
The future of green transportation hinges directly on the innovations shaping EV infrastructure. This advanced infrastructure is defined by three core pillars: intelligent grid integration for electric vehicles, superior user convenience, and universal access. As the global public charging infrastructure doubles to over 5 million points, the need for efficient EV charging becomes paramount. The future of EV charging is dynamic, with technologies like Vehicle-to-Grid (V2G) leading the way.
The V2G market alone is forecast to expand from USD 353.7 million to USD 1.7 billion by 2032.
Technologiquement avancé Fabricants de chargeurs de VE, including TPSON, are pivotal in developing the electric vehicle charging network for this electric future.
The Foundation: Expanding Access to Electric Vehicle Charging

A truly green transportation future begins with universal access to charge fiable. The expansion of charging networks provides the essential groundwork for all other smart technologies. This expansion is not just about adding more stations; it involves a strategic deployment of infrastructure to serve every driver, everywhere.
Scaling the Public Charging Network
The growth of the public charging network is fundamental to eliminating range anxiety and encouraging EV adoption. Governments and private enterprises are working together to build a robust charging infrastructure.
From Urban Hubs to Rural Highways
Strategic initiatives are placing charging stations in highly accessible locations. These include busy city centers, public parking areas, and critical highway corridors. States like California and New York are leading this charge, aligning the installation of charging stations with high EV ownership. This ensures drivers have confidence for both daily commutes and long-distance travel. Private businesses, from retail stores to hospitality venues, are also adding EV charging services to attract customers and capitalize on the growing demand.
The Role of DC Fast Charging
Speed is a critical factor for public charging. DC charge rapide, or ultra-fast charging technology, significantly reduces the time drivers spend waiting. The network requires a massive increase in this capability to support mainstream adoption.
- North America will need approximately 1 million more public chargers by 2030.
- Of these, about 170,000 should be new DC fast chargers, more than tripling the current count.
On-Street and Lamppost Solutions
Urban areas present unique challenges for drivers without dedicated parking. Innovative solutions like on-street charging points and chargers integrated into lampposts are vital. These technologies make electric vehicle charging a viable option for apartment dwellers and homeowners with limited space, increasing charging density in populated areas.
The NACS Revolution
Standardization is a powerful catalyst for growth. The adoption of the North American Charging Standard (NACS) is a landmark development for the EV infrastructure, promising to streamline the entire charging ecosystem.
Unifying a Fragmented Market
For years, the charging network operated with multiple, incompatible plug types, creating confusion for drivers. SAE International’s decision to standardize the NACS connector as SAE J3400 marks a turning point.
This move allows suppliers and manufacturers to produce and deploy a single, interoperable connector for electric vehicles and charging stations across North America, ending market fragmentation.
Simplifier l'expérience de l'utilisateur
A unified standard means EV drivers will no longer need to worry about carrying multiple adapters or finding a compatible station. This simplified “plug-and-play” experience is crucial for consumer confidence. A vast coalition of industry players has committed to this unified network.
| Catégorie | Companies Adopting NACS |
|---|---|
| Automakers | Ford, Stellantis, GM, Honda, BMW |
| Charging Networks | EVgo, FLO, ChargePoint, Electrify America |
| Hospitality | Hilton Worldwide (in partnership with Tesla) |
Accelerating Infrastructure Deployment
A single standard simplifies manufacturing and reduces costs. Standardization is projected to lower per-charger equipment and maintenance expenses by 10–15%. This makes the expansion of the charging network more economically feasible. Technologically advanced providers like TPSON are pivotal in developing the charging infrastructure in 2025 and beyond, leveraging standardized components to accelerate the deployment of reliable and efficient stations. This improved ROI encourages further investment, creating a positive feedback loop for infrastructure growth.
The Core Innovations Shaping EV Infrastructure

With a foundation of accessible charging points in place, the focus shifts to making the experience smarter and more convenient. The core innovations shaping EV infrastructure are centered on seamless connectivity and artificial intelligence. These advancements transform the simple act of charging into an integrated, efficient, and user-friendly process, further strengthening the EV infrastructure.
The Seamless Connection: Wireless and Plug & Charge
The ultimate goal of modern charging technology is to eliminate friction for the driver. Two key innovations, wireless charging and Plug & Charge, are making the process of powering an EV as simple as parking a car.
