An electric vehicle (EV) owner might wonder if all EVs use the same charger. The answer is no, especially concerning fast charging on the road. For slower, everyday charging, most electric vehicles use a standard plug. However, the landscape for fast charging is more complex. Three main plugs compete for dominance in DC fast charging: CCS, NACS (Tesla), and CHAdeMO. This variety means EV owners must understand their car’s specific charging needs. TPSON, a technologically advanced provider among Производители зарядных устройств для электромобилей, offers various Решения для зарядки электромобилей, в том числе портативные зарядные устройства для электромобилей, to navigate this diverse market. Understanding the different Зарядное устройство для электромобилей types is crucial for a seamless EV experience.
The Three Speeds of EV Charging Explained
Understanding the different speeds of electric vehicle charging is essential for any EV owner. Charging is categorized into three levels, each serving a different purpose, from overnight top-ups at home to rapid power boosts on a long drive.
Level 1 & 2 (AC Charging): For Home and Work
What is AC Charging?
Alternating Current (AC) charging is the most common method for daily use. This process uses the standard AC electricity supplied by the power grid. An EV contains an onboard charger that converts this AC power into Direct Current (DC) power to store in the battery. This conversion happens inside the car, which limits the charging speed. This type of electric car charging is typical for homes and workplaces, where electric vehicles can be plugged in for several hours. Technologically advanced providers like TPSON offer a range of AC charging solutions to meet these needs.
How Fast is Level 1 and 2 Charging?
The speed of AC charging varies significantly between Level 1 and Level 2.
- Зарядка уровня 1: This uses a standard household outlet and provides about 1.3 to 2.4 kW of power. It is the slowest method, adding only a few miles of range per hour.
- Зарядка уровня 2: This requires a dedicated charger, professionally installed. It delivers much faster speeds, with power outputs ranging from 3 kW to 22 kW. A Level 2 charger is the most practical solution for home charging.
The table below illustrates the practical differences in time and cost.
| Уровень зарядного устройства | Time to Add 100 Miles | Стоимость установки |
|---|---|---|
| Уровень 1 (медленный AC) | 8–10 hours | $0 (existing socket) + EVSE cable ($150–$300) |
| Уровень 2 (быстрый AC) | 2–5 hours | $800–$1,500 |
| Уровень 3 (DC Rapid) | 20–40 minutes | $50,000–$100,000+ |
Level 3 (DC Fast Charging): For Road Trips
Что такое быстрая зарядка постоянного тока?
DC fast charging delivers Direct Current (DC) power straight to the EV battery. This process bypasses the vehicle’s smaller onboard charger, enabling dramatically faster charging speeds. These powerful stations are the key to making long-distance travel in an EV practical and efficient.
How Fast is Level 3 Charging?
Level 3 charging is exceptionally fast. These stations, often called DC fast chargers, provide power outputs from 50 kW to over 350 kW. This high power allows an EV to gain 100-200 miles of range in just 20 to 40 minutes. The latest generation of ultra-fast charging stations can deliver speeds up to 350 kW, making a quick stop on a road trip very effective. The significant difference in power output across the three levels is a key factor in charging time.
