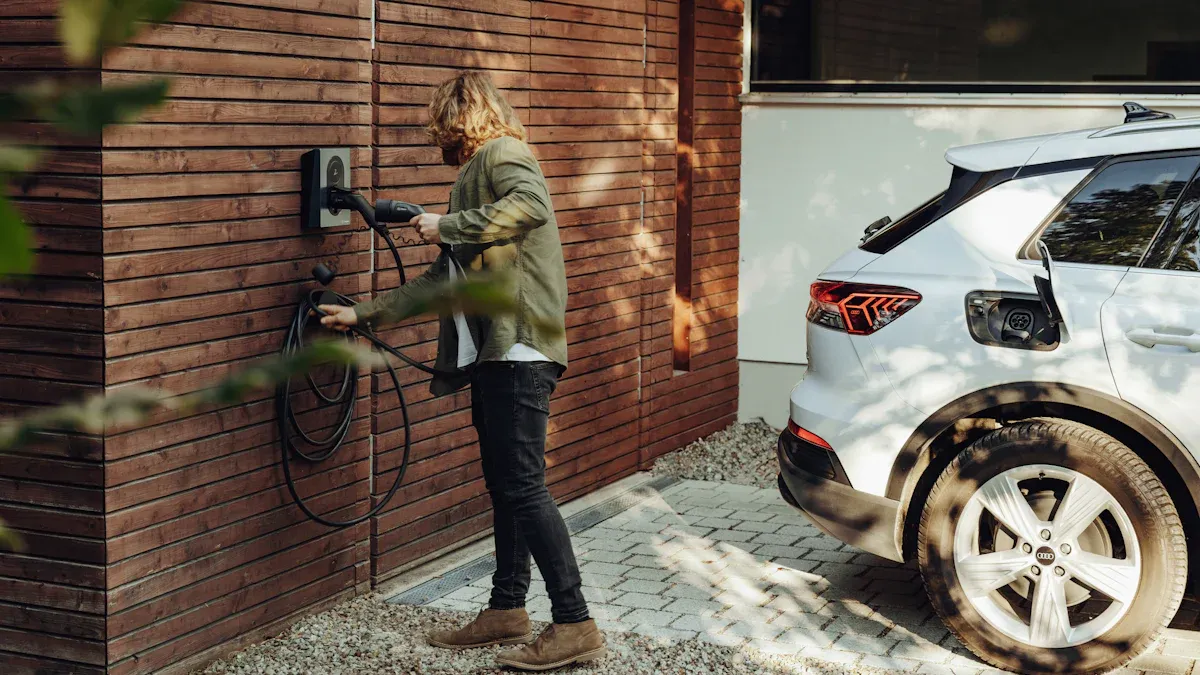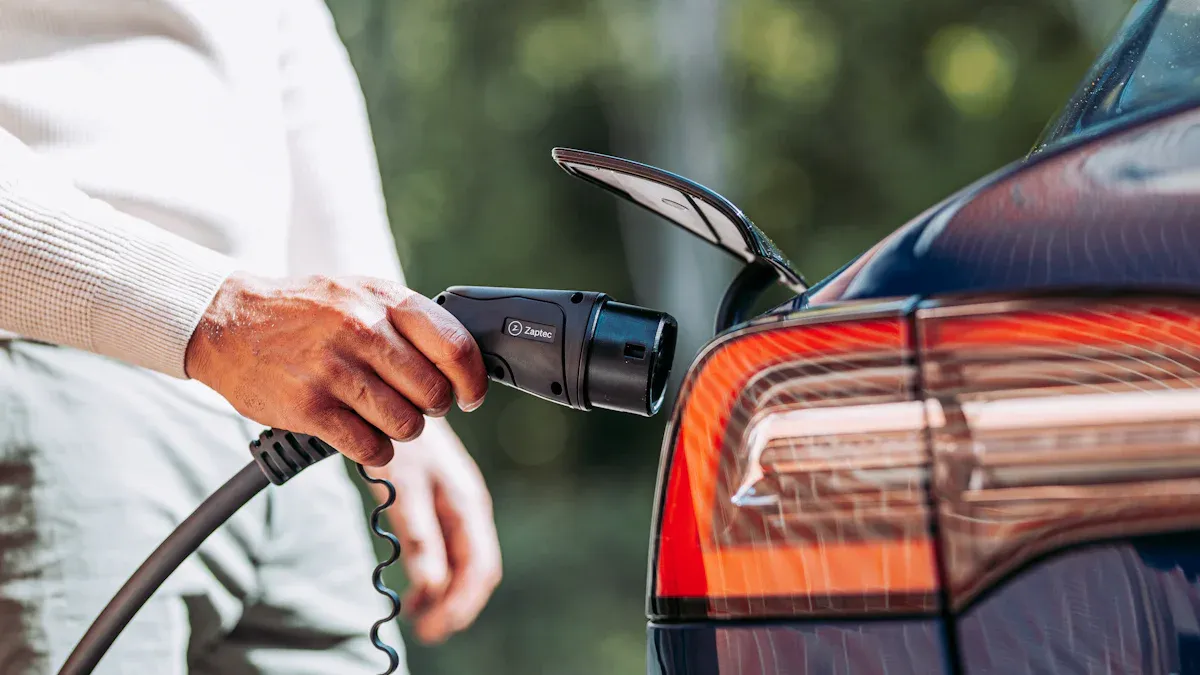
You can power your electric car with a solar electric car charger, making your daily drive cleaner and more sustainable. Many electric vehicle owners already embrace this technology—
Solar EV charging uses renewable energy to cut emissions dramatically. See how solar energy compares:
Método de carga | |
|---|---|
450 gallons of gas | 8,820 |
3,780 kWh from grid | 1,531 |
3,780 kWh from solar | 368 |
Charging your EV with solar power reduces pollution and helps you depend less on the grid. Leading Fabricantes de cargadores para VE now offer smart solutions for solar charging, letting you use solar energy for your electric vehicle at home or on the go. With a dedicated Cargador EV, you support renewable energy and enjoy efficient charging.
How Solar EV Charging Works

What Is Solar EV Charging?
Solar EV charging allows you to power your EV using energy from the sun. You use a solar panel system to capture sunlight and convert it into electricity. This electricity flows directly to your electric vehicle charger, providing clean energy for your EV. You can install solar EV charging systems at home or use portable setups for charging on the go.
Solar EV charging reduces your reliance on the grid and lowers your carbon footprint. You make a positive impact on the environment every time you charge your EV with solar energy.
The main components involved in a solar EV charging system include:
Solar PV panels: These convert solar radiation into electrical energy for your EV battery.
Microcontrollers: These optimize efficiency and control the alignment of the solar panels.
Motor for panel axis rotation: This adjusts the angle of the panels for maximum sunlight exposure.
DC-DC converter with MPPT: This device converts solar power to the voltage required for your EV battery.
Communication interface: This system connects your EV battery and the solar charging setup.
How Solar Energy Powers Your EV Charger
