likely involve a mix of these options.
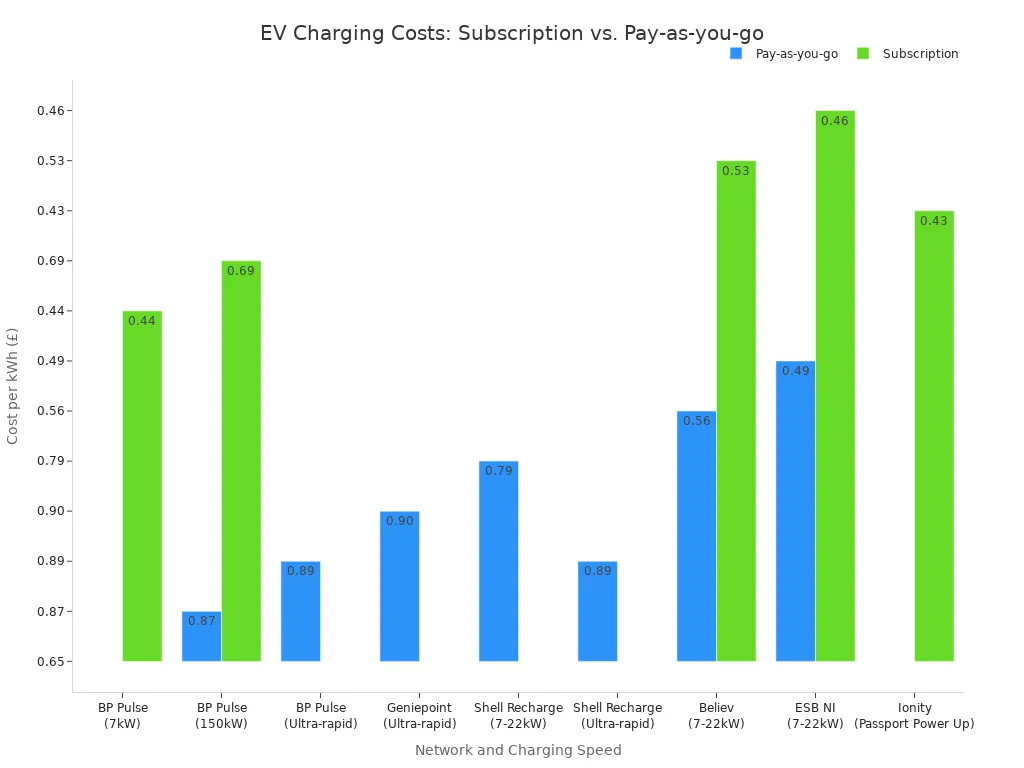
Not: Subscription models often provide substantial savings. A driver using a BP Pulse 150kW charger could pay £0.69/kWh with a subscription versus £0.87/kWh on a PAYG basis, highlighting the impact on the cost of EV charging stations.
Bundled Services and Loyalty Programs
Providers are bundling charging with other services. Some offer home charging solutions, like Pod Point’s ‘Pod Drive’ subscription, which includes a home charger and an annual mileage allowance.
The Impact of Free Charging Incentives
Some businesses, like IKEA, offer free charging as an incentive to attract customers. While not a long-term business model, these perks help normalize the EV charging process and encourage adoption.
Driver 3: Policy and Regulations Driving the Future of EV Charging
Supportive government policy is the third critical driver shaping the future of EV charging in the UK. Through a combination of mali̇ teşvi̇kler, forward-thinking regulations, and strategic planning, the government is actively accelerating the transition to electric mobility and ensuring the necessary infrastructure is in place.
Government Incentives and Regulatory Frameworks
The UK government has established a robust framework to encourage the adoption of electric vehicles and the build-out of charging infrastructure. These policies address everything from initial cost barriers to long-term usability.
The Role of Government Grants and Subsidies
Financial incentives significantly reduce the upfront cost of installing charging points. The government offers several key programs:
- İşyeri Ücretlendirme Programı (WCS): Provides businesses and state-funded education institutions with voucher-based support, covering up to 75% of purchase and installation costs.
- EV Chargepoint Grants: Offers grants to landlords and property managers for installing chargers in residential and commercial car parks.