The Mechanics of Wireless EV Charging
Wireless, or inductive, charging allows an EV to power up without cables. The system uses a transmission pad installed on the ground or in the pavement, which sends power across a short distance to a receiver pad on the underside of the vehicle. This technology is moving from concept to commercial reality, with several companies leading its development.
- WiTricity Corporation
- InductEV Inc.
- ENRX
- Plugless Power Inc.
- HEVO Inc.
For example, HEVO Inc.’s Rezonant E8 system offers 8-kilowatt wireless capability and adheres to key safety and performance standards like UL 2750 and SAE J2954. This makes wireless charging a safe and viable option for residential garages and public parking lots.
Automating Authentication with Plug & Charge
Plug & Charge technology streamlines the payment and authorization process at public stations. It enables secure, direct communication between the electric vehicle and the charging station based on the ISO 15118 standard. Once a driver plugs in, the station automatically identifies the vehicle and its associated payment account, initiating the charging session without needing an app or RFID card.
This automated handshake is gaining widespread support. A growing coalition of automakers and charging networks are enabling this feature, creating a more unified and hassle-free experience for drivers across thousands of charging stations.
Removing Friction from the Process
Together, these technologies remove the final hurdles from the electric vehicle charging experience. Imagine an EV driver simply parking over a wireless pad at home or work, with the charging process starting automatically. For public charging, the Plug & Charge protocol eliminates the need to fumble with apps or payment cards. These innovations shaping EV infrastructure make owning an EV more convenient than a traditional gasoline car, a critical step for mass adoption.
AI-Powered Efficiency in EV Charging
Artificial intelligence (AI) is the brain behind the next generation of smart charging solutions. By analyzing vast amounts of data, AI optimizes the entire charging ecosystem for cost, efficiency, and reliability. Technologically advanced providers like TPSON are instrumental in developing these intelligent charging solutions.
Smart Charging Algorithms
AI-powered smart charging algorithms act as intelligent managers for the charging process. These systems process multiple data points to create optimal charging schedules. Key inputs include the EV’s arrival and departure times, its state of charge, the total energy required, and real-time electricity costs. The algorithm then calculates the ideal charging plan to meet the driver’s needs while minimizing strain on the power grid.
Optimizing for Cost and Time
For EV owners, the most significant benefit of AI is cost reduction. AI algorithms capitalize on variable electricity pricing, such as Time-of-Use (TOU) rates.
- The system analyzes historical data and user behavior to predict charging needs.
- It automatically schedules charging sessions during off-peak hours when electricity is cheapest.
- This intelligent scheduling directly lowers the cost of EV charging, making electric transportation more economical.
This optimization ensures the vehicle is ready when needed without incurring peak energy prices, balancing convenience with cost-effectiveness.
Predictive Analytics for Station Availability
AI also addresses a common frustration for EV drivers: arriving at a charging station to find all ports occupied or out of service. Predictive analytics use AI to forecast the availability of stations. The system analyzes a wide range of data to make its predictions.
| Type de données | Application in Predictive Analytics |
|---|---|
| Historical Usage | Identifies peak times and usage patterns for specific stations. |
| Real-Time Data | Monitors current station status and traffic conditions. |
| External Factors | Considers weather forecasts and local events that may impact demand. |
This foresight allows navigation apps and charging network platforms to guide drivers to available chargers, improving the reliability of the public EV infrastructure.
AI for Battery Health Management
Beyond cost and convenience, AI plays a vital role in preserving the most expensive component of an electric vehicle: the battery. The innovations shaping EV infrastructure include AI-driven battery management. AI algorithms can adjust charging speeds and manage battery temperature during a session. This prevents overheating and reduces degradation over time, extending the battery’s lifespan and protecting the owner’s investment in their electric vehicle.
Vehicle-to-Grid (V2G): The Future of EV Charging and Energy Symbiosis
Vehicle-to-Grid (V2G) technology represents a paradigm shift, transforming electric vehicles from simple transportation devices into active participants in the energy ecosystem. This symbiotic relationship is a cornerstone of the future of EV charging, enhancing grid stability and promoting sustainability.
EVs as Mobile Power Banks
The core principle of V2G is to treat the massive, distributed battery capacity of parked electric vehicles as a collective energy storage network.
