
The era of waiting hours for an electric vehicle to charge is rapidly ending. The future of EV charging is transforming the experience into a quick routine. Soon, an EV will not only draw power but also support the energy grid. Wood Mackenzie forecasts the global EV charging port market will grow to 206.6 million ports by 2040. This expansion, driven by Производители зарядных устройств для электромобилей like TPSON, signals a major shift. The frustration of finding a working Зарядное устройство для электромобилей is being engineered away, paving the way for the future of electric car charge points and seamless electric vehicles integration.
The Need for Speed: The Rise of Ultra-Fast Charging Technology

The demand for faster refueling times is a primary driver of technological innovation in the EV sector. Drivers want convenience that mirrors the traditional gas station experience. This has ignited a race to develop and deploy ultra-fast charging technology, fundamentally reshaping the current landscape of зарядные станции. To appreciate this leap, one must first understand the different types of charging stations available today.
Understanding the EV Charging Spectrum
EV charging is not a one-size-fits-all process. The speed at which an EV gains range depends entirely on the power level of the charging station. These levels form a spectrum from slow overnight top-ups to rapid on-the-go boosts.
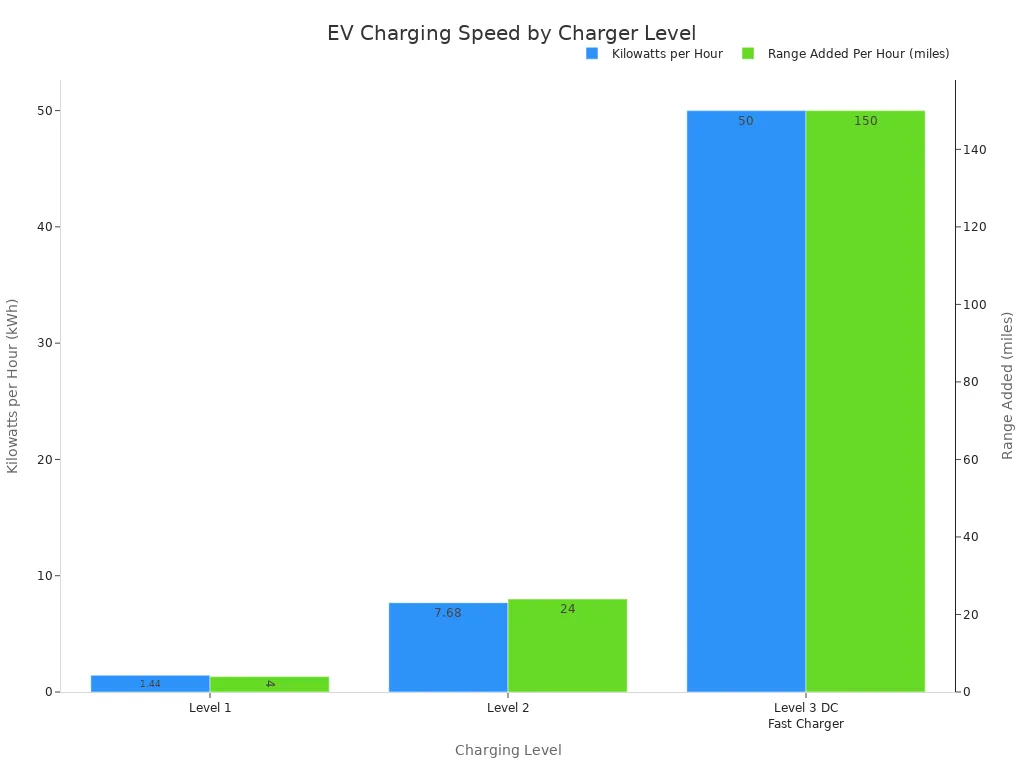
Level 1: Basic Overnight Charging
Level 1 charging uses a standard household electrical outlet. It is the slowest method, adding only about 3 to 5 miles of range per hour. This option is convenient for plug-in hybrids with smaller batteries or for EV owners who drive short distances daily. A full charge for a medium-sized EV can take up to 24 hours.
