Homeowners evaluating the cost of installing an EV charger often find total expenses for a home charger range from $500 to $2,500, depending on installation needs.
- Level 2 electric vehicle charger equipment typically costs $300 to $1,200.
- The cost of installing an EV charger rises with factors such as electrical panel upgrades, installation complexity, and the type of electric car charger selected.
| Factor | Description |
|---|---|
| Type of Charger | Different chargers require unique installation approaches. |
| Electrical Capacity | Panel upgrades may increase the cost of installing. |
| Installation Location | Garage or outdoor placement impacts home charging expenses. |
| Age of Electrical System | Older homes may need additional updates for EV charger manufacturers’ products. |
| Installation Complexity | Professional labor affects overall cost of installing an EV charger. |
Understanding these variables helps homeowners weigh initial investment against long-term savings and reliable home charging.
Electric Vehicle Charger Installation Cost Overview

National Average Cost of Installing an EV Charger
Recent surveys show that the national average cost to install a Level 2 electric vehicle charger in a single-family home stands at $1,400. This figure reflects typical installation conditions and includes both labor and equipment. Over the past five years, the average cost for installing a standard 7kW home fast charger has ranged from £500 to £1,000. The charger unit itself usually costs a similar amount, with some manufacturers offering bundled installation options. For instance, the Rolec WallPod:EV HomeSmart unit is priced at approximately £913 for the hardware alone or £1,249 for a complete installation package, assuming straightforward site conditions.
Tip: Homeowners should compare bundled installation packages with separate purchases to identify the best value for their needs.
Typical Price Range for Electric Car Charger Installation
The cost of installing an EV charger can vary significantly. Most homeowners encounter a price range between $500 and $2,500 for a complete installation. Several factors contribute to this variation:
- The type and capacity of the charger influence the total cost, with faster chargers generally commanding higher prices.
- Site conditions, such as the complexity of the installation, may lead to additional labor charges.
- Local demand for installation services and the availability of skilled electricians can affect pricing.
- Local building codes and regulations sometimes impose extra fees and extend installation timelines.
Homeowners should expect higher costs for complex installations or when upgrades to the electrical system are necessary.
What’s Included in the EV Charger Installation Cost Estimate
A comprehensive installation cost estimate for an electric vehicle charger typically covers several items and services. The following table outlines common components and their associated costs:
| Item/Service | Cost Range |
|---|---|
| Installing a 240-Volt Circuit/50-Amp Outlet | $300 to $800 |
| 200-Amp Electrical Panel Upgrade | $1,800 to $2,500 |
| Wiring for an EV Charger | $6 to $8 per foot |
| Underground Trenching | $4 to $12 per foot |
| Remodeling a Garage | $1,000 to $5,000 |
| Obtaining a Permit | $50 to $200 |
The installation cost estimate often includes labor, materials, permits, and any necessary upgrades to the home’s electrical system. Homeowners should review each line item to understand the total cost of installing an EV charger and avoid unexpected expenses.
Main Cost Components of Electric Vehicle Charger Installation

Electric Vehicle Charger Equipment Cost
The equipment cost forms a significant portion of the total investment for a home electric vehicle charger. Homeowners can select from a range of models and features, which directly affect the final price.
Level 1 vs. Level 2 Electric Car Chargers
Level 1 chargers use a standard household outlet and typically come included with most electric vehicles. These chargers offer slow charging speeds and suit drivers with minimal daily mileage. Level 2 chargers require a dedicated 240-volt circuit and deliver much faster charging, making them the preferred choice for most homeowners. The price difference between these two types is substantial. Basic Level 1 units may cost as little as $300, while Level 2 chargers often start at $399 and can exceed $1,000 for premium models.
Smart vs. Basic Electric Vehicle Chargers
Smart chargers provide advanced features such as Wi-Fi connectivity, scheduling, and energy monitoring. These features add convenience but also increase the price. Basic no-frills chargers remain available for around $300, while high-end smart chargers can surpass $1,000. The total cost for both the charger and installation typically falls between $800 and $2,500, depending on the chosen model and setup complexity.
- Budget options for electric vehicle chargers start at $399 (e.g., Emporia 48A)
- Basic units can be approximately $300
- High-end models can exceed $1,000
Labor and Installation Fees for EV Charger
Labor and installation fees represent another major cost component. Electricians charge based on the complexity of the installation and the region.
Standard Electric Car Charger Installation Tasks
Standard installation tasks include mounting the charger, running wiring, and connecting the unit to the electrical panel. In most cases, basic installations cost between $200 and $500. Electricians typically charge $50 to $130 per hour. Urban areas often see higher labor rates than rural locations.
Complex Installations and Extra Labor Costs
Complex installations may require panel upgrades, trenching, or longer wiring runs. These factors can push labor costs into the $500 to $1,500 range. The electrician’s experience and the home’s layout also influence the final labor cost.