Le concept V2G expliqué
V2G enables a two-way flow of energy between an EV and the power grid. While standard EV charging is a one-way process, V2G allows a connected EV to not only draw power from the grid but also discharge stored energy back to it when needed. This turns every compatible EV into a mobile power bank, ready to support the larger electric infrastructure.
Bidirectional Charging Hardware
This capability requires specialized hardware. Both the EV and the charging station must support bidirectional power flow. A growing number of automakers are equipping their vehicles with this technology.
- Kia EV9
- Mitsubishi Outlander (PHEV)
- Mitsubishi Eclipse Cross (PHEV)
- Nissan Leaf
These models, along with others from manufacturers like Volkswagen and Ford, are paving the way for a V2G-enabled future. Des fournisseurs technologiquement avancés comme TPSON are developing the sophisticated bidirectional charging stations essential for this EV infrastructure.
The EV as a Distributed Energy Resource
When aggregated, V2G-capable vehicles form a powerful Distributed Energy Resource (DER). Utilities can draw upon this network of batteries to manage grid load. For EV owners, participation can be financially rewarding. A demonstration project estimated that a V2G-enabled vehicle could generate approximately $1,525 annually through energy savings and demand response events.
Balancing the Grid for a Renewable Future
V2G technology is critical for creating a resilient grid capable of handling the intermittency of renewable energy sources.
Stabilizing Grid Frequency
Power grids must maintain a stable frequency to operate correctly. V2G offers a rapid response solution. A successful pilot project demonstrated how a fleet of parked EVs could store and return energy, effectively stabilizing the grid and providing instant backup during power failures. This capability turns the EV charging network into a virtual power plant.
Storing Excess Renewable Energy
Renewable energy generation from solar and wind is often variable. V2G provides a practical solution for this challenge. During periods of high sun or wind, EVs can absorb and store the excess renewable power. This stored clean energy can then be discharged back to the grid later, ensuring that valuable renewable generation is not wasted.
Reducing Peak Demand Strain
V2G helps utilities manage periods of high electricity consumption. Instead of firing up expensive and less efficient “peaker” power plants, grid operators can call upon the EV fleet to discharge energy. This reduces strain on the grid, lowers operational costs, and decreases reliance on fossil fuels for peak power generation, making the entire system more efficient.
The Expanding V2X Ecosystem
Vehicle-to-Grid is just one part of a larger “Vehicle-to-Everything” (V2X) ecosystem. This concept expands bidirectional charging capabilities to power homes, tools, and entire buildings, turning the electric vehicle into a versatile energy asset.
Véhicule à domicile (V2H)
Vehicle-to-Home (V2H) technology allows an EV to function as a backup generator for a residence, providing energy security and greater energy independence.
Powering Your Home During Outages
During a power outage, a V2H-enabled vehicle can automatically supply electricity to a house. The energy stored in a single EV battery is substantial. An average EV with a 69.5 kWh battery can power a typical home for about two days. Larger vehicles can extend this significantly; some models can supply power for three full days of normal use or up to 21 days with careful energy management. This capability offers homeowners peace of mind and a reliable alternative to noisy, fossil-fuel-powered generators.
Integrating with Home Solar
V2H creates a powerful synergy with residential solar panel systems. The EV battery can store excess solar energy generated during the day. This stored clean energy can then power the home during the evening or on cloudy days, reducing reliance on the grid and lowering electricity bills. Technologically advanced providers like TPSON are developing the sophisticated bidirectional charging stations that make this seamless integration possible.
