EV car chargers have gained significant traction as electric vehicles become mainstream. EV charging connectors such as J1772, CCS, CHAdeMO, Tesla/NACS, and Type 2 play a crucial role in charging efficiency and compatibility. The global fleet of electric cars reached nearly 58 million in 2024, with 785 electric car models available and 17 million units sold. Elektrikli araç şarj cihazı üreticileri continue to innovate, making charging faster and more accessible. The following table highlights the latest global statistics on charging connector adoption:
| Kategori | İstatistik |
|---|---|
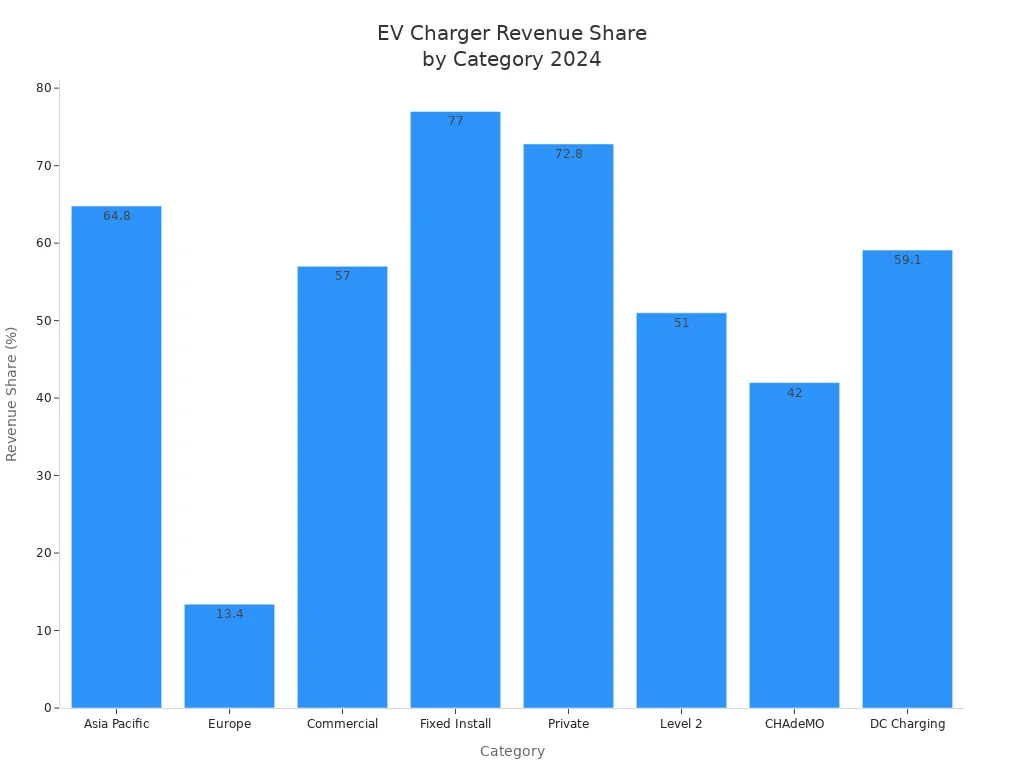
| Revenue Share (Asia Pacific) | 64.8% in 2024 |
| Revenue Share (Europe) | 13.4% in 2024 |
| Revenue Share (Commercial) | 57% in 2024 |
| Revenue Share (Fixed Install) | 77% in 2024 |
| Revenue Share (Private) | 72.80% in 2024 |
| Revenue Share (Level 2) | 51% in 2024 |
| Revenue Share (CHAdeMO) | 42% in 2024 |
| Revenue Share (DC Charging) | 59.10% in 2024 |
EV owners must understand charging connector compatibility to avoid inconvenience at home or on the road. A strong grasp of charging options ensures seamless use of EV Şarj Cihazı infrastructure.
EV car chargers: Charging Levels Explained

Level 1 EV Charging
What is Level 1?
Level 1 charging represents the most basic method for powering up EVs. This process uses a standard 120-volt AC outlet, which is available in most homes and garages. Owners do not need special equipment or installation for this type of charging. They simply plug the EV into the outlet using the provided cable.