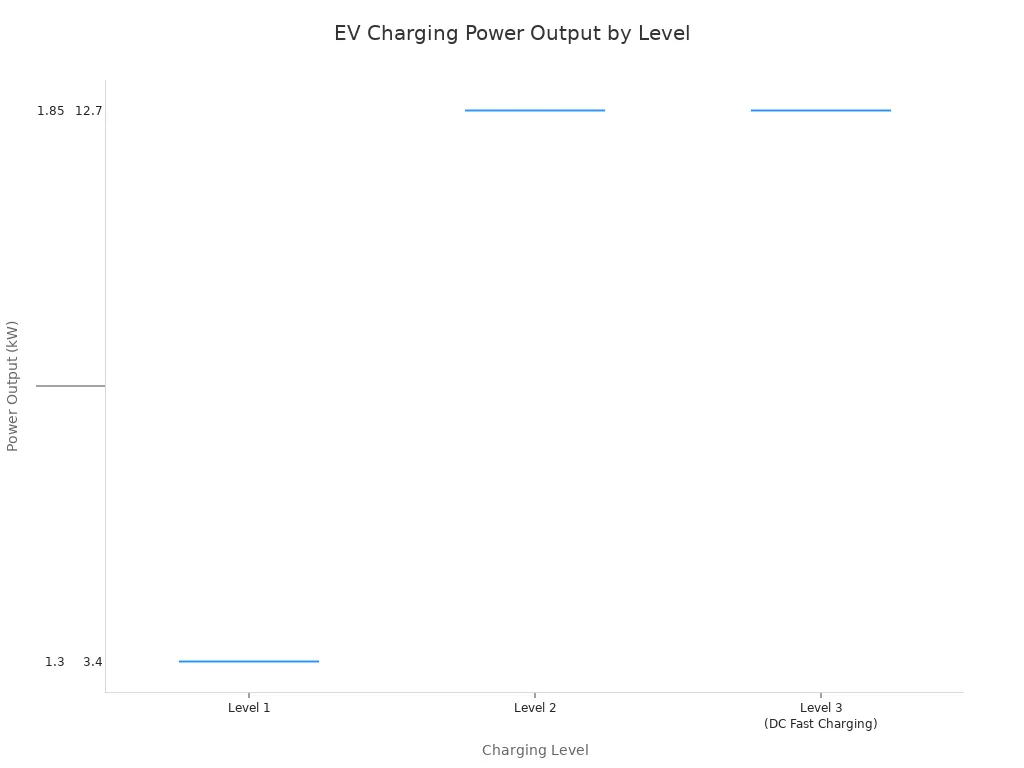
This capability for fast charging makes modern electric vehicles a viable option for almost any journey.
What Are the Different EV Charging Plugs?

The speed of charging is only one part of the equation. The physical connector, or plug, is what links an EV to a power source. There are several different electric car plug types, and understanding them is key to a hassle-free charging experience. Each plug is designed for specific charging levels and vehicle brands.
The J1772 Plug
The Standard for AC Charging
The J1772 connector is the universal standard for Уровень 1 and Level 2 AC charging for nearly all non-Tesla electric vehicles in North America. This single-phase plug is primarily used for slower charging, typically delivering a maximum of 7 kW. However, for Level 2 charging, the J1772 specification can support power outputs up to 22 кВт, making it highly effective for home and workplace charging. Technologically advanced providers like TPSON offer a variety of electric car chargers compatible with this standard.
Which Cars Use J1772?
Most major automakers equip their EVs with a J1772 port for AC charging. This includes popular models from:
- Ford
- General Motors (GM)
- Volkswagen (VW)
- Hyundai
- Kia
- Ривиан
The CCS (Combined Charging System) Plug
The Current Standard for DC Fast Charging
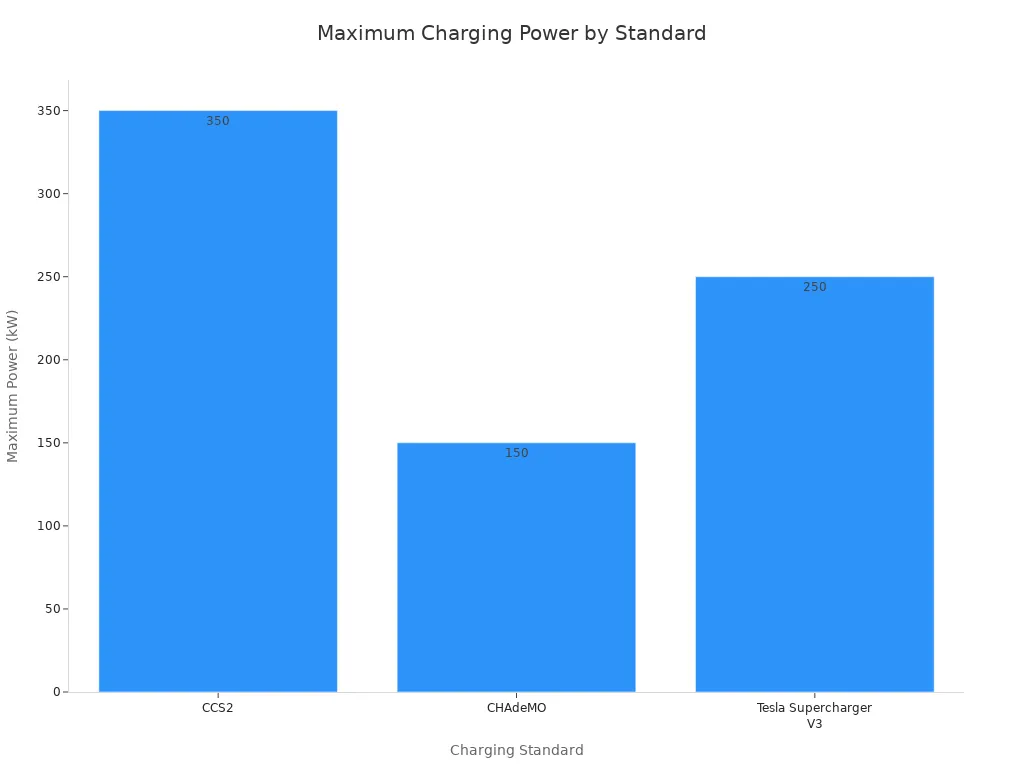
The CCS plug is an enhanced version of the J1772. It adds two large pins below the standard J1772 connector to handle high-power DC fast charging. This “combined” design allows a single port on an EV to accept both AC and DC power. The CCS specification supports a theoretical maximum charging speed of 350 kW, enabling ultra-fast power delivery for long-distance travel. This capability makes it one of the most powerful electric car plug types available.