Solar energy powers your EV charger through a series of steps. Solar panels capture sunlight and convert it into direct current (DC) electricity. A DC-DC converter with maximum power point tracking (MPPT) adjusts the voltage to match your EV battery’s requirements. The communication interface ensures that your EV battery and the solar charging system work together efficiently.
Componente | Function |
|---|---|
Solar PV panels | Convert solar energy into electricity for EV batteries. |
DC-DC converter with MPPT | Adjusts voltage from solar panels to match EV battery requirements. |
Communication Interface | Connects EV battery monitoring system with the solar charging system for optimal charging. |
You can also use a solar inverter to transform DC power into alternating current (AC) for home use. The AC power flows into your home’s electrical panel, making it available for your EV charger. The Electric Vehicle Supply Equipment (EVSE) manages the safe transfer of electricity to your EV.
Direct vs. Indirect Solar Electric Car Charging
You can choose between direct and indirect solar electric car charging methods. Direct charging uses solar panels to supply electricity straight to your EV. This method achieves higher energy efficiency because it minimizes energy loss during conversion. You benefit from immediate use of solar energy, but you need consistent sunlight for optimal performance.
Indirect charging involves generating electricity from solar panels and storing it in batteries or feeding it into the grid. You then use this stored or grid electricity to charge your EV. This method offers flexibility, allowing you to charge your electric vehicle even when sunlight is not available. However, indirect charging may result in slightly lower efficiency due to additional energy conversion steps.
Direct solar charging: Higher efficiency, requires sunlight, minimal energy loss.
Indirect solar charging: Greater flexibility, works in various conditions, slightly lower efficiency.