Tipik Kullanım Örnekleri
Drivers often rely on Level 1 charging for overnight charging at home. This method suits individuals who travel short distances daily or own plug-in hybrid electric vehicles. Many use Level 1 charging as a backup solution when other charging stations are unavailable.
Şarj Hızı
Level 1 charging offers the slowest charging speed among all EV car chargers. It typically delivers about 1 kW of power. Charging a battery electric vehicle from empty to 80% can take 40 to 50 hours. This method works best for those who do not need fast charging and have plenty of time to recharge.
Level 2 EV Charging
What is Level 2?
Level 2 charging uses a dedicated şarj istasyonu connected to a 208-240 volt AC power source. These stations require professional installation and provide a significant upgrade in charging speed compared to Level 1. Most public charging stations and many home setups feature Level 2 chargers.
Where You’ll Find It
Level 2 charging stations appear in residential garages, workplaces, commercial parking lots, and public charging station networks. Many businesses install these stations to support employees and customers who drive EVs.
Şarj Hızı
Level 2 charging delivers between 7 kW and 19 kW of power. This method can charge a battery electric vehicle from empty to 80% in 4 to 10 hours. The faster charging speed makes Level 2 ideal for daily use and longer commutes.
DC Fast EV Charging
DC Hızlı Şarj Nedir?
DC hızlı şarj uses direct current (DC) instead of alternating current (AC charging). These chargers operate at voltages ranging from 400 to 1000 volts and can deliver up to 350 kW of power. DC fast charging stations require specialized equipment and infrastructure.
Where It’s Used
Drivers find DC fast charging stations along highways, at major retail centers, and near transportation hubs. These stations support long-distance travel and quick top-ups during busy schedules. Many charging station networks prioritize DC fast charging for rapid service.
Şarj Hızı
DC fast charging provides the quickest charging speed available for electric vehicles. A typical DC fast charger can boost a 300-mile range battery from 10% to 80% in about 20 dakika. Some newer models offer even higher power outputs, reducing wait times further. The table below summarizes the differences in charging levels:
| Şarj Seviyesi | Gerilim | Tipik Güç Çıkışı | Estimated BEV Charge Time from Empty |
|---|---|---|---|
| Seviye 1 | 120 V AC | 1 kW | 40 – 50 hours |
| Seviye 2 | 208 – 240 V AC | 7 kW - 19 kW | 4 – 10 hours |
| DC Hızlı Şarj | 400 – 1000 V DC | 50 - 350 kW | 20 dakika - 1 saat |
Tip: Drivers who need fast charging for road trips or busy schedules should seek out DC fast charging stations for the best results.
EV charging connector types in 2025

Electric vehicle owners in 2025 encounter a diverse landscape of EV charging connectors. Understanding the main EV charging connector types ensures efficient charging and avoids compatibility issues. The table below highlights the most widely used connectors by region:
| Bölge | Konektör Tipi | Adoption Status |
|---|---|---|
| Kuzey Amerika | NACS | Rapid adoption by major OEMs like Ford, GM, and Rivian |
| Avrupa | CCS2 | Legally mandated standard, including Tesla’s adaptation |
| Asia-Pacific | GB/T | Continued reliance on national standard, CCS2 gaining traction in some areas |
Type 1 (J1772) EV Charging Connector
Uyumluluk
Bu SAE J1772 connector, also known as the type 1 connector, serves as the primary standard for most electric vehicles and plug-in hybrids in North America. Most major EV brands use this connector for Level 1 and Level 2 AC charging. Tesla vehicles feature a unique charging system, but owners can use adapters to connect to J1772 charging stations. This arrangement provides a high level of compatibility for non-Tesla vehicles and offers Tesla drivers access to a broader charging network through adapters.
Where It’s Used
Drivers find the type 1 connector at residential charging stations, workplaces, and public charging networks throughout North America. The SAE J1772 connector supports both Level 1 and Level 2 charging, making it a common sight in urban and suburban environments. Many commercial parking lots and retail locations also install these connectors to accommodate a wide range of electric vehicles.