Level 2: The Home and Public Standard
Level 2 represents the most common form of EV charging. These chargers are found in homes, workplaces, and public parking lots. They require a dedicated 240-volt circuit, similar to an electric dryer. A Level 2 charger can replenish a battery overnight, typically in 3 to 7 hours, making it the practical standard for daily use.
Level 3: DC Fast Charging Today
Level 3, or DC Fast Charging (DCFC), is the game-changer for long-distance travel. These powerful charging stations convert AC power to DC power before it enters the vehicle, bypassing the car’s onboard charger. This direct current allows for significantly faster speeds.
Примечание: While Level 1 and 2 use Alternating Current (AC), Level 3 uses Direct Current (DC). This is the key difference that enables much higher power delivery and faster charging times.
The following table summarizes the capabilities of these charging technologies.
| Уровень зарядки | Диапазон Добавление в час | Approximate Full Charge Time |
|---|---|---|
| Уровень 1 | 5 km (3.11 miles) | До 24 часов |
| Уровень 2 | 30 to 50 km (20 to 30 miles) | Ночь |
| Уровень 3 | Up to 20 miles per minute | Under an hour |
The Leap to Ultra-Fast Charging (UFC)
Standard DC fast chargers are impressive, but the industry is already pushing beyond them. The next evolution is Ultra-Fast Charging (UFC), which promises to reduce charging stops to the time it takes to grab a coffee.
Преодоление барьера в 350 кВт
Ultra-fast chargers operate at 350kW and higher, a significant jump from the common 50-150kW fast chargers. An EV with a compatible battery system can gain hundreds of miles of range in just 15-20 minutes. A growing number of vehicles can take advantage of these speeds.
- Hyundai IONIQ 5 & 6
- Kia EV6 & EV9
- Porsche Taycan
- Lucid Air
- Genesis GV60
The Lotus Eletre, for example, boasts a peak charging power of 350 kW, showcasing the incredible potential of modern fast charging technologies.
The Promise of Megawatt Charging for Trucks
The need for speed extends to the commercial sector. Electric semi-trucks require enormous amounts of energy. The Megawatt Charging System (MCS) is being developed to meet this demand, delivering power at an unprecedented scale.
| MCS Specification | Значение |
|---|---|
| Voltage Window | Up to ~1,250 V |
| Текущий | Up to ~3,000 A |
| Peak Power | Multi-megawatt |
| Early Pilot Power | 1 MW |
The design target for MCS is to charge a heavy-duty truck from 20% to 80% in approximately 30 minutes, making electric long-haul trucking a viable reality.
Slashing Charging Times to Minutes
The ultimate goal of these advanced charging technologies is to make the EV charging experience nearly identical to refueling a gasoline car. With power levels climbing and battery chemistries improving, a 5-to-10-minute charge that adds over 200 miles of range is no longer science fiction. It is the near-future benchmark that companies like TPSON, a technologically advanced EV charging solution provider, are working towards.
Key Technologies Enabling Extreme Speeds
Pushing such high levels of electrical current safely and efficiently requires sophisticated engineering. Three key areas of innovation are making ultra-fast charging possible: cooling systems, semiconductors, and battery technology.
Передовые системы жидкостного охлаждения
High-power EV charging generates immense heat. Without proper thermal management, cables and connectors would overheat, limiting charging speed and posing a safety risk. Advanced liquid-cooling systems are the solution. These systems circulate a coolant (typically a water-glycol mixture) through the charging cables and connector, actively drawing heat away. This allows a standard connector to handle up to 500kW, a massive increase from its 200kW uncooled limit. This technology also allows for thinner, lighter, and more flexible cables, improving the user experience at charging stations.