Tip: If you live in an area with abundant sunlight, direct solar EV charging can maximize your energy savings. If you need more flexibility, consider an indirect setup with battery storage.
Choosing the Right Solar Electric Car Charger
Selecting the best solar electric car charger for your needs requires careful consideration of charger types and essential features. You want a solution that matches your electric vehicle, maximizes solar energy use, and ensures safe, efficient charging.
Types of Solar EV Chargers
You can choose from several types of solar-compatible EV chargers. Each type offers unique benefits for different charging scenarios.
Portable Solar Chargers for EVs
Portable chargers provide flexibility for EV owners who travel or need backup charging options. You can plug these chargers into standard outlets, making them ideal for emergencies or remote locations. Portable solar chargers typically offer lower power ratings, so charging times may be longer. You gain convenience and mobility, but you sacrifice speed.
Home Solar EV Charging Stations
Home charging stations deliver faster, more reliable charging for daily use. You install these chargers in your garage or driveway, integrating them with your solar panel system. Home stations support higher power output, which reduces charging time and increases efficiency. You benefit from seamless solar integration and greater control over your EV charging schedule.
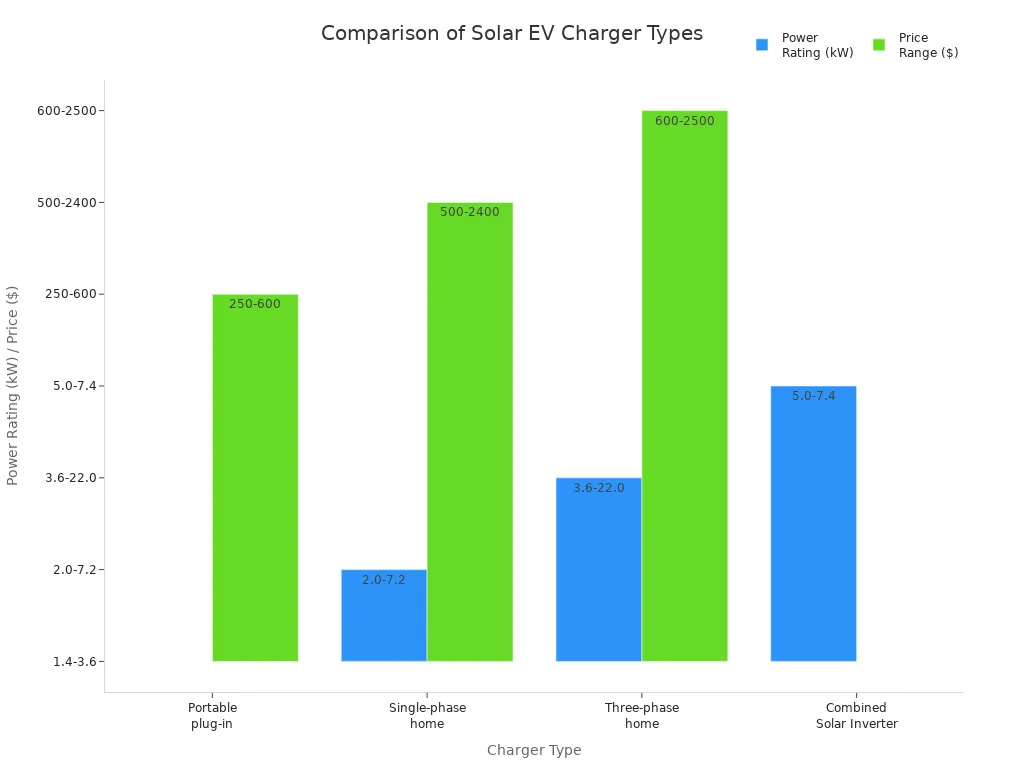
Tipo de cargador | Power Rating (kW) | Charge Rate (km/h) | Price Range ($) |
|---|---|---|---|
Portable plug-in (granny) chargers | 1.4 to 3.6 | 12 km (7.5 miles) | 250 to 600 |
Single-phase home EV chargers | 2.0 to 7.2 | up to 45 km (28 miles) | 500 to 2400 |
Three-phase home EV chargers | 3.6 to 22.0 | up to 130 km (80 miles) | 600 to 2500 |
Combined Solar Inverter and EV Charger | 5.0 to 7.4 | Carga de nivel 2 | N/A |
Key Features of an EV Charger
When you select a solar-compatible EV charger, you should focus on features that enhance performance, safety, and integration with your solar system.