Which Cars Use CCS?
Most modern non-Tesla EVs that support DC fast charging use the CCS standard. If an EV has a J1772 port, it will likely have the two additional DC pins for CCS fast charging, often covered by a small removable flap.
The NACS (North American Charging Standard) Plug
The Tesla Plug
The NACS plug was developed by Tesla and, until recently, was exclusive to its vehicles. A key advantage of this charger is its elegant and compact design. Unlike CCS, the NACS plug handles both AC and DC charging through the same sleek connector without needing extra pins. This makes the charging experience simpler and the hardware less bulky.
The Future Industry Standard
The NACS plug is rapidly becoming the new industry-wide standard. Many major automakers have announced plans to adopt NACS for their future EV models, starting around 2025. The industry’s shift toward this charger is driven by its superior design.
Key NACS Advantages:
- NACS ports are significantly smaller and more compact than CCS ports.
- The NACS plug is noticeably slimmer and less cumbersome to handle.
- Its smaller size allows for a more streamlined charge port design on an EV.
This transition promises a more unified network of electric car chargers and a simpler fast charging experience for all drivers.
The CHAdeMO Plug
CHAdeMO is one of the original DC fast charging standards. The name is an abbreviation of “CHArge de MOve,” which translates to “charge for moving.” Developed in Japan, it was an early pioneer in the fast charging space. Unlike CCS, the CHAdeMO plug requires a separate port from the vehicle’s AC charging inlet. This design choice makes it distinct from the combined systems that are now more common. While it was once a strong competitor, its adoption has declined significantly outside of Asia, positioning it as a legacy standard in the global EV market.
The Legacy Standard
CHAdeMO established the foundation for modern DC fast charging. A key feature of the standard is its support for bidirectional charging, enabling Vehicle-to-Grid (V2G) technology. This allows an EV to not only draw power from the grid but also send it back, a concept that is only now gaining traction with other standards.
The standard’s power capabilities have evolved considerably over time. CHAdeMO initially offered modest charging speeds but has since increased its power output significantly.
- CHAdeMO 0.9: 62.5 kW
- CHAdeMO 1.2: 200 kW
- CHAdeMO 2.0: 400 кВт
- CHAdeMO 3.0 (ChaoJi): Potential for up to 900 kW
Despite these advancements, most automakers have shifted to CCS and, more recently, NACS for their new models. This industry pivot means the network of CHAdeMO electric car chargers is no longer expanding, making this charger type increasingly rare in many regions.
Which Cars Use CHAdeMO?
The CHAdeMO plug is primarily associated with early EV models from Japanese manufacturers. The most common vehicles equipped with this port are the Nissan LEAF and the Mitsubishi Outlander PHEV. Owners of these vehicles rely on a shrinking network of compatible electric car chargers for their fast charging needs on the road.
Note for CHAdeMO EV Owners: Finding a compatible public charging station can be a challenge. It is crucial to use apps to verify that a location has a functional CHAdeMO charger before traveling.
As the industry consolidates around other standards, owners of a CHAdeMO-equipped EV face a more fragmented charging landscape. This situation highlights the importance of dependable charging equipment. Technologically advanced providers like TPSON offer a range of electric vehicle charging solutions that help EV drivers navigate the diverse and evolving infrastructure.