- Infrastructure Grants: Helps small and medium-sized businesses fund the underlying infrastructure for staff and fleet charging.
Mandating Contactless Payments for Simplicity
To improve the user experience, new regulations mandate that all new rapid chargers provide a simple, contactless payment option. This removes the need for multiple apps or subscriptions, making public EV charging as straightforward as paying for any other service.
New Build and Right-to-Charge Regulations
The government now requires that all new home and workplace chargers sold in the UK have smart functionality. This policy promotes smart charging, which allows vehicles to charge during off-peak hours. This manages electricity demand efficiently and supports a more stable grid.
How the ZEV Mandate Accelerates Infrastructure Demand
The UK’s Zero Emission Vehicle (ZEV) mandate is a powerful catalyst. It requires car manufacturers to sell an increasing percentage of zero-emission vehicles each year, starting at 22% in 2024 and rising to 100% by 2035. This policy directly fuels the demand for a comprehensive public charging infrastructure to support the growing number of EV drivers.
Addressing Geographic Gaps in Charging Stations
A key focus of UK policy is ensuring that charging is accessible to everyone, regardless of location. This involves tackling the disparity between urban and rural areas.
The Rural Charging Challenge
Data reveals a significant geographic imbalance. As of early 2025, over 84% of public charging devices in England were located in urban areas. This leaves rural communities underserved and creates a barrier to EV adoption outside of major cities.
On-Street Residential Charging Projects
To address this, the government’s On-Street Residential Chargepoint Scheme (ORCS) provides funding to local authorities. This helps them install public chargers for residents who lack private driveways, a common issue in many UK neighborhoods.
Community-Led Charging Initiatives
The government is empowering local authorities to lead the charge. Funds like the Local EV Infrastructure (LEVI) Fund help councils develop long-term charging strategies and attract private investment, ensuring solutions are tailored to local needs.
Ensuring Equitable Access for All
Reports like RECHARGE UK emphasize the urgent need to accelerate the rollout of charging infrastructure and address these geographical inequalities. The goal is to create a network with diverse charge point types in safe, accessible locations for all drivers.
The Push for Universal Interoperability
A fragmented network with different payment systems and connectors creates a poor user experience. Therefore, achieving universal birlikte çalışabilirlik is a top priority for the future of the UK charging network.
Solving the Plug and Connector Puzzle
While the UK has largely standardized on Type 2 and CCS connectors for AC and DC charging, ensuring all public chargers are compatible and reliable remains a focus for both industry and regulators.
Roaming Agreements Between Networks
True interoperability requires seamless roaming between different charging networks. While some commercial agreements exist, reluctance from some market players to cooperate presents a challenge. The government must balance encouraging collaboration with maintaining an attractive market for investment.
Ödeme Sistemlerinin Standartlaştırılması
Beyond mandating contactless payments, the industry is moving toward standardized systems that allow drivers to use a single account or payment method across all networks, eliminating a major point of friction.
The Open Charge Point Protocol (OCPP)
The Open Charge Point Protocol (OCPP) is a crucial technical standard that enables communication between charging stations and their management systems, regardless of the manufacturer. This open-source protocol satıcı kilitlenmesini önler and allows for greater flexibility. Technologically advanced providers use OCPP to build scalable and future-proof EV charging solutions that support smart charging and remote management, which are key trends for the industry.
The Evolving EV Charging Experience in the UK

The future of EV charging stations in the UK is defined by a user-centric approach. This evolution combines intelligent physical design with powerful data connectivity. The goal is a seamless, swift, and stress-free experience for every EV driver. These trends are making the şarj süreci more convenient and reliable.
Designing Future-Proof Charging Stations
Operators are designing charging stations to meet both current and future demands. This forward-thinking approach ensures the longevity and utility of the charging infrastructure.
Scalability and Modular Design
Future-proofing starts with scalable design. Planners are installing more capacity than currently needed, allowing for easy expansion. Modular designs enable operators to add more charging points as the number of EV models on UK roads grows, ensuring the sites remain effective for years.
Integrating User Amenities
Modern charging hubs are becoming destinations. They integrate amenities to improve the user experience during a charging session.
- Retail and Dining: Many sites now include coffee shops, restaurants, and retail stores.
