You see rapid changes in Southeast Asia’s ev charging infrastructure. Ambitious Pengisi daya listrik policies and consumer demand drive this momentum. In 2024, electric vehicles account for about 10% of new passenger vehicle sales in the region, a figure that trails behind China, Europe, and Norway.
- The expansion of charging stations supports sustainable mobility and energy independence.
- Produsen pengisi daya EV and EV Charger providers help reduce carbon emissions and reliance on fossil fuels.
- Regional cooperation and government action improve accessibility and affordability for every electric vehicle owner.
The State of EV Charging in Southeast Asia

Growth in EV Adoption and Charging Demand
You see a surge in ev adoption across Southeast Asia. This trend reflects a shift in consumer preferences and government priorities. Several factors drive the increase in demand for charging infrastructure. Fiscal and non-fiscal incentives encourage you to consider switching to an ev. Collaboration among manufacturers, green suppliers, and research institutions accelerates technological innovation. Early adopters, including urban users and ride-hailing services, shape market demand through green market sensing. You also face barriers such as limited charging infrastructure, high upfront costs, and low public awareness.
| Faktor | Deskripsi |
|---|---|
| Fiscal and non-fiscal incentives | These incentives encourage EV adoption but require consistency to be effective. |
| Collaboration among stakeholders | Involves manufacturers, green suppliers, and research institutions, fostering technological innovation through knowledge spillovers. |
| Role of early adopters | Early adopters, such as urban users and ride-hailing services, are crucial in shaping demand through green market sensing. |
| Barriers | Major barriers include limited charging infrastructure, high upfront costs, and low public awareness. |
Kebutuhan Pengisian Daya Perkotaan vs Pedesaan
You notice distinct differences in charging needs between urban and rural areas. Urban centers experience higher ev adoption rates, which leads to greater demand for fast and accessible charging stations. You benefit from denser ev charging networks in cities, making daily commutes and ride-hailing operations more convenient. Rural regions face challenges due to sparse infrastructure and longer travel distances. You may encounter range anxiety and limited access to public chargers outside major cities. Addressing these gaps requires targeted investments and innovative solutions.
Public vs. Private Charging Networks
You rely on both public and private charging networks to power your ev. Public charging stations offer convenience for daily use and long-distance travel. You find these stations in shopping malls, office complexes, and transportation hubs. Private charging networks, often installed at homes or workplaces, provide flexibility and control over charging schedules. You see companies and property developers integrating private chargers to attract tenants and customers. The balance between public and private networks shapes the overall accessibility and reliability of ev charging across the region.
Key Players in the Charging Ecosystem
Government Agencies
You observe government agencies setting the pace for ev adoption and infrastructure development. National and local authorities establish policies, incentives, and standards to guide the growth of ev charging networks. You benefit from public investments in charging stations and regulatory support for new technologies. These agencies also collaborate with industry stakeholders to ensure interoperability and safety.
Private Sector and Startups
You see private companies and startups driving innovation in the ev charging ecosystem. Leading providers such as Exicom and Gentari expand their market presence through strategic partnerships and aggressive rollout plans. Exicom holds a 40% share in Malaysia’s DC fast charger segment and partners with Tata Motors, MG, and Volvo. Gentari targets 2,000 additional charging points by the end of 2024 in Malaysia, Thailand, and Singapore. You experience improved access and reliability as these companies launch new products and services.
- Exicom leads in Solusi pengisian daya kendaraan listrik, building strong partnerships and expanding across Southeast Asia.
- Gentari grows rapidly in e-mobility, launching Gentari Go to enhance charging access in multiple countries.
You also notice the influence of major automotive and technology companies. BYD, Tesla, Toyota, VinFast, Honda, Nissan, and Bosch collectively hold about 48% of the market share in the ASEAN ev industry. Their investments and innovations shape the future of ev charging networks and infrastructure.
International Investors
You witness international investors fueling the expansion of ev charging infrastructure. Global partnerships bring capital, expertise, and advanced technology to Southeast Asia. You benefit from cross-border collaborations that accelerate the deployment of charging stations and support regional interoperability. International investment strengthens the ecosystem and helps bridge infrastructure gaps, especially in emerging markets.