The Role of Silicon Carbide (SiC) Semiconductors
Semiconductors are the silent heroes inside the charger, managing the flow of power. For years, silicon has been the standard. However, Silicon Carbide (SiC) is a superior material for high-power applications. SiC semiconductors can operate at higher voltages, temperatures, and frequencies with significantly lower energy loss.
| Характеристика | Silicon Carbide (SiC) | Traditional Silicon |
|---|---|---|
| Switching Speed | Выше | Нижний |
| Overall System Efficiency | Enhanced | Стандарт |
| Inverter Size/Weight | More compact and lightweight | Larger and heavier |
| Energy Loss | 6% lower in some designs | Стандарт |
By using SiC, manufacturers can build smaller, lighter, and more efficient chargers that waste less electricity as heat. Porsche’s Taycan, for instance, uses SiC to enable its rapid charging speeds, a feat not possible with traditional silicon components.
Solid-State Batteries: The Next Frontier
The final piece of the puzzle is the EV battery itself. Current lithium-ion batteries have limitations on how quickly they can absorb a charge. Solid-state batteries represent the next frontier. They replace the liquid electrolyte in today’s batteries with a solid material. This design promises higher energy density, improved safety, and, most importantly, the ability to accept ultra-high-speed charging without degradation. When solid-state batteries become commercially viable, they will unlock the full potential of megawatt-level charging, truly making a 5-minute charge a reality for the average EV.
Smart Grids and Software: The Brains Behind the Future of EV Charging
Blazing-fast charging speeds are only one part of the equation. The true revolution in the future of ev charging lies in the intelligence that powers it. Advanced software and grid communication are transforming chargers from simple power dispensers into smart, connected devices. Technologically advanced providers like TPSON are developing solutions that integrate this intelligence, ensuring the entire ecosystem is efficient, stable, and user-friendly.
The Intelligent, Connected Charger
A modern charger is more than just a plug; it is a data-driven node on an increasingly complex energy network. This connectivity is essential for managing the massive new demand from electric vehicles.
Что такое интеллектуальная сеть?
A smart grid is a modernized electrical grid that uses two-way communication to react and adapt to changes in energy demand. For EV charging, its functions are critical:
- Dynamic energy management to handle load fluctuations.
- Optimized distribution of power to prevent bottlenecks.
- Enhanced grid resilience for faster response to outages.
- Seamless integration of renewable energy sources like solar and wind.
This digital oversight allows the grid to anticipate charging patterns and improve overall power utilization.
Load Balancing for Grid Stability
Unmanaged EV charging, where many vehicles plug in simultaneously during peak hours, can overwhelm local electrical circuits. Load balance management intelligently distributes the available power across multiple chargers. This smart charging technology prevents grid overloads by dynamically adjusting charging rates based on overall demand, ensuring a reliable power supply for everyone. China, for example, aims for 60% of EV charging to happen during off-peak times by 2025, using incentives to encourage this grid-friendly behavior.
Optimizing Costs with Time-of-Use Rates
Smart grids enable utilities to offer Time-of-Use (TOU) electricity rates. These programs make electricity cheaper during off-peak hours, such as late at night. Smart charging systems can automatically schedule an EV to charge during these low-cost periods, saving the owner money and reducing strain on the grid.
Vehicle-to-Everything (V2X): A Two-Way Energy Street
V2X technology turns the EV into an active participant in the energy ecosystem. Instead of only drawing power, the vehicle can also supply it, creating a bidirectional flow of energy.
Vehicle-to-Grid (V2G): Powering the Community
With V2G, a fleet of parked EVs can act as a massive, distributed battery, sending power back to the grid during peak demand. This helps stabilize the grid and supports the integration of intermittent renewable energy. Large-scale V2G pilot projects are already underway in several cities across China, demonstrating how EVs can support community power systems.
Vehicle-to-Home (V2H): Your Car as a Backup Generator
V2H technology allows an EV to power a home directly during a power outage. A vehicle like the Ford F-150 Lightning или upcoming Volkswagen ID. models can function as a silent, emission-free backup generator, keeping lights and essential appliances running.