Artıları ve Eksileri
| Konektör Tipi | Avantajlar | Dezavantajlar |
|---|---|---|
| J1772 (Tip 1) | AC charging capability for Level 1 and Level 2 | Slower charging compared to DC options |
| Tesla Supercharger | Fast charging up to 250 kW | Limited to Tesla vehicles |
| CHAdeMO | High-power DC fast charging | Less popular than CCS1 or J1772 |
| CCS1 | Supports both AC and DC, up to 350 kW | Requires compatible vehicles |
- J1772 adapters are widely available for vehicles with other connectors.
- Tesla vehicles can use J1772 charging stations with adapters.
- CHAdeMO and CCS1 adapters exist but are less commonly used.
The J1772 connector offers practical AC charging for daily use. However, it does not provide the rapid charging speeds of DC fast charging options like CCS or Tesla Supercharger networks.
Note: The type 1 connector remains a reliable choice for home and workplace charging, but drivers seeking faster charging may prefer vehicles with DC fast charging capability.
Type 2 (Mennekes) EV Charging Connector
Uyumluluk
The type 2 connector, also known as the Mennekes connector, dominates the European market. Most new passenger electric vehicles in Europe feature type 2 charging ports. This connector supports both single-phase and three-phase AC charging, making it suitable for a wide range of charging scenarios. The type 2 connector can deliver up to 22 kW, providing faster charging than many other AC connectors.
Where It’s Used
- The Mennekes type 2 connector is the most common standard in Europe.
- Most new passenger electric vehicles in Europe are equipped with type 2 charging ports.
- A robust public charging infrastructure supports this interoperable AC charging standard.
Public charging stations, residential garages, and commercial parking facilities across Europe rely on the type 2 connector. Its widespread adoption ensures that drivers can access charging wherever they travel within the region.
Artıları ve Eksileri
- Artıları: Faster AC charging, bidirectional charging support
- Eksiler: Less common in North America
The type 2 connector features seven pins and can handle up to 32 amps at 400 volts, supporting a maximum power output of 22 kW. This design enables efficient charging for both daily commutes and longer journeys. However, drivers in North America may encounter limited availability of type 2 charging infrastructure.
Tip: European EV owners benefit from the interoperability and speed of the type 2 connector, especially when using public charging networks.
CCS (Combined Charging System) EV Charging Connector
Uyumluluk
The Combined Charging System (CCS) stands out as a global standard for fast charging. CCS connectors combine AC and DC charging capabilities in a single port, supporting both slow and rapid charging. In Europe, CCS2 is legally mandated and widely adopted, including by Tesla. In North America, CCS1 remains prevalent, although NACS is gaining ground. CCS connectors offer compatibility with a broad range of electric vehicles, but some models require adapters for cross-standard charging.
Where It’s Used
- In 2025, CCS is widely adopted globally, especially in Europe, while CHAdeMO is declining outside Japan.
- Tesla’s NACS is gaining popularity in North America, with several automakers transitioning to it.
- CCS remains prevalent for many EVs worldwide, indicating its long-term viability compared to CHAdeMO.
Public charging stations, highway rest stops, and commercial charging hubs frequently install CCS connectors. The system supports both AC and high-power DC charging, making it suitable for rapid charging during long-distance travel.
Artıları ve Eksileri
- Physical Incompatibility: Different EVs require specific connectors, leading to situations where a charger does not fit a vehicle’s inlet. For example, Tesla and CCS1 vehicles in the US need adapters to charge each other.
- Communication Issues: Different charging systems utilize various communication protocols, complicating interoperability. CCS uses PLC digital communications, while CHAdeMO employs CAN bus, which are not compatible.
- Infrastructure Complexity: Charging service providers must manage multiple standards, increasing costs and complicating maintenance. Public charging stations often need to offer various cables to accommodate different vehicle types.
CCS connectors support both AC and DC charging, with power delivery up to 350 kW for DC fast charging. This versatility makes CCS a preferred choice for many automakers and charging networks. However, regional differences and the need for adapters can create challenges for some drivers.
Tip: Drivers planning cross-country trips should verify their vehicle’s compatibility with CCS charging stations and carry appropriate adapters if necessary.