Government EV Charger Policies Shaping the Landscape
National Roadmaps and Targets
You see Southeast Asian governments setting ambitious goals for EV charging infrastructure. National roadmaps guide the expansion of charging networks and support the transition to electric mobility. These plans outline clear objectives and targets for charger deployment, manufacturing, and consumer adoption.
| Negara | Objectives and Targets |
|---|---|
| Malaysia | Target of 125,000 EV charging stations by 2030; 100% reduction of income tax for local manufacturers until 2032. |
| Thailand | Planned 700,000 charging stations by 2030; five-year tax exemption for investments in charging stations. |
| Indonesia | Need for 31,000 new charging stations and 52,000 battery swapping stations by 2030; government incentives for EVs. |
You notice that each country tailors its roadmap to local needs and market conditions. Malaysia focuses on both public and private charging points, while Thailand emphasizes rapid infrastructure growth and investment incentives. Indonesia prioritizes battery swapping and charging stations to support its large two-wheeler market.
Thailand’s EV Policy Initiatives
Thailand leads the region with aggressive EV charger policies. You see the government planning 700,000 charging stations by 2030. Tax exemptions for investments in charging stations encourage private sector participation. Thailand also aims to deploy 53,000 electric motorcycle taxis by 2022 and 5,000 electric buses by 2025.
Singapore’s Green Plan
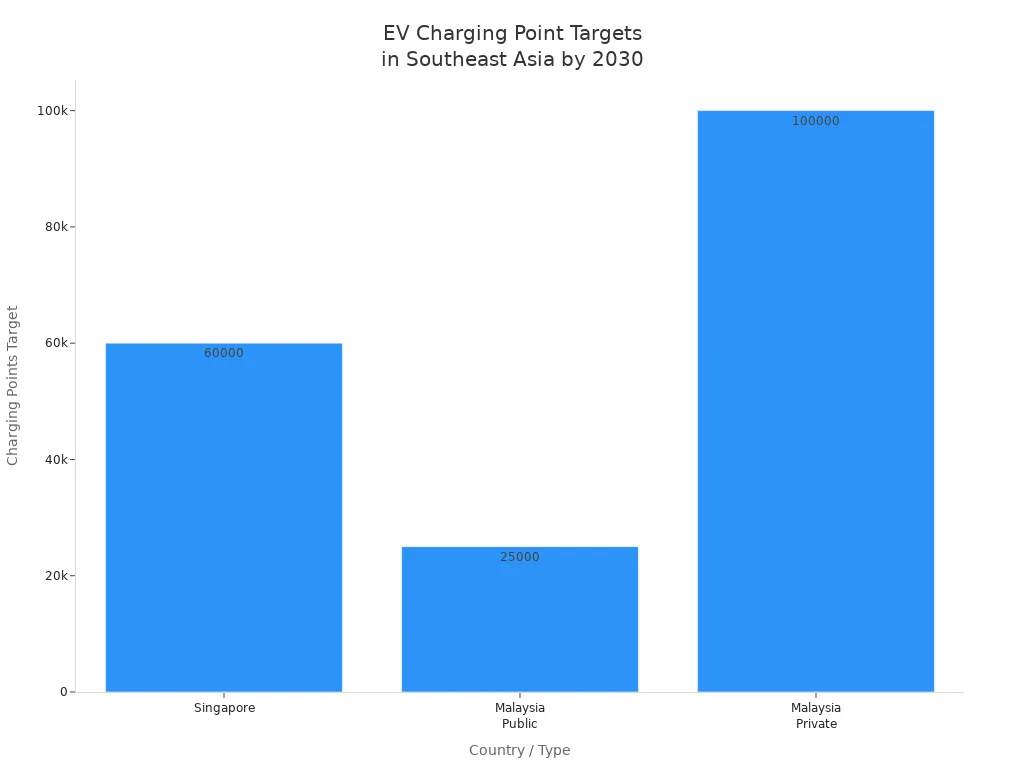
Singapore sets high standards for sustainability. You benefit from the Green Plan, which targets 60,000 charging points by 2030. The government allocates USD 22 million for EV adoption initiatives between 2021 and 2025. Singapore’s approach integrates charging infrastructure with urban planning and public transit.
Indonesia’s Battery and Charging Strategy
Indonesia’s policy focuses on battery storage and charging networks. You see the government aiming for 31,000 new charging stations and 52,000 battery swapping stations by 2030. Incentives support both manufacturers and consumers, with a special emphasis on two-wheelers.