- Bağlanabilirlik: Free Wi-Fi is a common feature, allowing drivers to work or relax.
- Comfort: Clean, accessible restrooms and comfortable waiting areas are standard.
Enhancing Safety and Lighting
Driver safety is a top priority. New charging stations feature bright LED lighting and CCTV surveillance. These measures create a secure environment, giving EV drivers peace of mind, especially when charging at night.
Accessibility for All Users
New UK sites are designed for everyone. They follow accessibility standards like PAS1899 to ensure level access for wheelchair users. Spacious bays accommodate different vehicle sizes and driver needs, making the EV charging experience inclusive.
The Role of Data and Connectivity
Data is the backbone of the modern charging network. Connectivity transforms isolated chargers into an intelligent, responsive system that improves reliability and convenience for the EV driver.
Real-Time Charger Availability Apps
Real-time data is eliminating range anxiety. Mobile apps show drivers the live status and location of available chargers. This information helps drivers plan their journeys and avoids the frustration of arriving at an occupied or out-of-service charging point.
Predictive Maintenance for Reliability
Connected chargers enable remote monitoring. Technologically advanced providers like TPSON use this data for predictive maintenance. Operators can detect potential faults and perform remote resets, reducing downtime and ensuring the charging equipment is always ready for the next EV.
Personalizing the User Experience
Data allows for a personalized charging experience. Apps can remember a driver’s preferences, suggest optimal charging times, and manage payments. Loyalty programs offer rewards and discounted rates, adding value for frequent users.
Cybersecurity in a Connected Network
A connected network also introduces security risks. Hackers can target charging stations to steal user data or install disruptive malware.
“If somebody can’t charge their car at the time they need to because of some malware or some sort of cybersecurity attack, that’s a big problem.” – Michael McCarthy, ICS-CERT
To protect the EV ecosystem, operators are adopting a Zero Trust security mindset, ensuring every connection is verified. Regular software updates and secure network protocols are essential to defend against evolving cyber threats.
The future of EV charging is a dynamic landscape driven by rapid technological progress, massive infrastructure investment, and supportive government action. These forces work together to eliminate key barriers like range anxiety. The UK government’s push for a robust charging infrastructure, targeting 300,000 public charge points by 2030, is central to this effort. For UK drivers, this means a future where charging an electric EV is as simple and fast as fueling a traditional car. The result will be a smarter, more resilient network built on sustainability, where providers like TPSON help create a user-centric infrastructure prepared for the all-electric future in the UK.
SSS
What is the UK’s main goal for its EV charging network?
The UK government aims to expand the public network to 300,000 charge points by 2030. This strategic growth ensures the infrastructure can support the rising number of electric vehicles, making charging convenient and widely available for all drivers.
How does Vehicle-to-Grid (V2G) technology benefit EV owners?
V2G technology allows EV owners to sell stored energy back to the grid. This process can generate income and significantly lower the cost of EV ownership. It also helps stabilize the national grid during periods of high energy demand.
Will I need multiple apps to pay for charging in the future?
No. New regulations require all new rapid chargers to include a simple contactless payment option. This change removes the need for drivers to manage multiple network-specific apps or subscriptions, streamlining the payment process.
What is being done about the lack of chargers in rural areas?
The government’s Local EV Infrastructure (LEVI) Fund provides funding to local authorities. This helps them partner with private industry to install chargers in rural and residential areas, addressing the geographic imbalance and ensuring equitable access for everyone.
How do smart chargers help EV owners save money?
Smart chargers automatically schedule charging sessions during off-peak hours when electricity rates are lowest. This intelligent process reduces charging costs for the owner and helps balance the overall demand on the power grid.
What role do companies like TPSON play in this evolution?
Teknolojik olarak gelişmiş electric vehicle charging solution providers like TPSON design and manufacture the hardware that powers the network. They develop the smart chargers and management systems that enable key innovations like V2G and predictive maintenance, building a reliable infrastructure.
Are new charging stations designed for drivers with disabilities?
Yes. New charging sites are being built to meet accessibility standards like PAS1899. Key features include:
- Spacious, clearly marked bays
- Level ground access to chargers
- Sufficient lighting for safety
This ensures a safe and convenient experience for all users.