- Labor costs for EV charger installation typically range from $50 to $130 per hour
- Costs vary by location, complexity, and electrician’s experience
Permits and Inspection Fees for EV Charger Installation
Local governments require permits and inspections to ensure safe and code-compliant installations. These fees vary by city and installation type.
Local Permit Requirements for Electric Vehicle Charger
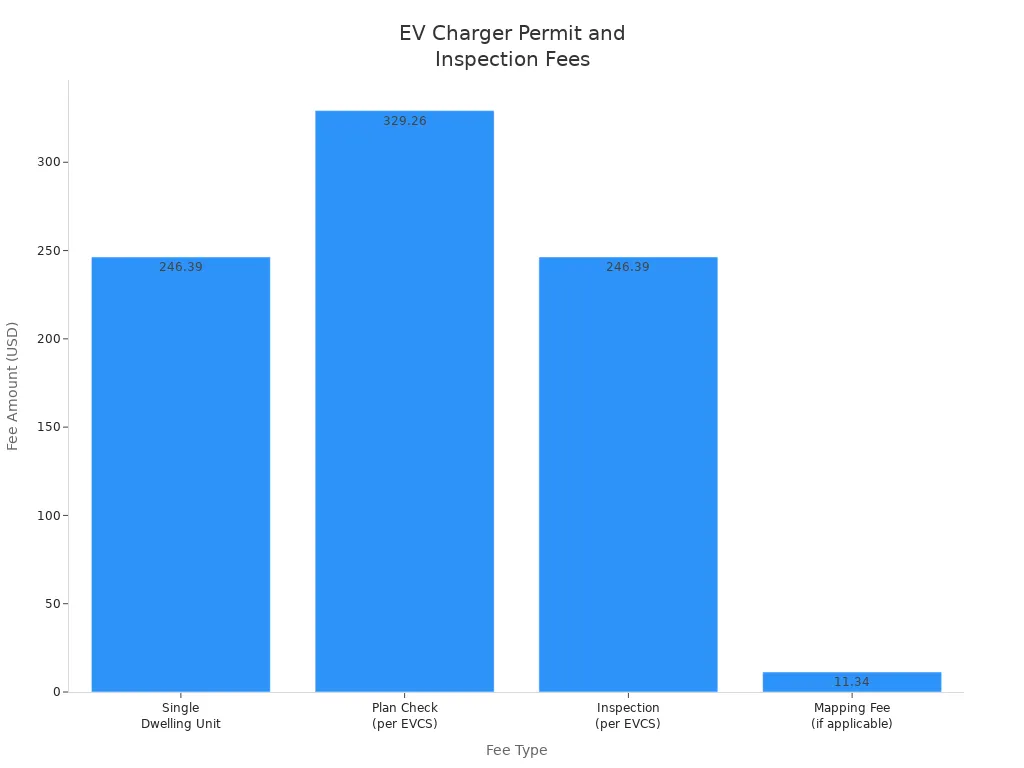
Permit fees depend on the jurisdiction and the type of dwelling. For example, a single dwelling unit, duplex, or townhouse may incur a permit fee of $246.39. Some cities require a plan check for each unique charger, which can cost $329.26.
Inspection Costs for Electric Car Charger Installation
Inspections confirm that the installation meets safety standards. Inspection fees often match permit fees, with a typical charge of $246.39 per charger. Additional mapping fees may apply in certain areas.
| Installation Type | Fee Amount |
|---|---|
| Single Dwelling Unit, Duplex or Townhouse | $246.39 |
| Plan Check (per unique EVCS) | $329.26 |
| Inspection (per EVCS) | $246.39 |
| Mapping Fee (if applicable) | $11.34 |
Note: Homeowners should check with their local building department for the most accurate and current permit and inspection fees.
Additional Materials and Miscellaneous EV Charger Fees
Installing an electric vehicle charger at home involves more than just purchasing the main unit and hiring an electrician. Homeowners often encounter additional materials and miscellaneous fees that can impact the total cost. These expenses cover essential supplies and accessories that ensure the charger operates safely and efficiently.
Wiring and Electrical Supplies for EV Charger
Wiring and electrical supplies play a crucial role in the installation process. Electricians use high-quality wires, conduits, and connectors to link the charger to the home’s electrical panel. The length and type of wiring required depend on the distance between the panel and the charger location. For most installations, wiring costs range from $6 to $8 per foot. If the charger sits far from the panel, the price increases due to longer wire runs and extra labor.
Homeowners may also need junction boxes, breakers, and weatherproof covers. These supplies help protect the charger and maintain compliance with local codes. The total cost for additional materials typically falls between $100 and $300. Electricians select supplies based on the charger’s specifications and the home’s electrical system.