Malaysia’s Incentives and Regulations
Malaysia’s ev charger policies target 125,000 charging stations by 2030. You benefit from a 100% reduction of income tax for local manufacturers until 2032. The National Low Carbon Cities 2030 plan encourages cities to adopt sustainable mobility solutions.
Vietnam’s Emerging EV Charger Policies
Vietnam’s policy landscape evolves rapidly. You see VinFast releasing new electric SUV models and the government introducing various policies to promote EV adoption. The country focuses on expanding charging infrastructure to support growing demand.
Cambodia’s Import Duty Reductions
Cambodia supports EV adoption through import duty reductions. You notice the government lowering taxes on electric vehicles and charging equipment. These measures make EVs more affordable and encourage infrastructure development.
Regulatory Frameworks for Charging Infrastructure
You rely on robust regulatory frameworks to ensure safe and reliable charging infrastructure. Governments issue clear licensing requirements and technical standards for charger installation and operation.
| Regulation/Policy | Deskripsi |
|---|---|
| GR 29/2018 | Government Regulation on Empowerment of Industry, amended by GR 28/2021. |
| PR 55/2019 | Presidential Regulation on the Acceleration of Battery EV Programs. |
| MIR 28/2020 | Ministry of Industry Regulation on Battery Electric Motor Vehicle Components. |
| MIR 6/2022 | Regulation on Specifications and Domestic Component Value Calculation for Battery EV. |
| Insentif Fiskal | Duty-free imports, tax exemptions for EV infrastructure. |
| Non-fiscal Incentives | Technology transfer, operational stability support. |
You benefit from policies that facilitate the replacement of fossil fuel vehicles and encourage EV adoption among individuals and businesses. National technical regulations set clear standards for charger safety and performance. Governments expand charging infrastructure and offer preferential electricity pricing for public charging stations.
Licensing and Standards
You see licensing requirements that streamline charger deployment. Governments set standards for charger specifications, installation, and maintenance. These measures ensure interoperability and protect consumer safety.
Land Use and Zoning for Chargers
You notice land use and zoning policies that support charger installation in strategic locations. Governments designate areas for public charging stations and encourage integration with commercial and residential developments. These policies improve accessibility and convenience for EV owners.
Financial Incentives and Subsidies
You benefit from financial incentives and subsidies that lower the cost of EV charger deployment. Governments offer tax breaks, grants, and public-private partnerships to accelerate infrastructure growth.
| Negara | Jenis Insentif | Deskripsi |
|---|---|---|
| Thailand | Insentif Pajak | Offers tax incentives for local EV manufacturers. |
| Indonesia | Focus on Battery Storage | Emphasizes development of battery storage and charging networks. |
| Vietnam | Government Support | Various policies to promote EV adoption and charging infrastructure. |
| Negara | Incentives Offered | Impact on EV Infrastructure Growth |
|---|---|---|
| Thailand | Tax cuts and subsidies for EVs | Promotes EV adoption and infrastructure development |
| Indonesia | Slashing value-added tax on electric car sales | Encourages more consumers to purchase EVs |
| Malaysia | Import duty and excise tax exemptions for EVs | Expected to boost EV sales and infrastructure expansion |
Tax Breaks and Grants
You see tax breaks and grants driving the expansion of charging networks. Thailand offers tax cuts and subsidies for EVs, which promote adoption and infrastructure development. Indonesia slashes value-added tax on electric car sales, encouraging more consumers to purchase EVs. Malaysia provides import duty and excise tax exemptions, boosting EV sales and charger deployment.
Public-Private Partnerships
You benefit from public-private partnerships that leverage government support and private investment. These collaborations accelerate charger installation and ensure long-term sustainability. Governments work with industry leaders to expand coverage and improve reliability.
Challenges to EV Infrastructure Development

Infrastructure Gaps and Grid Limitations
Limited Charging Coverage
You face significant gaps in infrastruktur pengisian daya across Southeast Asia. Many countries struggle to provide adequate coverage, especially outside major cities. The following table highlights the current state of charging infrastructure and electricity reliability in select countries:
| Negara | Rating of Charging Infrastructure | Reliability of Electricity Supply |
|---|---|---|
| Myanmar | 70.3% rated ‘Poor’ or ‘Very Poor’ | Very low |
| Filipina | 70.5% rated ‘Poor’ or ‘Very Poor’ | More than average |
| Cambodia | 57.1% rated ‘Poor’ or ‘Very Poor’ | Reliable |
You see that limited coverage restricts your ability to travel long distances with an ev. Urban-rural disparities remain a major obstacle, with rural areas often lacking public charging stations.