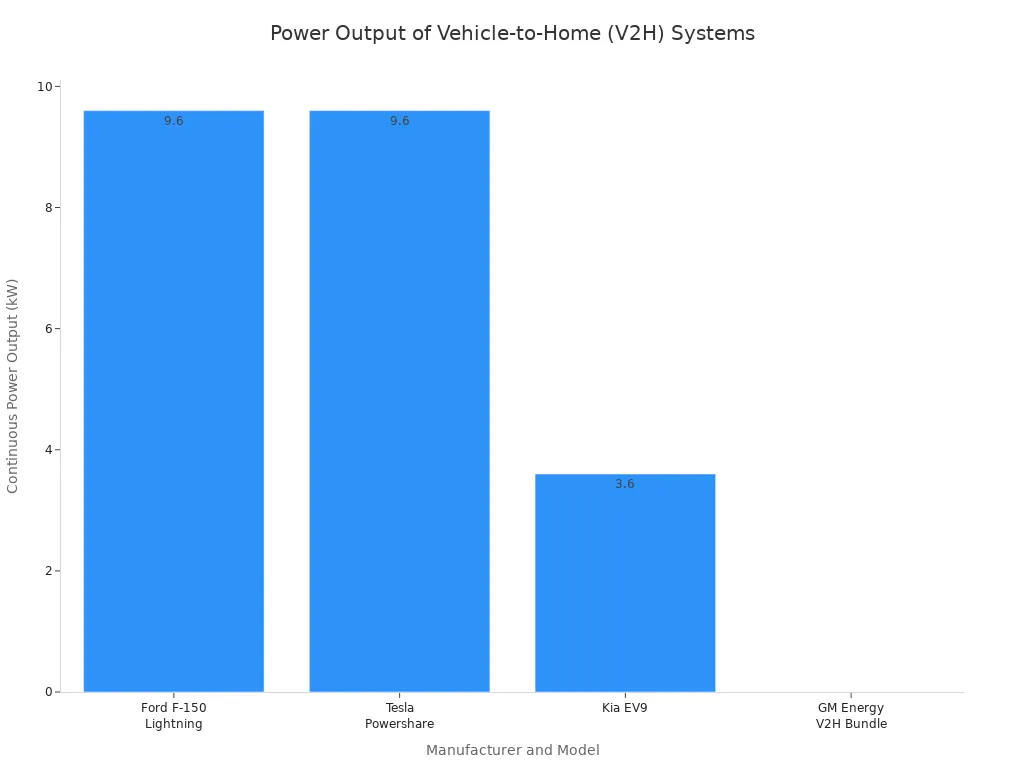
| Fabricant | Model/Technology | Puissance de sortie | Compatibility/Features |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ford | F-150 Lightning with Intelligent Backup Power | Up to 9.6 kW continuous | Works with Ford Charge Station Pro and Home Integration System; automatically switches to EV power during outages; equivalent to more than 10 home batteries. |
| Tesla | Powershare (Cybertruck) | 9.6 kW continuous (five outlets: two 120V 20A, one 240V 40A) | Supports V2H, V2L, V2V; acts as mobile power station; planned expansion to all models by 2025. |
| Kia Motors | EV9 with V2H Capability | Up to 3.6 kW continuous | Integrates with Kia Connect app; supports V2L and V2H; designed for seamless integration with home energy systems; planned U.S. expansion by 2026. |
| GM Energy | V2H Bundle (2024 Chevrolet Silverado EV First Edition RST) | Powers home for up to 21 days (with reduced energy usage) | Includes PowerShift Charger and V2H Enablement Kit; integrates with solar panels and stationary batteries via PowerBank; managed through GM Energy app; planned expansion to all Ultium-based EVs by 2026. |
Vehicle-to-Load (V2L)
Vehicle-to-Load (V2L) technology turns an EV into a mobile power source, equipped with standard outlets to run various devices.
Mobile Power for Work and Recreation
V2L functionality allows users to plug tools, appliances, and electronics directly into their vehicle. This feature is incredibly useful for worksites without grid access, camping trips, or outdoor events. It eliminates the need for separate portable generators, offering a quieter and emission-free power solution.
Use Cases and Applications
The utility of V2L depends on its power output. Models from Hyundai and Kia offer up to 3.6 kW, enough to power laptops, lights, and small appliances. High-power systems, like those found in electric trucks, can deliver 7 kW or more. This level of output can run heavy-duty power tools or even provide emergency charging for another stranded EV.
Vehicle-to-Building (V2B)
Vehicle-to-Building (V2B) applies the principles of V2H on a commercial scale, allowing a fleet of electric vehicles to support a building’s energy needs.
Supporting Commercial Operations
In a V2B system, employees’ or company fleet vehicles can discharge power to the office building during peak hours. This collective energy resource helps stabilize the building’s internal grid and provides a buffer against external power fluctuations, enhancing operational resilience.
Reducing Corporate Energy Costs
The primary benefit of V2B is financial. By using stored EV energy during times of high electricity prices, companies can significantly reduce their peak demand charges.