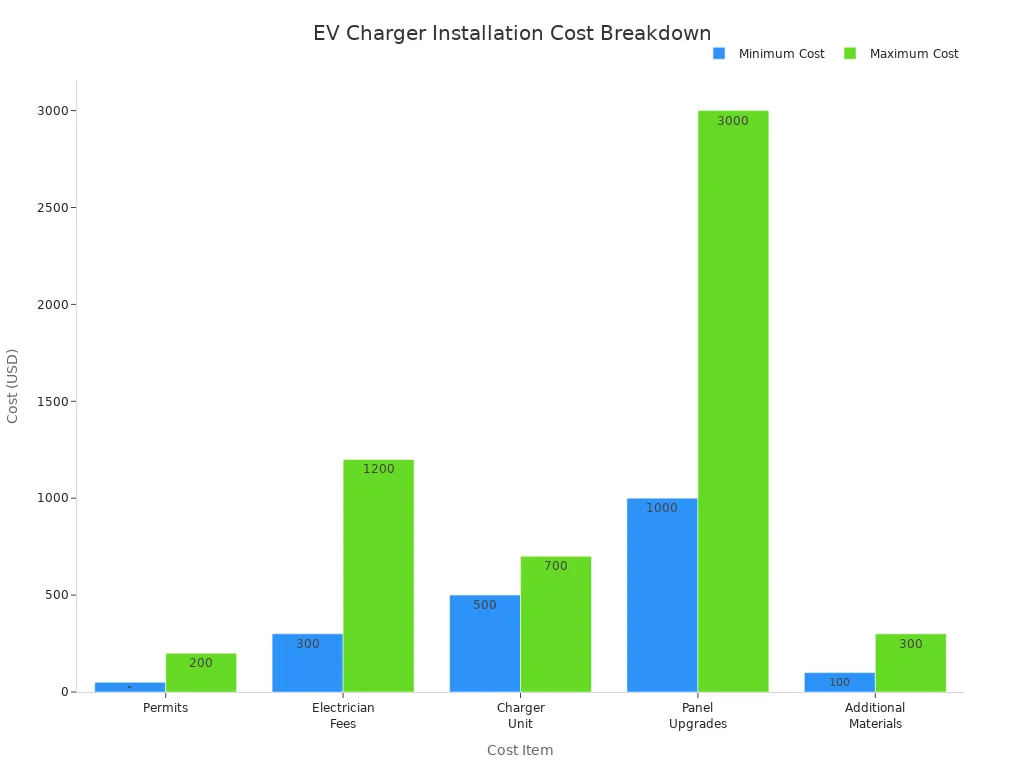
| Item | Cost Range |
|---|---|
| Permits | $50 – $200 |
| Electrician Fees | $300 – $1,200 |
| Charger Unit | $500 – $700+ |
| Panel Upgrades (If Needed) | $1,000 – $3,000+ |
| Additional Materials | $100 – $300 |
Note: Homeowners should request a detailed breakdown of material costs before installation begins.
Mounting Hardware and Accessories for Electric Vehicle Charger
Mounting hardware secures the charger to a wall or pedestal. Installers use brackets, bolts, and anchors designed for the charger’s weight and size. Outdoor installations may require weatherproof enclosures to shield the charger from rain and dust. Some homeowners choose cable management systems to keep charging cords organized and prevent tripping hazards.
Accessories such as connector holsters, signage, and protective covers add convenience and safety. These items usually cost between $50 and $150, depending on the charger model and installation site. Installers recommend accessories that match the charger’s features and the homeowner’s preferences.
A well-equipped installation ensures the charger remains reliable and easy to use. Homeowners benefit from professional advice when selecting mounting hardware and accessories. Proper supplies protect the charger and extend its lifespan.
Tip: Investing in quality mounting hardware and accessories can reduce maintenance needs and improve the overall charging experience.
Key Factors Influencing EV Charger Installation Cost
Type of Electric Vehicle Charger Selected
The type of EV charger chosen plays a major role in determining the overall cost of installation. Homeowners often select between Level 1, Level 2, and Level 3 chargers, each with distinct price points and installation requirements. Level 1 chargers offer basic charging capabilities and minimal installation expenses. Level 2 chargers provide faster charging and require a dedicated circuit, which increases both equipment and labor costs. Level 3 chargers, also known as DC Fast Chargers, are rarely installed in residential settings due to their high price and complex requirements.
| Charging Level | Charger Cost | Installation Cost | Operating Cost |
|---|---|---|---|
| Level 1 | $300 – $600 | Minimal to None | Low |
| Level 2 | $600 – $2,500 | $200 – $1,200 | Moderate |
| Level 3 | $30,000 – $150,000 | $10,000 – $50,000 | High |
Smart chargers add features such as Wi-Fi connectivity and energy monitoring, which can increase the total cost. Basic chargers remain more affordable but lack advanced functionality. Selecting the right type of EV charger depends on charging needs, budget, and desired features.
Home Electrical System Condition and Cost Impact
The condition of a home’s electrical system directly affects the ev charger installation cost. Electricians assess the panel’s capacity and the overall system before beginning installation. If the existing panel cannot support the new charger, upgrades become necessary.