Power Supply and Reliability Issues
You encounter challenges with power supply and reliability when using charging infrastructure. The region’s transportation sector contributes nearly 40% of global greenhouse gas emissions. Reliance on fossil fuels for electricity undermines the environmental benefits of ev adoption. ASEAN’s projected shift to net importer status for natural gas by 2025 and coal by 2039 increases the urgency for sustainable energy sources. You need reliable and clean electricity to maximize the impact of evs on climate goals.
Consumer Acceptance and Awareness
Range Anxiety and Charging Accessibility
You may hesitate to switch to an ev due to range anxiety and limited access to charging infrastructure. High initial vehicle costs and skepticism about charging convenience slow adoption. In Indonesia, a basic electric car can cost up to 30% more than a comparable internal combustion engine model, making it less accessible for middle-class consumers. You worry about finding a charging station during long trips, especially in rural areas.
- Charge time
- Access to charging, both at home and in public
- Charging convenience
- Efisiensi
- Jangkauan
- Keandalan
You expect charging infrastructure to be easy to use and widely available. The current lack of sufficient stations makes you cautious about investing in an ev.
Education and Outreach Efforts
You notice that awareness and acceptance of evs are growing. Research shows that consumer expectations for charging infrastructure are evolving. You see more outreach efforts from governments and companies, but skepticism persists. You need clear information about charging options and benefits to feel confident in making the switch. Innovation and investment in charging infrastructure will help address these concerns.
Policy and Regulatory Hurdles
Inconsistent Standards Across Countries
You encounter compatibility challenges due to inconsistent standards for charging infrastructure. Multiple DC fast charging protocols, such as CHAdeMO, CCS, and GB/T, force operators to invest in various charger types. This situation increases capital and maintenance costs by 30-50% compared to using a single standard. You also face difficulties with payment systems, which complicate the user experience and slow the rollout of new stations.
Bureaucratic Delays and Permitting
You experience delays in charger deployment because of policy gaps and regulatory uncertainty. Aging grid infrastructure complicates the transition to renewable energy. Lack of policy certainty discourages private investment. Unclear standards for charger interoperability and mandatory grid impact assessments add to the complexity. Structural hurdles in Thailand’s charging market and insufficient charger numbers for the growing ev fleet highlight the mismatch between targets and execution capacity.
Tip: You can advocate for harmonized standards and streamlined permitting processes to accelerate the development of charging infrastructure in your country.
Innovations Accelerating EV Charging Progress
Smart Charging and Digital Solutions
AI-Driven Load Management
You experience a new era of smart charging capabilities in Southeast Asia. AI-driven load management now plays a vital role in balancing energy demand and supply. When you charge your ev, artificial intelligence helps stabilize the grid by distributing power efficiently. This technology smooths out peak demand and prevents overloads. In many cities, AI systems orchestrate distributed energy resources, such as rooftop solar and battery storage, to optimize energy use. You benefit from these advancements because they support reliable stasiun pengisian daya and reduce the risk of power disruptions.
Mobile Apps and Payment Integration
You rely on mobile apps to locate, reserve, and pay for charging stations. These digital solutions make your charging experience seamless. Companies like Gentari have launched platforms such as Gentari Go, which give you access to chargers across Malaysia, Thailand, and Singapore. You can monitor charging status, receive notifications, and complete payments through a single interface. This integration saves you time and enhances convenience. As more providers adopt these tools, you see a growing network of interoperable charging stations that support your mobility needs.
Catatan: Huawei’s HiCharger technology in Rayong, Thailand, demonstrates how advanced digital solutions improve efficiency and reliability for local ev buses.
| Perusahaan | Deskripsi Inovasi | Lokasi Utama |
|---|---|---|
| Delta Electronics | Next-generation EV charging solutions, including a range of chargers from 22 kW to 500 kW. | Thailand, Singapore, Indonesia |
| Gentari | Partnership with Virta to expand EV charging network and interoperability. | Malaysia, Thailand, Singapore |
| Huawei | Launch of HiCharger technology for efficient EV charging in Thailand. | Thailand |
Fast Charging and Battery Swapping
High-Power Charging Stations
You see rapid growth in high-power charging stations throughout Southeast Asia. Delta Electronics offers chargers with capacities from 22 kW up to 500 kW, supporting both urban and highway locations. These stations allow you to recharge your ev quickly, making long-distance travel more practical. Gentari continues to strengthen its position in high-powered DC charging, expanding access for drivers in major cities.