A case study in a large administrative building demonstrated that a V2B framework could achieve a potential peak demand reduction of up to 37.9%.
Another strategy, where workers use their home-charged vehicles to power the office, projects a building demand reduction of up to 50%, showcasing a profitable and green business model.
The Next Frontier: Emerging Charging Technologies
Beyond conventional plugs and stations, the next frontier of electric vehicle charging is exploring revolutionary methods to power vehicles. These emerging charging solutions aim to solve specific challenges for heavy-duty transport and offer ultimate convenience for all drivers. This technologie de pointe is redefining the limits of electric mobility.
Megawatt Charging for Heavy-Duty Vehicles
Electrifying commercial transport requires a new class of charging infrastructure capable of delivering immense power quickly.
Powering Electric Semis and Buses
Heavy-duty electric vehicles like semi-trucks and buses have massive batteries. Standard fast charging is too slow for logistics and public transit schedules. A new approach is necessary to make electric fleets viable.
The Megawatt Charging System (MCS)
The Megawatt Charging System (MCS) is the industry’s answer. This powerful standard is designed to deliver over one megawatt of charging power, enabling a semi-truck to gain significant range during a driver’s mandatory rest break. Major manufacturers are already preparing for this shift. For instance, MAN Truck & Bus is developing systems to support MCS, et Scania plans to release its MCS-compatible electric trucks by mid-2026.
Impact on Logistics and Public Transit
MCS will transform the logistics industry by minimizing downtime for electric fleets. Faster charging makes long-haul electric trucking practical. It also allows electric buses to complete their routes with brief, high-power charging sessions at depots, improving operational efficiency.
Battery Swapping as a Niche Solution
Battery swapping offers an alternative to traditional charging, focusing on speed by replacing the entire battery pack.
The Instant “Refuel” Model
This model allows an EV driver to enter a swapping station and have a robot exchange their depleted battery for a fully charged one in minutes. This approach is gaining traction in specific markets.
| Entreprise | Geographic Market |
|---|---|
| Nio | Chine |
| Gogoro | Taiwan |
| Ample | ÉTATS-UNIS |
| Sun Mobility | Inde |
These companies have built networks of stations to support their users, proving the model’s viability for certain use cases.
Overcoming Standardization Hurdles
Widespread adoption faces significant obstacles. The technology requires massive investment and faces complex challenges.
- High Capital Costs: The initial expense for robotic machinery, spare battery inventory, and sophisticated management software is substantial.
- Lack of Standardization: EV manufacturers use different battery sizes, chemistries, and communication protocols, making a universal swapping station nearly impossible.
- Operational Complexity: Managing battery health, logistics, and supply chains for thousands of packs is a major operational hurdle.
Dynamic Charging and Electric Roads
The most futuristic concept involves charging electric vehicles while they are in motion.
The Vision of Charging While Driving
Dynamic charging, or Electric Road Systems (ERS), embeds charging technology directly into the pavement. This allows an EV to power up wirelessly or through a physical contact strip as it drives, potentially eliminating range anxiety and enabling smaller, lighter batteries.
Current Pilot Programs and Challenges
This concept is moving from theory to reality through various pilot programs. Sweden is a leader in this field, testing electric roads for trucks and buses between key logistic hubs. Other trials are active in locations like Tel Aviv for public buses. However, the immense cost of retrofitting highways and achieving a unified technology standard remain the primary challenges to large-scale deployment.
The Software-Defined Future of Charging
Hardware provides the physical connection for EV charging, but software defines the experience. The future of the charging network depends on intelligent, open, and user-centric software platforms. This digital layer is what transforms a simple power outlet into a smart, integrated component of our energy and transportation systems.
The Role of Open Standards
Open standards are the bedrock of a scalable and competitive charging network. They ensure that hardware and software from different companies can communicate seamlessly, preventing market fragmentation and empowering network operators.
OCPP and Interoperability
Le Open Charge Point Protocol (OCPP) is a critical open-source communication standard. It acts as a universal language between charging stations and the central management systems that control them. This technologie is fundamental for a unified charging network.
- It allows charging station hardware from any manufacturer to connect with any OCPP-compliant backend software.
- Il standardizes essential operations like starting or stopping a charging session, reporting status, and managing payments.