Power Output and Compatibility
You need a charger with the right power rating for your EV battery. Higher power output means faster charging, but you must ensure compatibility with your electric vehicle and solar setup. Single-phase chargers suit most homes, while three-phase chargers deliver rapid charging for larger batteries. Combined solar inverter and EV charger units simplify installation and optimize solar energy use.
Safety and Smart Controls
Modern EV chargers include advanced safety features and smart controls. You should look for:
Battery awareness to distinguish between solar generation and battery charging.
Prioritization settings to manage energy flow between your EV and home battery.
AC/DC coupling options for seamless integration with different solar systems.
Real-time solar data APIs for monitoring charging rates and system performance.
Green or solar settings that allow you to use only renewable energy for charging.
Tip: Choose an EV charger that maximizes free solar energy and offers smart controls for safe, efficient charging.
A solar electric car charger with these features ensures you get the most from your solar investment while protecting your EV and home.
Calculating Solar Panel Requirements for Charging Your EV
Understanding Your EV’s Battery Capacity
You need to understand your EV’s battery capacity before sizing your solar charging system. Battery capacity, measured in kilowatt-hours (kWh), determines how much energy your EV can store and how long it takes to charge. Larger batteries require more energy and longer charging times. For example:
Charging a fully discharged 120 kWh battery with a 6 kW solar panel system takes about 20 hours.
Charging a 40 kWh EV battery with a 30 kW DC charger takes roughly 1.33 hours.
The actual charging speed depends on the maximum output of your charger and your EV’s voltage and current specifications.
Tip: Always check your EV’s manual for battery size and recommended charging rates to optimize your solar setup.
Estimating Daily Solar Energy Needs
To estimate your daily solar energy needs, you must consider your EV’s energy consumption and your driving habits. Different EV models consume varying amounts of energy per 100 kilometers. The table below shows the average consumption for popular models:
Modelo | Consumption (kWh/100 km) | Average Range (km) |
|---|---|---|
Volkswagen e-up! | 11.5 | ~280 |
Volkswagen ID.3 | 13.3 | ~438 |
Volkswagen ID.7 | 13.1 | ~588 |
Hyundai Kona Electric | 13.4 | ~477 |
Tesla Modelo 3 | 14.7 | 450-580 |
Peugeot e-208 | 14.9 | ~340 |
Renault Mégane E-Tech | 13.3 | ~450 |
Dacia Spring | 13.9 | ~230 |

If you drive 50 km per day in a Tesla Model 3, you will use about 7.35 kWh daily (14.7 kWh/100 km × 0.5). Multiply your daily driving distance by your EV’s consumption rate to calculate your daily solar energy requirement.
Factors Affecting Solar Panel Quantity
Several factors influence how many solar panels you need to charge your EV efficiently.
Sunlight Hours and Local Climate
The amount of sunlight your location receives each day plays a major role in solar energy production. More sunlight means your solar panels generate more electricity. Cloudy weather or shorter daylight hours reduce output, so you may need a larger array in less sunny regions.
Solar Panel Efficiency
Solar panel efficiency measures how well your panels convert sunlight into usable electricity. High-quality, efficient panels produce more energy from the same amount of sunlight. Consider these factors:
Quality and efficiency: Better panels convert more sunlight and lose less energy.
Orientation: Proper positioning of solar panels maximizes performance.
Power rating: Higher wattage panels deliver more energy.
Charging patterns: Frequent or high-capacity charging requires more solar power.
Note: Your EV’s energy consumption, solar panel efficiency, available sunlight, and your charging habits all impact the number of panels you need.
By evaluating your EV’s battery size, daily driving habits, and local solar conditions, you can accurately determine the right solar power system for your needs.
Step-by-Step Installation of a Solar EV Charger

Preparing Your Site for Solar Energy
Assessing Roof or Ground Space
You begin by evaluating your property to determine the best location for your solar electric car charging system. Examine your roof or available ground space to ensure it can support solar panels. Structural integrity matters. Your roof must withstand the weight and wind load of the panels. If you choose ground installation, check for stable, unobstructed terrain.
Common challenges include shading from trees or nearby buildings, which can reduce solar efficiency. Roof orientation and tilt also affect how much sunlight your solar panels receive. South-facing roofs with a tilt angle between 15° and 40° usually offer optimal exposure. You should clear the installation area and ensure easy access for technicians.