EV Charger Compatibility: Which Plug Does Your Car Use?

Navigating the world of electric vehicle charging requires understanding your car’s specific plug. The type of port on an EV determines which charging stations it can use, especially for fast charging on the road. This section breaks down the compatibility landscape for owners of Tesla, CCS, and CHAdeMO vehicles, clarifying current options and future changes. Knowing your car’s requirements is the first step to avoiding проблемы совместимости.
For Tesla Owners
Tesla owners have historically enjoyed a streamlined and exclusive charging experience. Their vehicles use the proprietary NACS plug, which provides access to a vast and reliable network.
Using the Supercharger Network
The Tesla Supercharger network is a key advantage for Tesla drivers. It offers seamless, fast, and reliable charging across the country. The cost of using this network can vary based on the time of day.
- Off-peak charging rates are approximately 54p per kilowatt-hour.
- Peak charging rates climb to around 67p per kilowatt-hour, typically between 4pm and 8pm daily.
This pricing structure encourages charging during less busy hours. The network provides powerful DC fast charging, with some stations delivering up to 250 кВт.
Charging at Non-Tesla Stations with Adapters
Tesla drivers are not limited to the Supercharger network. Their EV comes with adapters that provide excellent flexibility and help overcome potential compatibility issues. A standard J1772 adapter allows a Tesla to connect to any Level 1 or Level 2 AC charger. For fast charging at third-party charging stations, Tesla owners can purchase a CCS Combo 1 adapter, granting them access to a wider range of public electric car chargers.
For Ford, GM, VW, and Other CCS Owners
Owners of electric vehicles from brands like Ford, GM, and Volkswagen currently use the CCS standard for fast charging. This standard is widely supported by public charging networks, but the industry is on the verge of a significant shift.
Your Current Charging Setup
For now, CCS is the dominant standard for non-Tesla DC fast charging. Major networks have prioritized cars compatible with this system. Electrify America, a significant charging network, plans to install 2,000 fast-charging stations across 484 locations. These stations will offer a range of power levels, from 50 kW in urban areas to powerful 350 kW chargers at highway locations, ensuring broad compatibility for CCS vehicles.
The Future Switch to NACS
The charging landscape is changing. Many major automakers are planning to adopt the NACS port, which will eventually reduce compatibility issues. This transition will happen over the next few years.
| Производитель | NACS Port Integration Timeline |
|---|---|
| GM | Первые EV, оснащенные системой NACS, появятся в 2026 модельном году |
| Volkswagen Group | Committed to having cars with the NACS port in 2025 |
| Ford | Did not respond to inquiry about timeline |
| Audi & Porsche | No concrete, public plans at this time |
This shift means future models will plug directly into Tesla Superchargers, simplifying the charging experience for all EVs.
For Nissan LEAF and Other CHAdeMO Owners
Owners of vehicles with a CHAdeMO port, such as the Nissan LEAF, face a more challenging charging environment. This standard is being phased out in favor of CCS and NACS, leading to significant compatibility issues.
Поиск совместимых зарядных устройств
The primary challenge for CHAdeMO owners is the shrinking network of compatible electric car chargers. As charging providers focus on building out CCS and NACS infrastructure, older CHAdeMO units are often not repaired or replaced. This makes finding a functional charger difficult. Owners must rely heavily on apps like PlugShare to locate and confirm the operational status of CHAdeMO charging stations before starting a trip.
Future Charging Options
The future for CHAdeMO is uncertain. Nissan is transitioning its newer EV models to the CCS2 standard for international markets, while continuing to support CHAdeMO in Japan. There have been no official announcements from Nissan about future charging solutions or adapters for legacy CHAdeMO vehicle owners. This trend suggests that CHAdeMO compatibility will continue to decline, making reliable home charging solutions from providers like TPSON even more critical for these drivers.
Do All EVs Use the Same Charger Adapters?
Charger adapters are essential tools that bridge the gap between different charging standards. They do not create universal compatibility, but they offer drivers more flexibility. The type of adapter an EV owner needs depends entirely on their vehicle’s charging port and the charging stations they wish to use. These devices are crucial for navigating the mixed landscape of electric car chargers.
Adapters for Tesla Drivers
Tesla drivers have access to a range of adapters that expand their charging options beyond the proprietary Supercharger network. These accessories enhance the versatility of their EV.