Vehicle-to-Load (V2L): Portable Power on Demand
V2L offers the ultimate convenience: using your car as a giant, mobile power bank. This feature allows you to plug tools, camping gear, or other electronics directly into the vehicle.
| Модель автомобиля | V2L Power Output |
|---|---|
| Hyundai Ioniq 5 | 3,6 кВт |
| KIA EV6 | 3,6 кВт |
| BYD Atto 3 | 2.4kW |
| MG ZS EV (2022) | 2.2kW |
The Seamless Software Experience
Software is eliminating the final points of friction in the public EV charging process, making it as simple as possible for the driver.
Plug & Charge (ISO 15118) Explained
The ISO 15118 protocol enables a feature known as Plug & Charge. It automates the entire authentication and billing process through a secure digital “handshake” between the car and the charger. The process is simple:
- The driver connects the charging cable.
- The EV and charger securely exchange encrypted credentials.
- The system verifies the driver’s account.
- Charging begins automatically.
Eliminating the Need for Apps and Cards
Plug & Charge removes the need to juggle multiple apps, RFID cards, or payment terminals. The driver simply plugs in, and the system handles the rest. This creates a truly seamless and hassle-free public charging experience.
AI-Powered Route and Charge Planning
Artificial intelligence is making range anxiety a thing of the past. Modern route planners, such as Zapmap, use AI to help drivers plan long journeys. These apps identify charging stops, show real-time charger availability, and estimate the necessary charging time, ensuring a smooth and predictable trip.
Universal Access: Key Innovations Shaping the Future of EV Charging
Speed and intelligence are transforming the charging experience, but their impact depends on one critical factor: accessibility. The future of EV charging hinges on creating a universal system where any driver can plug into any charger, anywhere, at any time. Key innovations shaping the future of ev charging are now focused on breaking down the final barriers of connector types, infrastructure gaps, and daily life integration. This push for universal access is making the public charging network more reliable and user-friendly than ever before.
The End of the Connector Wars
For years, the EV landscape was fragmented by competing charging standards, creating confusion and frustration for drivers. This era is finally drawing to a close as the industry consolidates around a single, dominant standard.
A Brief History: CHAdeMO vs. CCS
The early days of DC fast charging were defined by a rivalry between two main standards: CHAdeMO and the Combined Charging System (CCS).
- ЧАДЕМО: Primarily used by some Asian automakers, this standard requires a dedicated DC fast charging port on the vehicle, separate from the port used for slower AC charging.
- CCS: Developed to be an all-in-one solution, CCS extends the common J1772 AC connector with two large DC pins. This “combined” design allows a single port on the vehicle to handle both AC and DC charging.
This split meant that charging networks had to install multiple connector types, and drivers had to ensure their vehicle was compatible with the available charging stations.
The Rise of the North American Charging Standard (NACS)
Tesla developed its own connector, now known as the North American Charging Standard (NACS), which offers a more compact and elegant solution. NACS uses a single, slim plug for both AC and DC power by having the pins serve double duty. This “hybrid” approach, however, requires sophisticated vehicle and charger software to ensure safety when switching between low-voltage AC and high-voltage DC power.
In a landmark shift, the industry has rapidly moved to adopt NACS. Starting in mid-2023, nearly every major automaker announced plans to switch from CCS to NACS for their North American vehicles, beginning with the 2025 model year.

This transition will grant drivers of many different EV brands access to Tesla’s extensive Supercharger network, dramatically expanding the reliable charging options available.
| Компания | Announced Adoption | Supercharger Access |
|---|---|---|
| Ford | 25 мая 2023 года | February 29, 2024 |
| Дженерал Моторс | 8 июня 2023 года | September 18, 2024 |
| Ривиан | 21 июня 2023 года | March 18, 2024 |
| Volvo | 27 июня 2023 года | October 29, 2024 |
| Volkswagen Group | December 19, 2023 | Coming soon |
| Стеллантис | February 2, 2024 | Планируется |
What Standardization Means for Drivers
A unified charging standard is a game-changer for the EV owner. It eliminates the need for bulky adapters and removes the guesswork from finding a compatible charger. This simplification creates a more seamless and reliable public charging experience, bolstering driver confidence and accelerating EV adoption. A single, robust charging network benefits everyone.