Tip: Use a solar pathfinder or similar tool to identify potential shading issues before installation.
Checking Local Regulations and Permits
You must comply with local building codes and electrical regulations before installing your EV charger and solar panels. Apply for the necessary permits, including electrical and building approvals. Some municipalities require specific documentation or inspections. Navigating the permitting process can take time, so start early to avoid delays.
You should also assess your home’s electrical capacity. Confirm that your electrical panel can handle the additional load from the charger and solar system. Prepare the parking space and ensure clear access to the electrical panel for installation.
Site Preparation Checklist:
Evaluate optimal location for the EV charger and solar panels.
Assess electrical capacity and cable run distance.
Obtain required permits and approvals.
Prepare the property by clearing the installation area and ensuring access.
Installing Solar Panels for Charging Your EV
Mounting and Positioning Panels
You mount the solar panels on your roof or ground area, following manufacturer guidelines. Position the panels to maximize sunlight exposure throughout the day. Avoid shaded areas and ensure the panels face the direction that receives the most sunlight.
Use mounting hardware rated for your local climate. Secure the panels to withstand wind and weather. If you install on a roof, check for leaks or weak spots before mounting. For ground installations, use sturdy frames anchored into the soil.
Note: Proper orientation and tilt increase energy production and improve the efficiency of your solar electric car charging system.
Wiring and Connecting to the EV Charger
You connect the solar panels to your EV charger using dedicated wiring. Follow safety standards by using a dedicated circuit to prevent overloads. Engage a qualified electrician to ensure compliance with electrical codes and safe installation practices.
Install surge protection devices to safeguard your system against power surges. Keep the installation away from water sources for added safety. Use AC/DC coupling options if your charger supports them, which allows seamless integration with different solar setups.
Best Practices for Installation:
Evalúe la capacidad eléctrica de su vivienda.
Choose a location for the charger close to your parking area.
Use surge protectors and keep the system dry.
Hire a qualified electrician for installation.
Consider solar batteries to improve power independence.
Setting Up and Testing Your Solar EV Charger
Connecting to the Solar System
You connect the EV charger to your solar system after mounting and wiring the panels. Gather all necessary tools and materials. Turn off the power at the electrical panel before making any connections. Mount the charger according to the manufacturer’s instructions. Connect the power supply from the solar panels to the charger and then to the electrical panel.
Determine the number of solar panels needed based on your EV’s charging requirements. Choose a location for the charger that is easily accessible. Connect the charger to the solar system and test all components after installation.
Safety Checks and Initial Operation
You perform safety checks to ensure proper operation. Conduct electrical safety tests, such as earth loop impedance and RDC-DD tests. Set the PP state to 32 A and adjust the CP state through positions A, B, and C. Simulate charging and listen for the contacts closing. Check for error signals and confirm that the charger operates correctly.
Test the charger with your EV and monitor the charging process for two to three days. Observe solar energy production and EV energy usage. Regular maintenance keeps your system running efficiently. Clean the solar panels a few times a year to maintain peak performance.
Alert: Always follow manufacturer instructions and local safety standards when installing and testing your EV charger.
Installation and Testing Steps:
Gather tools and materials.
Turn off power at the electrical panel.
Mount the EV charger.
Connect the power supply to the electrical panel.
Test the charger with your EV.
Monitor charging for several days to ensure proper operation.
Operating and Maintaining Your Solar Electric Car Charger
Charging Your EV with Solar Energy
You can enjoy the benefits of solar energy every time you use your EV charger. The process of charging your EV with solar power depends on your solar array size, your EV’s battery capacity, and your daily driving needs. Charging times vary:
A typical home solar setup can provide daily top-ups in a few hours.
A full charge may take several days if you rely only on solar energy.
For example, a 42kWh Fiat 500e would need almost 5 days to fully recharge with a solar array generating 8.5 kWh per day.
Most drivers only need a daily recharge of about 12%, which takes around 2.25 hours of solar charging for an average 20-mile commute.
You should plan your charging sessions during peak sunlight hours to maximize efficiency. Smart chargers can help you schedule charging your EV when your solar panels produce the most energy. This approach reduces your reliance on the grid and ensures you use clean, renewable power.
Tip: Track your daily driving habits and adjust your charging schedule to match your solar production for the best results.