Panel Capacity and Required Upgrades for EV Charger
- Upgrading an electrical panel can add significant expense, especially for Level 2 or DC Fast Chargers.
- Customized installations, such as adding a new subpanel or increasing amperage, often result in higher costs.
Distance from Panel to Electric Car Charger Location
- Longer distances between the panel and charger location require additional wiring and labor.
- Underground cabling or routing through finished walls may increase installation complexity and cost.
Homeowners should consult with a licensed electrician to evaluate the current system and identify any required upgrades before installing an electric vehicle charger.
Installation Location for Electric Vehicle Charger
The location selected for installation influences both the cost and complexity of the project. Most homeowners choose between garage and outdoor setups.
| Installation Location | Cost Range |
|---|---|
| Garage | $800 to $1,500 |
| Outdoor | $800 to $2,500 |
Garage vs. Outdoor Electric Car Charger Installations
Installing a charger in a garage protects it from weather damage and reduces the risk of tampering. Garage installations typically involve less weatherproofing and fewer environmental challenges, which can lower costs. Outdoor installations require weatherproof enclosures and additional safety measures, leading to higher expenses.
Weatherproofing and Safety for EV Charger Installation
- Outdoor installations demand weatherproofing to shield the charger from rain, snow, and dust.
- Increased complexity arises from environmental factors, such as exposure to moisture and temperature fluctuations.
- Proper safety measures ensure reliable operation and extend the charger’s lifespan.
Tip: Choosing a protected location for the electric car charger can minimize maintenance needs and reduce long-term costs.
Need for Electrical Upgrades and Cost of Installing an EV Charger
Service Panel Upgrades for Electric Vehicle Charger
Many homes require electrical upgrades before installing a new charger. Electricians often inspect the service panel to determine if it can handle the additional load from an EV charger. If the panel lacks sufficient capacity, they recommend an upgrade. The cost for a 200-amp panel upgrade ranges from $1,500 to $6,000. This expense covers the labor, materials, and the new panel itself. Some installations also need subpanels, which add $750 to $2,000 to the total cost. Electricians may install basic load management devices to help balance the electrical demand. These devices cost between $200 and $800, with installation fees from $250 to $500.
| Upgrade Type | Cost Estimate |
|---|---|
| 200A panel upgrade | $1,500 – $6,000 |
| Additional costs (wiring, meter upgrades, permit fees) | $500 – $2,000 |
| Basic load management devices | $200 – $800 |
| Installation of load management | $250 – $500 |
| Subpanel installation | $750 – $2,000 |
Note: Electricians recommend panel upgrades when the existing system cannot support the chosen charger type. Homeowners should budget for these upgrades to avoid delays in installation.
Dedicated Circuit Installation for EV Charger
A dedicated circuit ensures safe and reliable operation of the charger. Electricians install a separate 240-volt circuit for most Level 2 chargers. This process involves running new wiring from the panel to the charger location. The cost for wiring and related materials typically falls between $500 and $2,000, depending on the distance and complexity. Load management devices may also be required if the home’s electrical system is near capacity. These upgrades help prevent overloads and maintain consistent charging performance.
Tip: Homeowners should ask electricians about the need for a dedicated circuit during the initial installation consultation. This step helps avoid unexpected costs and ensures the charger operates efficiently.
Regional Labor Rates and Permit Costs for Electric Car Charger
Labor rates and permit fees for charger installation vary widely across the United States. Regional differences impact the total cost, with urban areas often charging more than rural locations. The following table outlines how location affects installation expenses:
| Region | Cost Multiplier | Typical Factors |
|---|---|---|
| Rural/Low-cost areas | 0.8-0.9x | Lower labor rates, simpler permitting |
| Suburban/Average areas | 1.0x | Baseline cost structure |
| Urban/High-cost areas | 1.2-1.5x | Higher labor rates, complex permitting |
| Premium markets (SF, NYC) | 1.5-2.0x | Extreme labor costs, regulatory complexity |
Electricians in rural regions, such as Georgia or Ohio, often charge less for installation. Permit fees in Texas usually range from $100 to $200. In contrast, urban markets like San Francisco or New York City present higher costs. Permit fees in California can reach $1,000 or more, while the Pacific Northwest often sees fees above $300.
- Cheapest Regions:
- Southeastern U.S. (Georgia, Florida)
- Texas (permit fees often between $100 to $200)
- Midwestern U.S. (Ohio, Indiana)
- Most Expensive Regions:
- California (permit costs ranging from $200 to $1,000 or more)
- Northeastern U.S. (New York, Massachusetts, New Jersey)
- Pacific Northwest (Seattle, Portland, often over $300)
Homeowners should research local labor rates and permit requirements before scheduling installation. Regional differences can significantly affect the final price for an EV charger.