CHAdeMO EV Charging Connector
Uyumluluk
The CHAdeMO connector has established itself as a dependable solution for DC fast charging, especially in Japan and parts of Asia. Many electric vehicles, such as the Nissan Leaf and Mitsubishi i-MiEV, feature CHAdeMO ports. Japanese automakers continue to support this standard, although its adoption outside Asia remains limited. Drivers with CHAdeMO-equipped vehicles often require adapters when traveling in regions where other standards dominate. The connector only supports DC fast charging, which restricts its versatility compared to systems that offer both AC and DC options.
Where It’s Used
Charging networks in Japan and select Asian markets rely heavily on CHAdeMO. Public charging stations in these regions frequently install CHAdeMO connectors to serve local EV fleets. Some European and North American stations offer CHAdeMO ports, but their presence is less common. Owners of compatible vehicles benefit from a robust infrastructure in Asia, while those in other regions may face challenges finding suitable charging locations.
Artıları ve Eksileri
The following table summarizes the key benefits and drawbacks of CHAdeMO connectors for fast charging:
| Benefits of CHAdeMO Connectors | Drawbacks of CHAdeMO Connectors |
|---|---|
| Widely available in Japan and parts of Asia | Limited utility outside of Asia |
| Can charge an electric vehicle to 80% in less than an hour | Only used by a few Japanese automakers |
| Compatible with many vehicles like Nissan Leaf and Mitsubishi i-MiEV | Less widespread outside of Asia |
| Proven dependable and efficient over a decade | Only for DC fast charging, limiting AC charging options |
| Less expensive than other fast-charging systems | Requires adapters for vehicles without CHAdeMO ports, which can be costly |
Note: CHAdeMO remains a reliable choice for fast charging in its primary markets, but drivers outside Asia should verify connector compatibility before planning long trips.
Tesla/NACS (North American Charging Standard) EV Charging Connector
Uyumluluk
Tesla introduced the North American Charging Standard (NACS) to streamline charging for its vehicles. The connector design supports both AC and DC charging, offering flexibility for various charging scenarios. Since the introduction of NACS, adoption has accelerated among major automakers. Ford led the transition, announcing that all new electric vehicles would feature native NACS ports starting in 2025. Earlier models gained access to NACS chargers through adapters beginning in 2024. Other manufacturers have followed suit, recognizing the reliability and extensive coverage of Tesla’s Supercharger network.
Non-Tesla EVs primarily use Combined Charging Standard (CCS) ports, which do not fit Tesla’s NACS ports directly. Adapters enable non-Tesla owners to access the Supercharger network, but the experience varies. Some Supercharger stations provide adapters, while others require drivers to bring their own. The transition period may present challenges for seamless charging.
Where It’s Used
Tesla Supercharger stations across North America utilize the NACS connector. These stations offer widespread coverage, especially in major cities such as Las Vegas, Los Angeles, and Miami, where EV adoption rates are high. The network continues to expand, with more ports available for non-Tesla vehicles each year. Non-Tesla charging networks have begun implementing NACS-enabled ports, although their numbers remain limited compared to Tesla’s infrastructure.
- The adoption of Tesla/NACS connectors has significantly increased since the introduction of NACS.
- Major automakers, including Ford, announced plans to integrate NACS into their vehicles starting with the 2025 model year.
- Ford was the first major automaker to adopt NACS, with all new electric vehicles featuring native NACS ports from 2025, and earlier models using NACS chargers through an adapter starting in 2024.
- The shift reflects the recognition of the Tesla Supercharger network’s reliability and extensive coverage.
Artıları ve Eksileri
Tesla/NACS connectors offer several advantages for EV owners, but some limitations persist during the transition phase.
Artıları:
- Extensive Supercharger network coverage
- Fast charging speeds and high reliability
- Increasing compatibility with new EV models
Eksiler:
- Non-Tesla EVs primarily use CCS ports, which do not fit Tesla’s NACS ports
- Adapters are necessary for non-Tesla EV owners to access Tesla’s Supercharger network during the transition to NACS
- Some Tesla Superchargers have adapters available, but the experience may not be seamless
Tip: Drivers should confirm connector compatibility and carry necessary adapters when planning to use Tesla Supercharger stations with non-Tesla vehicles.