Monitoring System Performance
You need to monitor your solar EV charger system to ensure optimal performance. Regular checks help you spot issues early and keep your system running smoothly. Consider these best practices:
Calculate your solar panels’ output and confirm they meet your EV’s daily charging needs.
Use sun trackers to adjust panel angles throughout the day and boost energy output.
Upgrade your solar array by adding more panels or choosing higher-efficiency models if your energy needs increase.
Integrate smart charging technology. Timed charging and home energy management systems help you use solar energy more efficiently.
Many modern EV chargers offer real-time monitoring through apps or web dashboards. These tools let you track energy production, charging rates, and system health from your phone or computer.
Note: Consistent monitoring helps you identify trends, optimize solar charging, and maintain reliable EV performance.
Routine Maintenance and Troubleshooting
Routine maintenance keeps your solar EV charger system efficient and safe. You should:
Inspect solar panels, chargers, and electrical connections regularly for signs of wear or damage.
Clean your solar panels to remove dust and debris, ensuring maximum sunlight capture.
Update software and firmware to maintain system efficiency and security.
Tighten all electrical connections and check for loose wires.
Perform seasonal checks for wear and tear, especially after storms or extreme weather.
Clear debris from around the charger and test ground fault interrupters (GFIs) frequently.
Contact certified technicians for complex repairs or servicing.
Alert: Regular maintenance prevents unexpected breakdowns and extends the lifespan of your solar EV charger system.
By following these steps, you ensure your solar charging setup delivers reliable, clean energy for your electric vehicle every day.
Benefits and Drawbacks of Solar EV Charging
Environmental Benefits of Solar Energy
You make a significant impact on the environment when you choose solar EV charging. Solar-integrated EV charging systems reduce greenhouse gas emissions and promote the adoption of renewable energy sources. You help decrease dependence on fossil fuels and contribute to cleaner air in your community. Solar energy allows your electric vehicle to run on 100% renewable energy, producing zero emissions during operation. This practice enhances overall energy efficiency in the transportation sector and helps mitigate climate change.
Solar EV charging reduces carbon emissions.
You support the transition to renewable energy.
Cleaner air benefits public health.
Solar power improves energy efficiency for electric cars.
Tip: Charging your EV with solar energy is one of the most effective ways to lower your carbon footprint and support a sustainable future.
Financial Savings and Incentives
Switching to solar EV charging brings substantial financial savings. You can save hundreds of dollars each year by using solar power for your electric car. The table below shows typical annual savings for electric vehicle owners who use solar energy:
Savings Estimate | Amount Saved (USD) |
|---|---|
Ahorro medio | $620.50 |
High Savings | $1,058.50 |
Low Savings | $427.05 |
General Estimate | $700 |
You also benefit from government incentives and rebates designed to make solar EV charging more affordable. These programs include tax credits, grants, net metering, and low-interest loans. The following table outlines some popular incentives available for solar-powered EV charging systems:
Tipo de incentivo | Descripción |
|---|---|
Créditos fiscales | Up to 30% or $1,000 for residential EV charger purchase and installation by December 31, 2032. |
Alternative Fuel Infrastructure Tax Credit | 30% tax credit for businesses, up to $100,000 for electric charging infrastructure until December 31, 2032. |
Grants & Rebates | Local and national programs providing partial funding or cash rebates for solar-powered EV charging. |
Net Metering | Ability to sell excess solar energy back to the grid, creating a revenue stream. |
Low-Interest Loans | Financing programs offering low-interest loans for solar-powered charging station installations. |
Incentivos de servicios públicos | Discounts or reduced electricity rates for businesses installing solar EV chargers. |
Note: You can maximize your savings by combining solar energy with available incentives and rebates.
Maintenance and System Longevity
You enjoy long-term reliability when you invest in a solar EV charging system. Modern solar panels have an average lifespan of at least 25 years before you notice any performance degradation. Some high-quality solar panels can last for 40 years or more. Routine maintenance, such as cleaning panels and checking connections, helps you maintain peak efficiency. You spend less time worrying about repairs and more time enjoying the benefits of solar power for your electric vehicle.
Solar panels provide decades of reliable service.
You minimize maintenance costs with durable equipment.
Long lifespan increases the value of your solar investment.
Alert: Regular inspections and cleaning keep your solar EV charger operating efficiently for years.