Battery Swapping Pilots
You also witness the rise of battery swapping pilots. In Indonesia, Gojek and Gesits launched a program in Yogyakarta, deploying electric motorcycles with swappable batteries. This approach addresses limited charging infrastructure and reduces downtime for drivers. In Malaysia, a pilot project in Putrajaya tests swappable batteries for electric buses, helping evaluate safety and feasibility. Standardization remains crucial for scaling these solutions across the region.
- Battery swapping supports quick turnaround for commercial fleets.
- Pilots help measure technology readiness and stakeholder engagement.
Strategic Partnerships and Investments
Cross-Border Collaborations
You benefit from strategic partnerships that accelerate the rollout of charging stations. Gentari collaborates with Virta to enhance interoperability and expand its network. V-Green and partners plan to invest US$300 million in Indonesia, focusing on major provinces like Jabodatebek, Bandung, and Surabaya. These investments drive infrastructure growth and support your transition to electric mobility.
Utility and Energy Company Involvement
You notice strong involvement from utility and energy companies. In Thailand, a consortium backed by a green loan from the Asian Development Bank and Energy Absolute supports the construction of charging stations. Malaysia aims to install 10,000 charging stations by 2025, with help from GreenTech Malaysia and EV Connection. In Singapore, SP Group leads the largest network, targeting 60,000 charging points by 2030. Indonesia’s state-owned PLN and private firms like GoTo also invest in new networks, ensuring you have more options for charging your ev.
Regional Cooperation and Interoperability in EV Charger Policies
ASEAN Initiatives for EV Integration
Harmonizing Charging Standards
You see ASEAN countries working together to create a seamless charging experience for electric vehicles. Harmonizing charging standards stands as a top priority. When you travel across borders, you want to use charging stations without worrying about compatibility. ASEAN governments recognize this need and have introduced national technical regulations for EV charging stations. These regulations, effective from June 15, 2025, mandate safety and interoperability standards. This move helps you benefit from cross-border compatibility and supports the growth of regional travel by EV.
| Peraturan | Tanggal Efektif | Tujuan |
|---|---|---|
| National technical regulations for EV charging stations | June 15, 2025 | Mandate safety and interoperability standards, promoting cross-border compatibility within ASEAN |
Tip: Standardized ev charging protocols make it easier for you to charge your vehicle anywhere in the region.
Cross-Border Charging Networks
You gain more freedom to travel as ASEAN countries build cross-border charging networks. These networks allow you to drive your EV from one country to another without facing charging barriers. Interoperability between charging stations ensures that your charging experience remains smooth, whether you are in Singapore, Malaysia, or Thailand. Regional partnerships between governments and private companies help expand these networks quickly. You can expect more reliable and accessible charging options as these collaborations grow.
Local Initiatives Scaling Up
City-Level Pilot Projects
You notice that cities like Bangkok, Jakarta, and Hanoi lead the way in scaling up EV charging infrastructure. These cities focus on building extensive networks of charging and battery-swapping stations. Their efforts target range anxiety, which often discourages you from choosing electric two-wheelers. Local governments encourage private investment in charging infrastructure, following successful models from other regions. You see more pilot projects that test new technologies and business models, helping cities adapt to your needs.
Community Charging Hubs
You benefit from the rise of community charging hubs in urban and suburban areas. These hubs provide convenient access to charging for residents who may not have private parking. Local authorities and private partners work together to install chargers in public spaces, shopping centers, and residential complexes. Community hubs support daily commutes and encourage more people to switch to EVs. As these initiatives expand, you find it easier to charge your vehicle close to home or work.
Impact on Sustainable Mobility and Energy Goals
Reducing Emissions and Urban Pollution
You play a vital role in shaping cleaner cities when you choose electric vehicles. Southeast Asia’s rapid urbanization brings challenges like air pollution and greenhouse gas emissions. EV infrastruktur pengisian daya helps you address these issues by supporting the shift from fossil fuel vehicles to electric alternatives. In Indonesia, the transportation sector contributed to 21% of the country’s energy-related climate pollution in 2020. Road transportation made up 90% of that figure. The government now targets 13 million electric two-wheelers and 2 million electric four-wheelers on the road by 2030. When you drive an EV, you produce zero tailpipe emissions. This change can significantly reduce urban pollution and improve air quality in cities such as Jakarta.