Emerging and Regional EV Charging Connectors
GB/T (China)
China has developed its own national standard for ev charging connectors, known as GB/T. This connector supports both AC and DC charging, serving the world’s largest electric vehicle market. Most Chinese EVs feature GB/T ports, and public charging stations across the country use this standard. International automakers entering the Chinese market must equip vehicles with GB/T compatibility to access local infrastructure. The connector design differs from those used in North America and Europe, which can complicate cross-border charging for travelers.
South Korean and Indian Standards
South Korea and India have introduced regional standards for ev charging connectors to address local market needs. South Korea relies on a mix of global and domestic connector types, with CCS gaining popularity among newer models. India has adopted a combination of Type 2 and GB/T connectors, reflecting its diverse EV landscape. Public charging stations in these countries offer multiple connector options to accommodate various vehicle types. The evolving standards in these regions highlight the importance of understanding connector compatibility when traveling or importing vehicles.
- The North American Charging Standard (NACS) is the leading emerging EV charging connector in 2025.
- NACS is being implemented primarily in Tesla’s Supercharger network, with 931 ports available for non-Tesla EVs.
- Non-Tesla networks have only 104 NACS-enabled ports.
- Major cities for implementation include Las Vegas, Los Angeles, and Miami, where EV adoption is high.
Note: Regional differences in ev charging connectors require careful planning for international travel and vehicle imports. Drivers should research connector types and availability before visiting new markets.
How EV charging connectors affect your charging experience
Elektrikli Aracınızla Uyumluluk
Matching Plugs and Ports
EV owners encounter a wide range of charging connectors when using public charging points or installing home charging stations. Matching the plug on the charging cable to the port on the electric car is essential for charging compatibility. Type 1 and Type 2 connectors use a common signaling protocol, which helps manufacturers standardize their vehicles. However, the fragmentation of standards, such as CCS and CHAdeMO in North America versus Type 2 in Europe, complicates access to charging infrastructure. Drivers must check their vehicle’s charging port before using a charging station to avoid inconvenience.
- Bu variety of connectors leads to compatibility issues for EV owners.
- Type 1 and Type 2 connectors support easier standardization.
- Fragmented standards complicate charging station access.
Manufacturer Differences
Automakers design electric vehicles with different charging ports and software. Some vehicles use J1772 connectors, while others rely on NACS or CCS. These differences can cause communication protocol mismatches, encryption conflicts, and electrical mismatches. Safety features may block charging if the connector does not meet the car’s requirements. The table below highlights common compatibility issues:
| Cause Type | Specific Issue | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Protocol Mismatch | ISO 15118 vs DIN 70121 | Older EV fails to communicate with a new charging station |
| Software Differences | Firmware incompatibility | Car’s BMS handshake fails with updated charger |
| Electrical Limits | Voltage/current mismatch | 800V charger cannot step down for a 400V-only electric car |
| Mechanical Connection | Incomplete insertion/dirt | Connector not seated, signaling failure |
| Safety Protections | Grounding/fault detection | Charger lacks ground, EV blocks charging |
| Regional Implementation | Vendor-specific details | Same connector, but software differs by country |
Şarj Hızı ve Verimliliği
Connector Impact on Speed
The choice of connector directly affects charging speed. Larger cables allow a higher flow of electricity, resulting in fast charging times. Smaller cables limit the amount of electricity, leading to slower charging. DC fast charging connectors, such as CCS and CHAdeMO, deliver rapid charging for electric vehicles, while AC charging connectors like J1772 and Type 2 provide moderate speeds. The efficiency of charging depends on cable quality and temperature. Most charging losses occur during the conversion of AC power to DC, making DC fast charging generally more efficient.
- Larger cables enable fast charging.
- Smaller cables restrict charging speed.
- Temperature and cable quality influence charging efficiency.