Potential Drawbacks
Costes iniciales
You may notice that the initial investment for a solar electric car charging system can be substantial. The cost includes purchasing solar panels, an EV charger, mounting hardware, and professional installation. You also need to budget for electrical upgrades if your home’s panel cannot support the new system. Many homeowners find that the price of a solar setup exceeds the cost of a standard grid-powered charger.
Componente | Typical Cost (USD) |
|---|---|
Solar panels | $6,000 – $12,000 |
Cargador EV | $500 – $2,500 |
Instalación | $2,000 – $5,000 |
Mejoras eléctricas | $1,000 – $3,000 |
Note: Incentives and rebates can help offset some of these expenses, but you should prepare for a significant upfront commitment.
Weather and Sunlight Dependence
You rely on sunlight to generate power for your solar EV charger. Cloudy days, rain, or snow can reduce the amount of energy your solar panels produce. Seasonal changes also affect solar output. In winter, shorter days and lower sun angles mean less energy for charging your electric vehicle. You may need to supplement your charging with grid electricity during extended periods of poor weather.
Solar energy production drops during cloudy or stormy weather.
You experience lower charging rates in winter months.
You may need backup charging options for consistent EV use.
Tip: You can install a battery storage system to save excess solar energy for use during low sunlight periods.
Espacio necesario
You need adequate space to install a solar charging system. Most homes require several solar panels to meet daily EV charging needs. You must assess your roof’s size, orientation, and structural integrity before installation. If your roof cannot support the panels, you may need to use ground mounts, which require clear, unobstructed land.
Large solar arrays need significant roof or yard space.
Shading from trees or buildings can limit solar panel placement.
You must ensure easy access for maintenance and cleaning.
Requisito | Impacto en la instalación |
|---|---|
Roof size | Determines panel quantity |
Sun exposure | Affects solar efficiency |
Structural strength | Supports panel weight |
Alert: You should consult with a solar professional to evaluate your property’s suitability for a solar EV charger.
Cost Considerations and Tips for Efficient Charging Your EV
Initial Setup and Equipment Costs
When you plan to install a solar EV charging station at home, you need to consider several upfront expenses. The main costs include the charger unit, solar panels, and installation services. In the United States, a 7kW solar charging station for your EV typically costs around $1,300. If you look at the installation, you can expect to pay between $800 and $2,500, with most homeowners spending about $1,700 for a standard setup. The price for the charger itself varies. Level 2 charging stations usually range from $500 to $2,200. Some installations, including both the device and labor, may cost between $463 and $1,126.
7kW solar charging station: about $1,300 (USA)
EV charger installation: $800–$2,500 (average $1,700)
Level 2 charger unit: $500–$2,200
Total device and installation: $463–$1,126 (typical range)
You should also budget for any electrical upgrades if your home’s panel cannot support the new system. These costs can add up, but you gain long-term value and energy independence.
Ongoing Operating Expenses
After you install your solar EV charger, your ongoing expenses remain low. Solar panels generate electricity from sunlight, so you avoid most utility costs for charging your EV. You may still pay for occasional grid electricity if your solar system does not meet all your needs, especially during cloudy days or high usage periods. Routine maintenance, such as cleaning panels and checking connections, helps keep your system efficient. Most modern chargers require minimal upkeep. You might spend a small amount each year on inspections or minor repairs, but these costs are much lower than traditional fueling or grid-only charging.
Tip: Regularly monitor your system’s performance to catch issues early and maximize your solar energy output.
Incentives, Rebates, and Savings
You can take advantage of several incentives and rebates to lower your initial investment in a solar EV charging setup. Federal tax credits in the United States can cover up to 30% of your installation costs, including both the charger and solar equipment. Many states and local governments offer additional rebates or grants for solar and EV charger installations. Some utility companies provide special rates or discounts for customers who use solar energy for EV charging. Net metering programs allow you to sell excess solar power back to the grid, creating extra savings over time.
Tipo de incentivo | Potential Benefit |
|---|---|
Crédito fiscal federal | Up to 30% of installation costs |
State Rebates | Varía según el lugar |
Utility Discounts | Lower rates for solar EV charging |
Net Metering | Credit for excess solar generation |
You should research available programs in your area before you purchase your charger or solar panels. These incentives can make solar EV charging more affordable and help you achieve greater savings in the long run.