The J1772 Adapter
Most Tesla vehicles include a J1772 adapter. This simple device allows the car to connect to the vast number of Level 1 and Level 2 AC charging stations. It makes daily charging at workplaces, hotels, and public parking garages incredibly convenient. The adapter simply clicks onto the J1772 charger plug before being inserted into the Tesla’s charge port.
The CCS Combo 1 Adapter
For access to third-party DC fast charging networks, Tesla owners can purchase a CCS Combo 1 adapter. This accessory enables a Tesla EV to use fast chargers from networks like Electrify Canada. It provides a significant boost in charging flexibility, especially in areas where Superchargers are less common. This adapter is a key tool for ensuring maximum compatibility on long road trips.
Adapters for Non-Tesla Drivers
Drivers of CCS-equipped vehicles also have emerging adapter solutions. These tools are becoming more important as the industry shifts toward the NACS standard.
NACS to CCS Adapters
As automakers adopt the NACS port, adapters that allow CCS vehicles to use the Tesla Supercharger network are becoming available. Ford and Rivian have already begun providing these adapters to their customers. These devices will be critical during the transition period, ensuring drivers can access Tesla’s reliable charging infrastructure. Technologically advanced providers like TPSON are developing charging solutions to support this evolving ecosystem.
Tesla “Magic Dock” Superchargers
Tesla has also developed its own solution called the “Magic Dock.” This is not a separate device for drivers to carry; it is a CCS adapter built directly into the Supercharger station. An EV driver can select the adapter through the Tesla app, which releases the dock for use. This innovation makes select Tesla electric car chargers accessible to any CCS-compatible EV.
Примечание: The Magic Dock rollout is still in its early stages. A small but growing number of Supercharger sites in North America are equipped with this technology, including:
This integrated charger design simplifies the charging experience and is a major step toward greater network compatibility.
Are There Universal Electric Car Chargers?
The idea of universal electric car chargers is a goal for the industry, but the current reality is complex. While no single charger works for all EVs in every situation, the experience differs greatly between slow and fast charging. The search for universal compatibility is much simpler for daily, slower charging. However, the landscape for fast charging remains fragmented, preventing a truly universal solution for every EV driver.
The Reality of AC Charging
For everyday Level 1 and Level 2 charging, the industry is very close to a universal standard. This makes topping up at home, work, or public locations a relatively simple affair.
J1772 as the Near-Universal Plug
The quest for universal electric car chargers finds its greatest success in AC charging. The J1772 plug has become the nearly universal connector for almost every non-Tesla EV. This standardization means drivers of many different brands can use the same public Level 2 electric car chargers without worrying about the plug type. This widespread adoption creates a dependable and nearly universal charging experience for daily needs.
Tesla Destination Chargers
Tesla’s network of Level 2 “Destination Chargers” also improves the availability of charging options. These units, found at locations like hotels and restaurants, use the NACS plug. However, many are accessible to the public. Non-Tesla EV drivers can often use these stations with a simple adapter, further enhancing the feeling of having universal electric car chargers for slower charging sessions.
The Problem with DC Fast Charging
The dream of universal electric car chargers falls apart when it comes to DC fast charging. This is where the differences between vehicle brands and charging networks become most apparent.
The “Plug War” Explained
A “plug war” is the primary reason a universal fast charging solution does not exist yet. Three main standards have been competing for dominance:
- CCS (комбинированная система зарядки)
- NACS (Североамериканский стандарт зарядки)
- CHAdeMO
This competition has fragmented the market. It means a driver cannot pull into just any station for a fast charge. The lack of a single, universal standard for DC fast charging creates significant compatibility issues and confusion for EV owners on the road.
How to Find the Right Charger
Navigating the world of fast charging requires preparation. An EV driver must know their vehicle’s specific plug type to ensure compatibility with charging stations. Finding the right charger is crucial for a successful road trip.
Совет профессионала: 💡 Use mobile apps like PlugShare. These powerful tools allow drivers to filter charging stations by plug type, check for a charger’s operational status, and see recent user reviews. This is the most effective way to manage the absence of truly universal electric car chargers for fast charging.
The Future: A Single Charging Standard for All EVs
The fragmented charging landscape is rapidly consolidating. A future with a single, universal standard for all EVs is becoming a reality. This shift promises to simplify the ownership experience for every EV driver and create a truly universal charging network.