Incentives, Rebates, and Grants for EV Charger Installation Cost
Federal Tax Credits for Electric Vehicle Charger
Federal tax credits provide substantial financial relief for homeowners and businesses installing a charger. The IRS offers credits for both residential and commercial installations. Homeowners may claim up to 30% of the total cost, including the charging port, components, and labor, with a maximum credit of $1,000. Businesses can receive a 6% credit for depreciable property, up to $100,000 per item. Projects meeting prevailing wage requirements may qualify for a 30% tax credit on eligible costs.
| Tax Credit Type | Eligibility Requirements | Maximum Credit |
|---|---|---|
| Residential EV Charger | Principal residence, eligible census tract | $1,000 |
| Business EV Charger | Depreciable property, each charging port and energy storage | $100,000 |
| Prevailing Wage Projects | Specific wage and census tract requirements | 30% of costs |
Homeowners must install the charger at their principal residence. Businesses should verify eligibility for each charging port and energy storage property. The installation must occur in an eligible census tract.
State and Local Incentives for EV Charger Installation
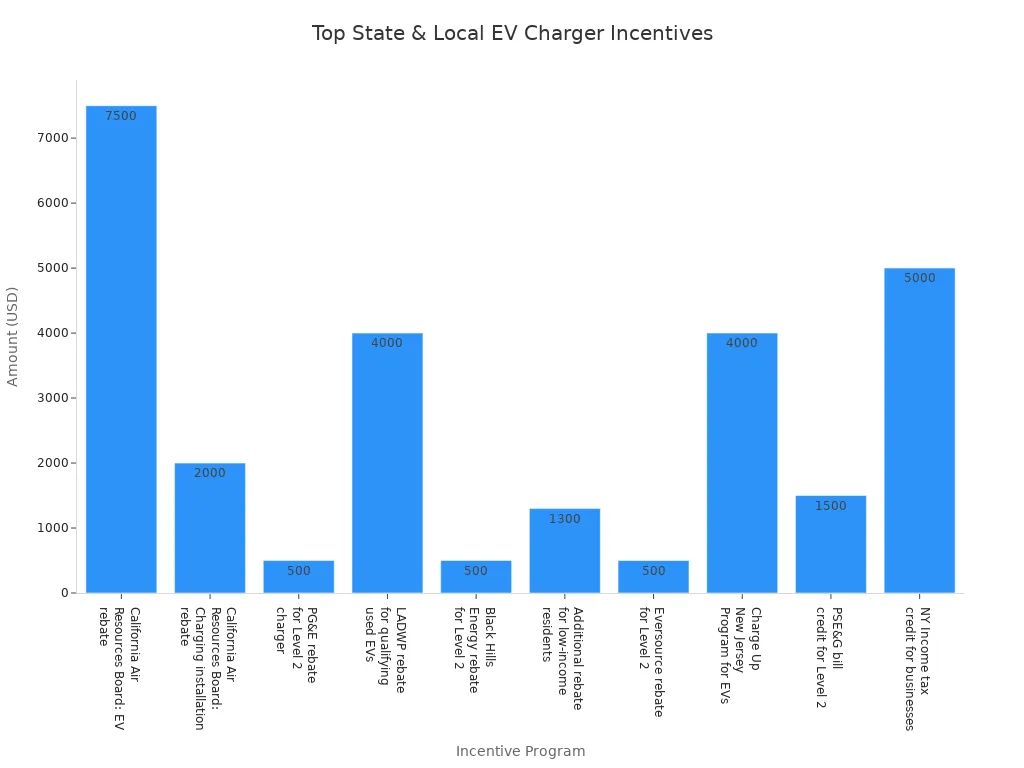
State and local governments offer additional incentives to encourage charger adoption. California leads with rebates up to $7,500 for electric vehicles and $2,000 for charger installation. Utilities such as PG&E and LADWP provide rebates ranging from $500 to $4,000. Colorado, Connecticut, New Jersey, and New York also support charger installation with rebates and tax credits for both residential and commercial projects.
| State | Incentive Description | Amount |
|---|---|---|
| California | EV rebate, charger installation rebate, PG&E, LADWP rebates | $500-$7,500 |
| Colorado | Black Hills Energy rebates, low-income support | $500-$1,300 |
| Connecticut | Eversource rebate | $500 |
| New Jersey | Charge Up NJ, PSE&G bill credit | $1,500-$4,000 |
| New York | Income tax credit for businesses | Up to $5,000 |
Residents should check with their state energy office and local utility for current incentives. Eligibility and amounts vary by location and program.