- This prevents “vendor lock-in,” giving network operators the freedom to choose the best hardware and software without being tied to a single provider.
Technologically advanced providers like TPSON build their charging solutions on open standards like OCPP. This ensures their hardware can be integrated into any charging network, supporting the flexible expansion of public infrastructure.
Fostering Innovation and Competition
When companies build on a common standard, they compete on features and quality, not on proprietary connections. This open environment accelerates innovation across the industry. Competition fostered by open standards has led to the development of advanced features, including:
- Intégration des réseaux intelligents: Optimizing charging to prevent grid overloads.
- Bidirectional Charging (V2G): Allowing EVs to return power to the grid.
- IoT Systems: Using AI and cloud platforms for real-time monitoring and predictive maintenance.
The Importance of a Customer-First Mindset
Ultimately, the success of the electric transition rests on the experience of individual drivers. A customer-first mindset means designing charging systems that are intuitive, reliable, and transparent for all consumers.
User Interface and Experience (UI/UX)
A poor user experience is a significant barrier to EV adoption. Drivers often face a frustrating landscape of inconsistent interfaces and unreliable systems. Common pain points include:
- App Overload: Many drivers must juggle three to six different apps to access various charging networks.
- Confusing Pricing: Opaque pricing structures with varying rates, session fees, and idle charges create confusion and mistrust.
- Payment Failures: Malfunctioning payment terminals and poor network connectivity are common, leading to failed charging attempts.
Roaming and Payment Systems
Solving these issues requires a focus on interoperability and simplicity. Roaming networks allow drivers to use a single account across multiple different charging networks, much like a mobile phone works on different carriers. The ultimate goal is a truly seamless payment process. Technologies like Plug & Charge, based on the ISO 15118 standard, are making this a reality. This technology allows a vehicle to automatically and securely authenticate itself to the charger, handling payment without any driver intervention. This removes the final layer of friction from the public charging experience.
The innovations shaping EV infrastructure are evolving electric vehicles beyond simple transport. They are becoming active components of a resilient energy network, enhancing grid sustainability. The future of the EV infrastructure depends on the convergence of an expanded charging network, intelligent software, and bidirectional charging. This synergy creates a truly sustainable transportation future, integrating renewable energy sources more effectively.
Realizing this future vision requires a collaborative effort. Automakers, utilities, policymakers, and consumers must work together to build the intelligent infrastructure and electric network for generations to come.
FAQ
Qu'est-ce que la recharge intelligente ?
Smart charging uses intelligent technology to manage how and when an electric vehicle charges. It optimizes charging sessions for cost, grid stability, and user convenience. This technology connects EVs, charging stations, and grid operators into a responsive network.
Comment fonctionne la technologie V2G (Vehicle-to-Grid) ?
Technologie V2G enables a two-way energy flow between an EV and the power grid. A compatible vehicle can discharge stored energy back to the grid during peak demand. This process helps stabilize the electrical system and can generate revenue for the EV owner.
Why is the OCPP standard important?
The Open Charge Point Protocol (OCPP) ensures interoperability between charging stations and management software from different manufacturers.
This open standard prevents vendor lock-in. It allows network operators to build flexible and competitive charging networks using hardware from various providers.
What is the difference between V2H and V2L?
- Véhicule à domicile (V2H) allows an EV to power a house, acting as a backup generator during outages.
- Vehicle-to-Load (V2L) turns an EV into a mobile power source with outlets to run tools or appliances.
What is the purpose of the Megawatt Charging System (MCS)?
The Megawatt Charging System (MCS) is a high-power charging standard designed for heavy-duty electric vehicles like semi-trucks and buses. It delivers over one megawatt of power. This capability dramatically reduces charging times, making electric logistics and public transit more practical.
How does AI improve the EV charging experience?
Artificial intelligence optimizes charging schedules to reduce costs by using off-peak electricity rates. AI also predicts station availability to prevent driver frustration. Furthermore, it manages battery health by adjusting charging speeds, which extends the battery’s lifespan and protects the owner’s investment.
What are the benefits of Plug & Charge technology?
Plug & Charge automates the authentication and payment process at public charging stations. The driver simply plugs in the vehicle. The station automatically identifies the car and its payment account, creating a seamless and hassle-free experience without needing apps or cards.