- The transportation sector contributed to 21% of Indonesia’s energy-related climate pollution in 2020, with 90% from road transportation.
- Indonesia aims for 13 million electric two-wheelers and 2 million electric four-wheelers by 2030.
- EVs have zero tailpipe emissions, which can significantly reduce urban pollution and improve air quality in cities like Jakarta.
Contribution to National Climate Targets
You help your country meet its climate goals when you support EV adoption. Governments across Southeast Asia set ambitious targets to cut emissions and transition to renewable energy. By using EVs and supporting charging infrastructure, you contribute to these national commitments. Cleaner transportation options help your country move closer to net-zero emissions. You also encourage policymakers to invest in a sustainable mobility ecosystem that benefits everyone.
Health and Environmental Benefits
You notice the health benefits as air quality improves in your city. Fewer tailpipe emissions mean lower levels of harmful pollutants like nitrogen oxides and particulate matter. Cleaner air reduces respiratory illnesses and supports healthier communities. You also see positive effects on the environment. Less reliance on fossil fuels helps protect natural resources and reduces the impact of climate change.
Shaping the Future of Transportation
Integration with Public Transit
You experience greater convenience when EV charging infrastructure connects with public transit systems. Cities across Southeast Asia invest in charging stations for electric buses and shared mobility services. You can travel farther and more efficiently when you combine EVs with trains, buses, and other public transport. This integration supports a seamless journey and reduces congestion on city roads.
Note: Integrated charging networks make it easier for you to switch between different modes of transport, saving time and reducing your carbon footprint.
Enabling New Mobility Services
You see new mobility services emerge as charging infrastructure expands. Companies introduce electric ride-hailing, car-sharing, and micro-mobility options. You gain more choices for sustainable travel, whether you need a quick ride across town or a shared vehicle for daily commutes. These services rely on reliable charging networks to operate efficiently. As a result, you help drive innovation and shape the future of transportation in your city.
You see Southeast Asia’s EV charging infrastructure advancing at a remarkable pace. Robust policies, technological breakthroughs, and regional partnerships drive this progress.
- You unlock new opportunities for sustainable mobility through continued investment and harmonized standards.
- You play a key role by engaging with public initiatives and supporting innovation.
Your commitment to EV adoption helps the region achieve long-term energy independence and climate targets. The future of transportation depends on your choices and involvement.
PERTANYAAN YANG SERING DIAJUKAN
What types of EV chargers can you find in Southeast Asia?
You encounter AC chargers for home and workplace use. DC fast chargers appear at public stations and highways. Battery swapping stations support electric motorcycles and commercial fleets.
Tip: DC fast chargers reduce charging time for long-distance travel.
How do you locate EV charging stations in your city?
You use mobile apps like PlugShare, Gentari Go, or SP Group’s platform. These apps show real-time availability, pricing, and station locations.
- Search by city or zip code
- Filter by charger type
- View station ratings
Are EV charging stations safe to use?
You benefit from strict safety standards set by national regulations. Certified installers maintain and inspect chargers regularly.
Note: Always follow manufacturer instructions and report any issues to the station operator.
Metode pembayaran apa yang diterima stasiun pengisian daya listrik?
You pay using mobile apps, RFID cards, or credit/debit cards at most public stations. Some networks offer subscription plans for frequent users.
| Metode Pembayaran | Ketersediaan |
|---|---|
| Aplikasi Seluler | Common |
| Kartu RFID | Widespread |
| Kartu Kredit | Tersedia |
Can you charge your EV at home?
You install a home charger for daily use. Home charging offers convenience and lower costs. You check with local authorities for installation guidelines and safety requirements.
How long does it take to charge an EV?
You spend 30 minutes to several hours charging, depending on the charger type and battery size. DC fast chargers provide quicker charging than AC units.
Example: A 50 kW DC charger adds up to 100 km range in 30 minutes.
Apa yang harus Anda lakukan jika stasiun pengisian daya tidak berfungsi?
You report the issue using the station’s app or hotline. You locate alternative stations nearby using your mobile app.
- Contact support
- Check for updates
- Plan your route accordingly
Do you need special permits to install a private EV charger?
You check local regulations before installing a charger at home or work. Some countries require permits or inspections to ensure safety and compliance.
Tip: Consult a certified electrician for installation and maintenance.