Utility Company Rebates for Electric Car Charger
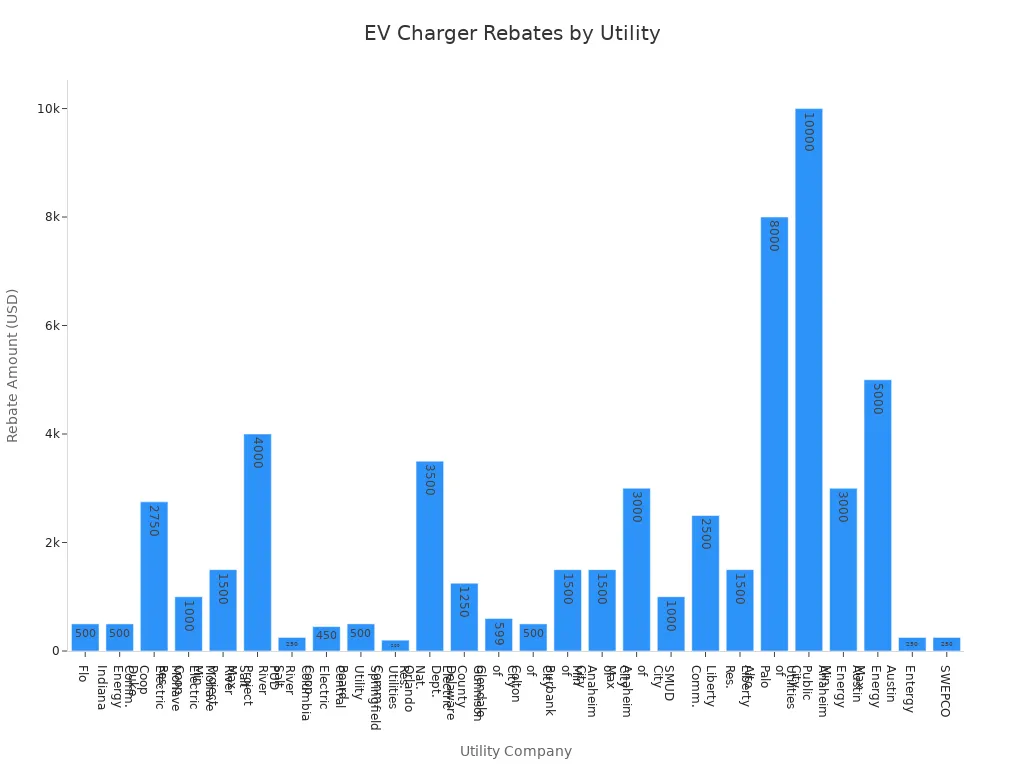
Utility companies across the country offer rebates to reduce the upfront cost of installing a charger. Flo provides a $500 rebate and discounted off-peak rates for clients with average use below 4,500 kWh per month. Duke Energy Indiana offers $500 for Level 2 charger installations in multi-unit dwellings and workplaces. Mohave Electric Cooperative supports both commercial and residential installations, with rebates up to $2,750 for commercial and $1,000 for residential chargers. Salt River Project, Columbia River PUD, and Central Electric Cooperative also provide rebates ranging from $250 to $4,000.
| Utility Company | Rebate Amount | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Flo | $500 | Rebate and discounted off-peak rate |
| Duke Energy Indiana | $500 | Level 2 charger in MUDs and workplaces |
| Mohave Electric Cooperative | $2,750 (commercial) | Up to 50% of installation cost |
| Mohave Electric Cooperative | $1,000 (residential) | Up to 50% of installation cost |
| Salt River Project | $1,500-$4,000 | Per Level 2 charger, varies by organization type |
| Columbia River PUD | $250 | Level 2 charger in specific counties |
| Central Electric Cooperative | $450 | Residential Level 2 charger in specific counties |
| Springfield Utility Board | $500 | Residential Level 2 charger |
| City of Glendale | $599 | Smart/networked residential chargers |
| City of Colton | $500 | Approved Level 2 charger installed |
| City of Burbank | $1,500 | Level 2 charging station |
| City of Anaheim | $1,500-$3,000 | Reimbursement for Level 2 charger expenses |
| SMUD | $1,000 | EV charging equipment and installation costs |
| Liberty | $2,500 (commercial) | $1,500 (residential) |
| City of Palo Alto Utility | $8,000 | Level 2 or DC Fast Chargers |
| Anaheim Public Utilities | $10,000 | Publicly accessible locations |
| Austin Energy | $3,000-$5,000 | Level 2 and DC Fast charging stations |
| Entergy | $250 | Level 2 residential charger installed |
| SWEPCO | $250 | Level 2 residential charger installed |
Utility rebates can significantly lower the cost of a charger. Homeowners should review eligibility requirements and application deadlines for each program.
How to Find and Apply for EV Charger Installation Incentives
Homeowners seeking to reduce the cost of electric vehicle charger installation often benefit from available incentives. These programs, offered by federal, state, and local agencies, as well as utility companies, help offset upfront expenses. To maximize savings, individuals should follow a structured approach when searching for and applying for incentives.
Recommended Steps for Finding and Applying for Incentives:
- Review the list of rebate-eligible EV charger models. Select a charger that meets personal charging needs and complies with program requirements.