Fast Charging vs. Standard Charging
Charging efficiency decreases above 80% state of charge. Extreme temperatures can reduce efficiency, as energy is used to warm the battery. DC fast charging offers quick top-ups at public charging points, while AC charging suits overnight charging at home. Drivers seeking fast charging should use DC fast charging stations for the best results. Standard charging remains suitable for daily use and longer battery life.
- Charging efficiency drops above 80% battery level.
- Extreme temperatures affect charging speed.
- DC fast charging is more efficient than AC charging.
Availability and Convenience
Kamusal Şarj Ağları
The expansion of halka açık şarj noktaları has improved convenience for EV owners. The UK’s rapid charging network grew from 5,871 chargers in 2021 to 14,471 by December 2024. In 2024, 4,535 new rapid or ultra-rapid charging points were installed, with 84% being ultra-rapid. Different charging patterns among EV drivers impact network utilization and convenience. Charging inconvenience is not evenly distributed, affecting certain areas and user groups more than others.
- Charging patterns influence network utilization.
- Some regions experience more charging inconvenience.
- Ultra-rapid charging points increase fast charging options.
Home Charging Options
Home charging remains a popular choice for electric car owners. Level 1 charging uses a standard 120V outlet, while Level 2 charging requires a 240V installation for faster charging. Level 3 charging, with voltages between 400-800V, is not compatible with home wiring. J1772 is a common connector for many EVs, and NACS is gaining adoption among automakers. Adapters allow compatibility between J1772 and NACS, which is important for installation decisions.
| Şarj Seviyesi | Gerilim | Açıklama |
|---|---|---|
| Seviye 1 | 120V | Basic charging, uses standard household outlets. |
| Seviye 2 | 240V | Fast charging, suitable for most home setups. |
| Seviye 3 | 400-800V | DC fast charging, not compatible with home use. |
Tip: EV owners should verify charging compatibility before installing a home charging station or using public charging points.
Choosing the right EV car charger and connector
Assessing Your EV’s Needs
Checking Your Car’s Port
Selecting the right EV charger begins with understanding the vehicle’s charging port. Each EV model supports specific konnektör türleri, such as CCS, CHAdeMO, or NACS. Owners should verify the connector on their vehicle before purchasing a charger. Compatibility between the charger and the car’s port ensures efficient charging and prevents costly installation errors. Manufacturers often provide clear documentation about supported connector types, making it easier for drivers to match their EV with the correct charging equipment.
Tip: Always check the connector type on your EV before installing a home charger or using public charging stations.
Considering Battery Size
Battery size plays a significant role in choosing an appropriate charger. Larger batteries require higher amperage for faster charging. Most modern EVs accept between 40 to 50 amps, while some models support up to 80 amps. Level 1 charging, which offers 12 to 16 amps, suits smaller batteries but results in slow charging for larger battery electric vehicles. Level 2 charging ranges from 15 to 80 amps, providing flexibility for different battery sizes. Matching the charger’s amperage to the EV’s capacity optimizes charging speed and avoids unnecessary expenses.
- Amperage ratings for EVs typically range from 16 to 80 amps.
- Level 1 charging is best for small batteries and overnight charging.
- Level 2 charging offers faster charging for larger batteries.
Location and Lifestyle Factors
Home vs. Public Charging
Location influences the choice of charger and connector. Drivers who own single-family homes often install Level 2 chargers for daily use. Home charging provides convenience and cost savings. In contrast, those living in multi-unit dwellings may rely on public charging infrastructure. Public stations offer a variety of connector types, but access can be limited in some areas. Understanding the available charging infrastructure helps drivers select the most practical solution for their lifestyle.
| Şarj Konumu | Typical Charger Level | Connector Types Available |
|---|---|---|
| Ev | Seviye 1, Seviye 2 | J1772, NACS |
| Kamu | Level 2, DC Fast | CCS, CHAdeMO, NACS |
Urban vs. Rural Considerations
Urban and rural settings present different challenges for EV charging. Rural drivers, especially in states like Maine, Virginia, and Vermont, are more likely to own single-family homes, making home charging easier. Over 85% of rural households in these states live in single- or two-family homes. Urban drivers often face difficulties due to limited access to charging infrastructure in multi-unit buildings. Evaluating the local charging infrastructure and housing type helps determine the best charging solution.