Massive Infrastructure Expansion Efforts
With the connector wars ending, the focus has shifted to the rapid and strategic expansion of charging networks. A combination of public funding and private investment is building out the charging infrastructure needed to support a fully electric future.
The National Electric Vehicle Infrastructure (NEVI) Program
In the United States, the federal government is driving a significant part of this expansion through the National Electric Vehicle Infrastructure (NEVI) Program. This program provides funding to states to build a dependable charging network. The primary goal is to place fast charging stations every 50 miles along major highways, ensuring that no driver is left stranded. This massive public investment is foundational to creating a truly national charging network.
Building Out National Highway Charging Corridors
The NEVI program helps establish official Alternative Fuel Corridors (AFCs) along the nation’s interstate system. This strategic placement of charging stations makes long-distance travel in an EV practical and predictable. Progress is already visible along corridors like Interstate 95 on the East Coast. Similar efforts are underway globally.
Europe’s AFIR Mandate: The Alternative Fuels Infrastructure Regulation (AFIR) in Europe mandates fast chargers at least every 60 kilometers on major highways. This shows a coordinated international push to eliminate range anxiety for long-distance travel.
These efforts also extend to heavy-duty trucks, with initiatives like the ‘SuperTruck Charge’ program demonstrating megawatt-scale charging to support electric freight.
Private Investment from Automakers and Networks
Public funding is matched by massive private investment. Automakers and dedicated charging networks are pouring billions of dollars into building out their own charging stations. This private investment fosters competition, drives innovation, and accelerates the expansion of charging networks far beyond what government funding alone could achieve. This dual-pronged approach of public and private investment is one of the most important trends in charging infrastructure development.
Integrating EV Charging into Daily Life
The ultimate goal is to make EV charging an invisible and effortless part of everyday routines. This means moving beyond highway corridors and integrating charging opportunities where people live, work, and shop.
The Push for Multi-Unit Dwelling Charging
One of the biggest hurdles to EV ownership is the lack of at-home charging for people living in apartments and condominiums. Building managers often face significant challenges:
- High Costs: Retrofitting older buildings with the necessary electrical capacity is expensive.
- Limited Power: Existing electrical systems may not support numerous chargers running at once.
- Complex Allocation: Fairly assigning charging spots to residents is a logistical puzzle.
Solutions are emerging to tackle these issues. Smart load management systems can balance power across multiple chargers to prevent overloads. Government grants can help offset the initial investment cost. Technologically advanced providers like TPSON offer scalable solutions designed for these complex environments, making EV charging in apartment buildings a feasible reality.
Workplace Charging as a Modern Employee Perk
Workplace charging is becoming an essential employee benefit. It offers a convenient and reliable charging option for commuters. For employers, providing on-site electric vehicle charging stations is a powerful tool for attracting and retaining top talent while demonstrating a commitment to sustainability. It also helps distribute energy demand, as cars can charge during daytime solar production hours.
The Growth of Retail and Destination Charging
Businesses are realizing that offering EV charging is a great way to attract customers. Supermarkets, shopping malls, hotels, and restaurants are increasingly installing charging stations as an amenity. This “destination charging” allows drivers to top up their battery while they shop, dine, or run errands. This seamless integration makes EV ownership more convenient by turning necessary stops into productive charging opportunities.
Next-Generation Hardware: The Future of Electric Car Charge Points

Beyond speed and software, the physical form of chargers is undergoing a radical transformation. The future of electric car charge points is not just about power, but also about seamless integration into our environment and daily lives. Innovations in hardware are making ev charging more convenient, accessible, and even invisible.
Innovations in Physical Charger Design
The traditional charging post is evolving. New charging station technologies are designed to solve specific challenges related to space, accessibility, and user convenience.
Роботизированные и автоматизированные зарядные манипуляторы
Automation is poised to eliminate the physical effort of plugging in. Robotic charging systems use cameras and sensors to automatically locate an EV’s charge port and connect the cable. Companies like Charging Robotics are already launching pilot programs for these systems. This technology promises a new level of convenience, especially for drivers with mobility challenges.