- Purchase the chosen charger from an approved supplier. Ensure the unit is new, not refurbished or used, and carries the necessary certifications for sale and use in the region.
- Schedule installation with a licensed electrician. The professional may complete required electrical upgrades and ensure the charger meets safety standards.
- Gather documentation, including proof of purchase and installation. Most programs require submission of these documents within a specified timeframe, often 90 days after installation.
- Submit the application through the appropriate channel. This may involve online portals, mail-in forms, or direct submission to the utility or government agency.
Tip: Homeowners should keep all receipts and installation records organized. Quick access to documentation speeds up the application process and reduces the risk of missing deadlines.
Eligibility criteria for incentives vary by program. Many require the charger to be a Level 2 unit (208V or 240V), purchased from a local supplier, and approved for residential use. Some programs restrict eligibility to new chargers only, excluding refurbished or used equipment. Homeowners should verify that the selected charger appears on the official rebate-eligible list before making a purchase.
Common Eligibility Requirements:
- The charger must be on the rebate-eligible model list.
- The unit must be purchased from a supplier within the country.
- The charger must have proper certifications for residential use.
- Only new chargers qualify; used or refurbished units do not meet requirements.
- Installation must occur at a principal residence.
The following table summarizes typical documentation required for incentive applications:
| Required Document | Description |
|---|---|
| Proof of Purchase | Receipt or invoice for charger |
| Installation Record | Electrician’s statement or permit |
| Charger Model Information | Certification and eligibility proof |
| Application Form | Completed incentive application |
Homeowners who follow these steps improve their chances of receiving incentives. Careful attention to eligibility and documentation ensures a smooth application process.
Tips to Save on Cost of Installing an EV Charger
Use Existing Electrical Infrastructure for Electric Vehicle Charger
Homeowners can lower the cost of installing a home charger by making use of existing electrical infrastructure. When a property already has sufficient electrical capacity, the need for expensive upgrades decreases. Adding EV Ready infrastructure during other groundwork projects, such as renovations, allows for the installation of conduits and junction boxes in advance. This approach streamlines future charger installations and reduces labor expenses.
A few practical steps help maximize savings:
- Assess the current electrical capacity to determine if additional power is necessary.
- Plan the charger location to minimize tunneling and wiring runs.
- Consult with a licensed electrician or EV charging installation service for a thorough evaluation.
By leveraging existing wiring and strategically placing the charger, homeowners can avoid unnecessary construction and material costs. This method plays a crucial role in reducing installation costs and ensures a smoother project scope.
Tip: Early planning and coordination with professionals can prevent costly surprises and make future upgrades more affordable.
Choose the Right Electric Car Charger for Your Needs
Selecting the appropriate charger involves balancing cost, functionality, and charging speed. Homeowners should consider their daily driving habits, the range needed on a single charge, and the availability of public charging infrastructure. For most residential settings, Level 2 chargers offer a practical solution, providing faster charging without the complexity of commercial-grade equipment.
Key factors to evaluate include:
- The range provided by the charger per hour of charging.
- The total cost of operation, including electricity usage.
- The suitability of the charger for the intended location.
DC fast chargers deliver rapid charging but come with high equipment and installation costs. These units require a 480V DC utility service and are best suited for commercial or high-traffic areas, such as shopping centers. For home use, a Level 2 charger meets most needs while keeping costs manageable.
Note: Choosing a charger that matches actual usage patterns prevents overspending on unnecessary features.
Get Multiple Quotes for EV Charger Installation Cost
Obtaining several quotes from qualified contractors can lead to significant savings. Industry analysis shows that installation quotes for the same work can vary by $500 to $1,500 among different providers. By comparing offers, homeowners often save between 20% and 40% on the total cost.
A simple process can maximize value:
- Request detailed quotes from at least three licensed electricians or installation companies.
- Compare the scope of work, materials, and warranty terms.
- Select the provider offering the best balance of price and service.
This strategy not only helps in reducing installation costs but also ensures transparency and quality in the installation process.
Tip: Always review each quote carefully to confirm that all necessary components and services are included.
Bundle Electric Vehicle Charger Installation with Other Electrical Work
Homeowners often seek ways to reduce the total expense of adding a charger at home. One effective strategy involves bundling the charger installation with other electrical projects. This approach can streamline the process and unlock several financial benefits.
- Bundling projects leads to significant cost savings. Electricians can complete multiple tasks during a single visit, which reduces labor charges.
- The permitting process becomes simpler when grouped under one application. This consolidation can lower administrative fees and shorten approval times.
- Homeowners may take advantage of time-of-use rates and stack available incentives, further decreasing the overall cost.
- Coordinating upgrades, such as panel replacements or wiring improvements, with charger installation ensures the home’s electrical system meets current and future needs.
By planning ahead and combining projects, homeowners can maximize efficiency and minimize disruption. This method also helps avoid repeated service calls and redundant permit applications.