Practical Tips for Maximizing Solar EV Charging Efficiency
Charging During Peak Sun Hours
You can maximize the efficiency of your solar EV charger by scheduling charging sessions during peak sun hours. Solar panels generate the most electricity when the sun is highest in the sky, usually between 10 a.m. and 4 p.m. Charging your EV during these hours ensures you use the maximum amount of renewable energy and reduce reliance on the grid. Tecnología de carga inteligente helps you automate this process by aligning your charging times with solar production. Many modern chargers offer apps that let you monitor solar output and schedule charging for optimal periods.
Tip: Use charging apps to track your solar energy production and set reminders for charging your EV when your solar panels reach peak output.
You should also consider environmental factors. Charging during periods of cleaner energy generation not only boosts efficiency but also supports a greener grid.
Using Battery Storage Solutions
Battery storage solutions add flexibility to your solar EV charging setup. By storing excess energy from your solar panels, you can charge your EV even when the sun is not shining. This approach helps you avoid drawing power from the grid during cloudy days or at night. A home battery system works seamlessly with your EV charger, providing a reliable backup and enhancing your energy independence.
Store surplus solar energy for later use.
Maintain consistent charging regardless of weather or time of day.
Protect your EV battery health by managing charge levels and temperature.
You should monitor your energy usage patterns. Smart systems and apps allow you to analyze your charging habits and adjust for greater efficiency and savings.
Taking Advantage of Utility Tariffs
Utility tariffs play a significant role in the cost-effectiveness of solar EV charging. Many utilities offer time-of-use rates, which means electricity costs less during off-peak hours. By charging your EV when rates are lowest, you can reduce your expenses and make the most of your solar investment. The following table highlights how utility tariffs impact your charging strategy:
Impact of Utility Tariffs on EV Charging Timing | Descripción |
|---|---|
Carga fuera de horas punta | Encourages EV owners to charge during off-peak hours, reducing costs. |
Solar Generation Utilization | Promotes charging during peak solar generation times, optimizing renewable energy use. |
Network Utilization | Shifts charging to times that improve overall network efficiency, such as late night. |
You can also benefit from time-of-use tariff advantages:
Time-of-Use Tariff Benefits | Descripción |
|---|---|
Avoiding Peak Demand | Keeps EV charging away from high demand periods, lowering costs. |
Excess Solar Utilization | Encourages charging during the day when solar energy is abundant. |
Improved Network Utilization | Shifts charging to night hours, enhancing grid efficiency. |
Note: Leverage smart charging features to automatically schedule your charger for the most cost-effective times.
By combining smart charging, battery storage, and strategic use of utility tariffs, you can optimize your solar EV charging system for maximum efficiency and savings.
You can achieve significant savings and environmental benefits by switching to a solar electric car charger. Charging your EV at home with solar power costs less than public or grid charging. An average EV uses about 4,666 kWh each year, so you may need up to 12 extra solar panels for effective charging.
Integrating solar with EV charging supports ESG goals and reduces your reliance on grid electricity.
Assess your needs and site feasibility.
Choose the right equipment.
Take advantage of government incentives.
PREGUNTAS FRECUENTES
Can you charge any electric car with a solar EV charger?
You can charge most electric cars with a solar EV charger if the charger matches your vehicle’s charging standard and power requirements. Always check your EV’s compatibility with the charger and solar system before installation.
How many solar panels do you need to charge an EV?
You usually need 8 to 12 solar panels to charge an average electric car for daily use. The exact number depends on your driving habits, your EV’s battery size, and your local sunlight hours.
Do solar EV chargers work on cloudy days?
Solar EV chargers still work on cloudy days, but they produce less electricity. You may need to supplement charging with grid power or use stored solar energy from a battery system during low sunlight periods.
Is it safe to install a solar EV charger yourself?
You should hire a licensed electrician for installation. Professional installation ensures safety, meets local codes, and protects your equipment warranty. DIY installation can lead to electrical hazards or system failures.
How long does it take to charge an EV with solar power?
Charging time depends on your solar system’s size and your EV’s battery capacity. For daily top-ups, you can expect a few hours. A full charge from solar alone may take a day or longer.
Can you use solar power to charge your EV at night?
You cannot use solar panels directly at night. You can store excess solar energy in a home battery during the day and use it to charge your EV after sunset.
What maintenance does a solar EV charging system require?
You should clean your solar panels regularly and inspect connections for wear. Most systems need minimal maintenance. Schedule annual professional inspections to ensure optimal performance and safety.