Pop-Up Chargers for Urban Spaces
Curb space is a premium in dense cities. To solve this, companies are developing retractable chargers that hide away when not in use.
- Trojan Energy has launched pop-up stations in several London boroughs.
- Urban Fox is rolling out fully retractable 7kW charge points that sit flush with the pavement.
These discreet solutions preserve the urban landscape and reduce street clutter, making widespread on-street charging more feasible.
Mobile and Portable Charging Solutions
Mobile ev charging offers a flexible solution for on-demand power. Companies are developing van-mounted DC fast chargers that can provide roadside assistance to stranded EVs or serve as temporary power sources at events. Technologically advanced providers like TPSON are exploring such versatile charging technologies to meet diverse market needs.
The Promise of Wireless Charging
Wireless charging eliminates cables entirely, offering the ultimate seamless experience. This technology uses magnetic induction to transfer energy from a pad on the ground to a receiver on the vehicle.
How Inductive Charging Works
Inductive charging works by creating a magnetic field between two coils. A transmitting coil in a ground-based pad generates the field, and a receiving coil on the underside of the EV captures the energy. This process allows for efficient power transfer without any physical connection.
Static vs. Dynamic Wireless Charging
Wireless charging comes in two forms:
- Static: Charging while the vehicle is parked over a pad.
- Dynamic: Charging the vehicle as it drives over electrified roadways.
Pilot projects for dynamic charging are active across Europe. Initiatives in Germany, France, and Sweden are testing dedicated e-road lanes that charge buses and trucks while in motion, showcasing a key part of the future of electric car charge points.
Overcoming Efficiency and Cost Hurdles
Early concerns about wireless charging efficiency have largely been resolved. Modern static systems achieve an efficiency of 88-93%, a rate comparable to many standard Level 2 plug-in chargers. As manufacturing scales, costs are expected to decrease, making this technology a viable mainstream option.
Battery Swapping: An Alternative Model
Battery swapping offers a different approach to refueling. Instead of recharging the battery, this model replaces the entire depleted pack with a fully charged one in just a few minutes.
The Instant “Refuel” Concept
Такие компании, как NIO and CATL are pioneering this model, primarily in China. NIO has built thousands of automated swap stations where a robotic mechanism can exchange a battery in under five minutes. This provides an experience very similar to a traditional gas station visit.
Logistical Challenges and Standardization Hurdles
Widespread adoption faces significant obstacles. The primary challenge is the lack of battery standardization; different automakers use unique battery sizes, chemistries, and locking mechanisms. Additionally, the high upfront investment for a network of swap stations and complex battery inventory logistics are major hurdles.
Niche Applications for Commercial Fleets
Battery swapping currently finds its best fit in controlled environments. It is an ideal solution for commercial fleets, such as taxis or ride-hailing services, where vehicles follow predictable routes and require minimal downtime.
Sustainability and Resilience in the Charging Ecosystem
A fast and intelligent charging network is only effective if it is also sustainable and reliable. The industry is now focusing on powering chargers with clean energy and ensuring they work every time a driver plugs in. These efforts are crucial for building a truly sustainable transportation future.
Powering Chargers with Clean Energy
The environmental benefit of an EV is maximized when the electricity it uses comes from renewable sources. This has led to a major push to integrate clean energy directly into the charging infrastructure.
Integrating Solar Canopies at Stations
Solar canopies are becoming a common feature at charging stations. These structures generate clean electricity on-site, which can power building loads and EV chargers directly. This approach significantly reduces reliance on grid electricity and lowers the carbon footprint of each charging session. For operators, this strategy decreases operational costs by offsetting energy bills and avoiding expensive peak demand charges, aligning with corporate sustainability goals.
On-Site Battery Storage Systems
On-site batteries are a critical component for managing power at fast charging sites. These systems store energy, either from the grid during off-peak hours or from on-site solar panels. When a vehicle demands high power for fast charging, the battery discharges to supplement the grid connection.
Most DC fast charging stations use on-site battery storage systems with capacities from 100 kWh to 500 kWh. A system can supplement a 100 kW grid limit to deliver nearly 400 kW of power, ensuring reliable fast charging during peak periods.