Why NACS is Becoming the New Standard
The North American Charging Standard (NACS) has gained incredible momentum. Its superior design and the reliability of the Tesla Supercharger network have driven its widespread acceptance, positioning it as the future universal plug.
Automaker Adoption
A wave of major automakers has committed to adopting the NACS port. This industry-wide pivot is the primary force behind the move toward a universal standard. Charging network operators like EVgo and Electrify America are reacting to this automaker-led trend by adding NACS connectors to their stations. This ensures their infrastructure remains relevant. Key automakers making the switch include:
- Ford
- Дженерал Моторс (GM)
- Стеллантис (including brands like Jeep and Ram)
- Volkswagen Group (including Audi and Porsche)
- Nissan
- Volvo
- Ривиан
Most of these brands plan to release their first NACS-equipped electric vehicles starting in the 2025 model year.
Benefits of a Single Plug
A single, universal plug offers significant advantages for the entire EV ecosystem. It eliminates the “plug war” and removes a major point of confusion for new EV buyers.
A universal standard means drivers will no longer need to worry about finding a compatible charger. This creates a seamless and predictable charging experience, making long-distance travel as simple as stopping for gas. The goal is a truly universal network where any car can use any fast charger.
What This Means for Current EV Owners
The transition to a universal standard will affect current owners differently depending on their vehicle’s charging port.
For CCS Vehicle Owners
Owners of vehicles with a CCS port are in a strong position. During the transition, automakers will provide NACS-to-CCS adapters. These devices will grant them access to Tesla’s extensive Supercharger network, significantly expanding their fast charging options. This adapter ensures that their EV remains compatible with the growing universal infrastructure.
For CHAdeMO Vehicle Owners
The path forward for CHAdeMO vehicle owners is less clear. The industry’s focus on NACS means the CHAdeMO network will continue to shrink. Currently, no official adapters exist to connect a CHAdeMO car to a NACS charger. This makes reliable home charging even more essential. Technologically advanced providers like TPSON offer dependable charging solutions that help these owners manage their daily needs as public options decline.
To summarize, not all EVs use the same charger, but the landscape for electric vehicles is simplifying. Daily AC charging is straightforward, while the world of fast DC fast charging remains fragmented. The industry is moving toward a single fast charging standard. An EV owner must know their EV’s specific charger port. Using apps to find a compatible fast charger is essential for any EV journey, and providers like TPSON offer solutions for this evolving market.
ЧАСТО ЗАДАВАЕМЫЕ ВОПРОСЫ
В чем основная разница между зарядкой переменным и постоянным током?
AC charging uses a car’s onboard charger to convert power, making it slower and ideal for overnight use. DC fast charging bypasses this internal converter to deliver power directly to the battery. This method provides significantly faster charging speeds for road trips.
Can a Tesla use a non-Tesla charger?
Yes, a Tesla can use other chargers. Most Teslas include a J1772 adapter for common Level 2 AC stations. Owners can also buy a CCS adapter. This accessory grants them access to third-party DC fast charging networks for greater flexibility.
Is the J1772 plug universal?
The J1772 plug is the near-universal standard for Level 1 and Level 2 AC charging for almost all non-Tesla EVs. This widespread adoption creates a consistent and dependable charging experience for daily use at home, work, or public locations.
Why are there different fast charging plugs?
Different plugs exist because of competing standards developed by various automakers. This “plug war” between CCS, NACS, and CHAdeMO created a fragmented market. The industry is now consolidating around the NACS standard to simplify the experience for all drivers.
How do I find the right charger for my EV?
An EV owner must know their car’s specific plug type. Mobile apps like PlugShare are essential tools. They allow drivers to filter charging stations by connector type and check operational status, ensuring a compatible and successful charging session.
What are my options if I own a CHAdeMO vehicle?
Owners of CHAdeMO vehicles face a shrinking public network. Finding compatible stations requires careful planning. Reliable home charging is therefore critical. Technologically advanced providers like TPSON offer dependable home charging solutions to ensure daily power needs are consistently met.
What does the shift to NACS mean for current EV owners?
The industry’s shift to NACS promises a simpler future.
- CCS Owners: Will use adapters to access an expanded charging network.
- CHAdeMO Owners: Will rely more on home charging as public options decline.
- Tesla Owners: Will see more vehicles using their native network.