- Rural drivers benefit from easier home charging installation.
- Urban drivers may depend on public charging stations.
Future-Proofing Your EV Setup
Adapters and Upgrades
Industry standards for EV charging continue to evolve. Investing in adapters allows owners to use multiple connector types, increasing compatibility with various charging stations. Modular hardware and scalable power distribution units make upgrades easier as new technologies emerge. Owners should consider chargers that support remote firmware updates, ensuring their setup remains current with industry changes.
Anticipating Industry Changes
Planning for future needs protects against obsolescence. Installing pre-wired conduits for future chargers reduces the need for extensive electrical work. Flexible site layouts and scalable infrastructure maximize charging capacity without overloading the grid. Solutions that allow remote updates and modular upgrades help drivers adapt to new connector standards and charging technologies.
Note: Future-proofing an EV charging setup ensures long-term compatibility and reduces costs as the industry evolves.
Regional differences in EV car chargers and connectors
Kuzey Amerika
Common Standards
North America features a unique mix of charging connector standards. Most AC charging stations use the Type 1 (SAE J1772) connector. For DC fast charging, CCS1 and the North American Charging Standard (NACS) dominate public infrastructure. Many public chargers with Type 1 connectors are being phased out as the market shifts toward faster and more universal solutions. The following table summarizes the main connector types by region:
| Bölge | AC Charging Connector | DC Fast Charging Connector | Ek Notlar |
|---|---|---|---|
| Kuzey Amerika | Tip 1 (SAE J1772) | CCS1, NACS | Type 1 public chargers are being phased out. |
| Avrupa | Tip 2 (Mennekes) | CCS2 | Older stations may still have CHAdeMO. |
| Asia-Pacific | N/A | CCS2, CHAdeMO (Japan) | GB/T is the main standard in China. |
Unique Considerations
Government incentives in North America encourage both private and public investments in charging stations. These policies make it easier for businesses to install new charging points and support research into advanced charging technologies. Regulations also help standardize infrastructure, which improves compatibility for ev owners. Some incentives target rural and underserved areas, promoting broader access to charging. As a result, drivers in North America benefit from a growing network of fast and reliable charging options.
Avrupa
Common Standards
Europe relies on the Type 2 (Mennekes) connector for AC charging. For DC fast charging, CCS2 is the legal standard across the region. Most new public charging stations use these connectors, ensuring a high level of interoperability for drivers. Some older stations may still offer CHAdeMO connectors, but their presence continues to decline as the market standardizes around CCS2.
Unique Considerations
European governments play a significant role in shaping the charging landscape. Regulations require new public chargers to use Type 2 and CCS2 connectors, which simplifies the charging experience for ev drivers. Incentives also support the installation of charging stations in rural areas and along major highways. These policies help create a seamless charging network that supports both local and long-distance travel.
Asia and Other Regions
China (GB/T)
China uses its own national standard, known as GB/T, for both AC and DC charging. This standard supports the world’s largest ev market. Most public charging stations and vehicles in China use GB/T connectors. International automakers must equip their vehicles with GB/T compatibility to access the local infrastructure.
South Korea and India
South Korea and India show a mix of global and regional connector standards. South Korea increasingly adopts CCS2 for new vehicles, while India uses both Type 2 and GB/T connectors. Public charging stations in these countries often provide multiple connector types to serve a diverse range of vehicles. Government incentives in these regions encourage the development of charging infrastructure, especially in areas that lack sufficient coverage.
Note: Regional differences in charging connectors require drivers to plan ahead, especially when traveling internationally or importing vehicles.
The future of EV charging connectors and EV car chargers
Trends to Watch in 2025
Standardizasyon Çabaları
Industry leaders continue to push for greater standardization in EV charging connectors. Automakers and charging network operators recognize that a unified approach simplifies the charging process for every EV owner. In 2025, several trends shape this movement:
- Standardized connectors across different vehicle models make charging more user-friendly and accessible.
- The adoption of ISO 15118 compliance ensures secure and efficient charging sessions, supporting features like Tak ve Şarj Et.
- Plug & Charge protocols allow automatic authentication between EVs and chargers, eliminating the need for cards or apps.