This technology allows high-power charging stations to be installed in locations with grid limitations, accelerating the network rollout.
Connecting to Renewable Energy Grids
Beyond on-site generation, charging networks are increasingly sourcing power from renewable energy grids. Many providers are entering into Power Purchase Agreements (PPAs) with wind and solar farms. This ensures that the electricity dispensed by their chargers is matched with clean energy generation, making the entire ecosystem greener.
Ensuring Network Reliability and Uptime
A frustratingly common problem for EV drivers is arriving at a charger only to find it out of order. Building robust and dependable networks is a top priority.
The Role of Cellular Connectivity
Reliable connectivity is the backbone of a smart charging network. Most modern chargers use cellular modems (4G/5G) to communicate with central management systems. This connection enables:
- Remote monitoring and diagnostics
- Over-the-air software updates
- Real-time payment processing
- Live status updates for driver apps
Stable connectivity ensures that operators can manage their assets effectively and that drivers have access to accurate information.
Predictive Maintenance with AI
Artificial intelligence is revolutionizing charger maintenance. Instead of reacting to failures, AI systems proactively predict them. These systems analyze operational data, usage patterns, and sensor readings to identify anomalies that signal a potential issue. This allows operators to schedule maintenance before a charger fails, a practice that reduces downtime and improves the reliability of the charging infrastructure. Technologically advanced providers like TPSON leverage these smart systems to keep their charging stations operational.
Building Redundancy into Charging Hubs
While some studies show charger uptime hovering around 70-80%, the industry benchmark is much higher. Many government mandates and network operators aim for an annual uptime greater than 97%. To achieve this, operators are building redundancy into charging hubs. This means installing multiple power cabinets and components so that if one part fails, the station can continue to operate at a reduced capacity instead of shutting down completely. This design philosophy is key to creating dependable networks that drivers can trust.
Сайт future of electric car charge points rests on three pillars: unprecedented speed, deep intelligence, and universal accessibility. Innovations in ultra-fast charging and standardization are dismantling the final barriers to mass adoption. EV charging evolves from a necessary chore into a seamless part of the energy ecosystem. The journey towards a fully electric future accelerates, powered by a smarter charging network. Technologically advanced providers like TPSON help build this robust charging network, ensuring the entire charging network defines the future of electric car charge points.
ЧАСТО ЗАДАВАЕМЫЕ ВОПРОСЫ
В чем основная разница между зарядкой переменным и постоянным током?
AC chargers (Level 1 and 2) use the car’s onboard converter to change AC grid power to DC for the battery. DC fast chargers (Level 3) convert the power before it enters the car. This direct delivery allows for significantly faster charging speeds.
Can any EV use an ultra-fast charger?
No, not every EV can use ultra-fast charging. The vehicle’s battery management system must be designed to handle high power levels. Only specific models equipped with 800V architecture or similar advanced technology can accept charging speeds of 350kW or more.
Is Vehicle-to-Grid (V2G) technology widely available now?
V2G is still an emerging technology. While many new EVs are V2G-capable, its use depends on compatible chargers and utility programs. Large-scale pilot projects in regions like Europe and China are testing its capabilities before widespread public rollout becomes common.
How efficient is wireless EV charging?
Modern static wireless charging systems are highly efficient. They achieve power transfer rates between 88% and 93%. This level of performance is comparable to many standard plug-in Level 2 chargers, making it a viable and convenient future option for EV owners.
What is the biggest challenge for battery swapping?
The primary obstacle for widespread battery swapping is the lack of standardization. Automakers use different battery sizes, shapes, and connection systems. This variation makes it nearly impossible to create a universal network of swap stations that can serve all vehicle brands.
How is charger reliability being improved?
Networks are improving reliability through better hardware and smart maintenance. Technologically advanced providers like TPSON use AI for predictive maintenance, identifying potential issues before a failure occurs. This proactive approach significantly increases charger uptime and builds driver trust in the public network.