These efforts reduce confusion at public stations and help drivers access fast charging without compatibility concerns. As more manufacturers align with these standards, the industry moves closer to seamless charging experiences.
New Technologies
New technologies continue to transform the EV charging landscape. Charging stations increasingly utilize renewable energy sources, such as solar and wind power, to improve efficiency and sustainability. Araçtan Şebekeye (V2G) technology enables EVs to act as energy storage units, balancing supply and demand on the grid. This innovation not only supports grid resilience but also creates new opportunities for cost savings.
Charging infrastructure also benefits from advancements in hardware. The integration of sıvı soğutmalı kablolar enhances energy transfer efficiency, resulting in faster charging times. Portable EV charging solutions gain popularity, allowing users to charge vehicles conveniently anywhere and reducing reliance on fixed stations. Second-life EV batteries find new roles in energy storage, further lowering emissions and supporting the transition to clean energy.
Tip: Drivers should look for charging stations that support these new technologies to maximize efficiency and future-proof their EV experience.
Impact on EV Owners
What to Expect
EV owners can expect a more streamlined and efficient charging experience in 2025. Standardized connectors and Plug & Charge protocols remove many of the barriers that previously complicated fast charging. The expansion of renewable-powered charging stations means drivers will see more sustainable options at public locations. Liquid-cooled cables and improved hardware deliver faster charging, reducing wait times and making long trips more practical.
Portable charging solutions also empower drivers to charge their vehicles wherever they go. This flexibility proves especially valuable for those living in areas with limited fixed infrastructure. As V2G technology matures, owners may even contribute to grid stability and benefit from new revenue streams.
Preparing for Change
To prepare for these changes, EV owners should stay informed about the latest charging standards and technologies. Choosing vehicles and home chargers that support ISO 15118 and Plug & Charge ensures compatibility with future networks. Investing in adapters and modular charging equipment provides flexibility as the industry evolves. Owners should also consider the benefits of renewable-powered charging and V2G capabilities when selecting new vehicles or charging solutions.
Note: Staying proactive about new charging trends helps EV owners maximize convenience, efficiency, and long-term value.
Every electric car owner in 2025 should understand the main ev car chargers and connector types. Checking compatibility before using a charging station prevents issues and saves time. Drivers benefit from carrying adapters, planning charging station stops, and staying informed about new ev car chargers. The right choices help an electric car charge efficiently at home or on the road. Knowledge of ev car chargers and charging station options supports a smooth electric car experience.
SSS
What is the difference between Level 1, Level 2, and DC Fast charging?
Level 1 uses a standard outlet and charges slowly. Level 2 requires a dedicated station and charges faster. DC Fast charging delivers the quickest charge using direct current, suitable for long trips or quick stops.
Which connector type should an EV owner prioritize in North America?
Most drivers in North America use J1772 for AC charging and CCS or NACS for DC fast charging. Tesla owners rely on NACS. Checking the vehicle’s port ensures compatibility with local infrastructure.
Can adapters solve all EV charging connector compatibility issues?
Adapters help connect different charging standards, but not every adapter works with every vehicle. Some charging stations may not support adapters due to safety or communication limitations.
How does charging speed vary by connector type?
DC fast charging connectors like CCS and CHAdeMO deliver higher power, reducing charging time. AC connectors such as J1772 and Type 2 provide moderate speeds, suitable for daily charging at home or work.
Are public charging stations available in rural areas?
Public charging stations exist in rural regions, but coverage remains limited compared to urban centers. Rural drivers often install home chargers for convenience and reliability.
What should EV owners consider before installing a home charger?
Owners should verify the vehicle’s connector type, battery size, and available electrical capacity. Professional installation ensures safety and optimal charging performance.
Will EV charging standards change in the next few years?
Industry trends indicate ongoing standardization, especially with NACS and CCS gaining traction. Owners should stay informed about updates and consider future-proofing their charging setup.
Do all EVs support vehicle-to-grid (V2G) technology?
Not every EV supports V2G. Manufacturers include V2G capability in select models. Owners should check specifications before expecting grid integration features.