Tip: Schedule a comprehensive electrical assessment before starting any major upgrades. This step allows the electrician to identify opportunities for bundling and recommend the most cost-effective solutions.
DIY vs. Professional Electric Car Charger Installation
Many homeowners consider installing a charger themselves to save money. However, the risks and benefits of DIY versus professional installation differ greatly. The following table highlights key differences:
| Aspect | DIY Installation | Professional Installation |
|---|---|---|
| Compliance and Safety | May not meet local codes | Ensures compliance with local codes |
| Cost | Lower upfront costs | Higher upfront costs |
| Warranty Protection | May void warranties | Maintains warranty validity |
DIY installation offers savings on labor fees. However, it introduces risks such as electrical hazards and code violations. Insurance coverage may not apply if the work fails to meet local standards. Warranties on the charger or related equipment could become void if a licensed professional does not perform the installation.
Professional installation costs more but provides peace of mind. Licensed electricians ensure the charger meets all safety and code requirements. They also help maintain warranty protection and offer ongoing support.
- DIY installation can lead to electrical hazards and costly repairs.
- Professional installation ensures safety, compliance, and warranty coverage.
A homeowner who attempted to install a Level 2 charger without professional help experienced frequent breaker trips and overheating of the electrical panel. This situation resulted in expensive repairs and fines for unpermitted work, demonstrating the potential pitfalls of DIY approaches.
Bottom line: Unless someone holds a valid electrician’s license, DIY EV charger installation is rarely recommended due to safety and compliance concerns.
Ongoing Costs After Electric Vehicle Charger Installation
Electricity Usage and Charging Cost for EV Charger
Homeowners who install an EV charger at home experience a noticeable change in their monthly electricity bills. The average increase in monthly electricity costs reaches approximately $46.75. This figure reflects the national average electricity rate and assumes a typical driving distance of 1,000 miles per month. The actual charging costs depend on local utility rates, the efficiency of the vehicle, and the frequency of use. Some utility companies offer special time-of-use rates for EV charging, which can help reduce expenses during off-peak hours. Monitoring usage through smart charger features allows homeowners to optimize their charging schedule and manage costs effectively.
Tip: Scheduling charging sessions during off-peak hours can lower electricity expenses and maximize savings.
Maintenance and Repairs for Electric Car Charger
Routine maintenance ensures the charger operates safely and efficiently. Most residential chargers require minimal upkeep. Homeowners should inspect cables and connectors for wear, clean the unit regularly, and check for signs of damage. Professional inspections may be necessary if the charger displays error codes or fails to charge the vehicle. Repair costs vary based on the type of charger and the nature of the issue. Replacing a damaged cable or connector typically costs between $100 and $300. Advanced chargers with smart features may require specialized service, which can increase repair expenses. Regular maintenance extends the lifespan of the charger and reduces the likelihood of unexpected failures.
- Inspect cables and connectors monthly.
- Clean the charger exterior to prevent dust buildup.
- Schedule professional service if problems arise.
Software Updates and Connectivity Fees for EV Charger
Modern chargers often include smart features such as Wi-Fi connectivity, remote monitoring, and energy usage tracking. Manufacturers release software updates to improve performance, enhance security, and add new functions. Some chargers require a subscription for advanced connectivity services, including remote diagnostics and integration with smart home systems. Subscription fees range from $5 to $10 per month, depending on the manufacturer and service level. Homeowners should review the terms of service before activating these features. Keeping the charger’s software up to date ensures compatibility with new vehicles and maintains optimal charging performance.
| Feature | Typical Cost | Frequency |
|---|---|---|
| Software updates | Usually free | As released |
| Connectivity fees | $5–$10/month | Monthly |
| Remote diagnostics | Included/subscription | As needed |
Note: Regular software updates and connectivity services help maintain charger reliability and support new technology advancements.
Is the Cost of Installing an EV Charger at Home Worth It?
Convenience and Time Savings with Electric Vehicle Charger
Installing an electric vehicle charger at home transforms the daily routine for EV owners. Charging at home eliminates the need to visit public stations, saving valuable time each week. Homeowners can simply plug in their vehicles overnight and wake up to a fully charged battery. This convenience means no more waiting in line or searching for available chargers during busy hours. The ability to charge at any time, regardless of weather or location, adds flexibility to daily schedules. For families with multiple drivers or vehicles, a dedicated charger ensures everyone has access when needed. The benefits of installing an EV charger extend beyond convenience, offering peace of mind and reliability.
Long-Term Cost Benefits of Electric Car Charger Installation
The cost of installing an EV charger may seem significant at first, but the long-term savings often outweigh the initial investment. Home charging typically costs less per mile compared to public charging stations. Many utility companies offer special rates or incentives for EV owners, further reducing electricity expenses. Over time, these savings accumulate, making the total cost of ownership more manageable. Maintenance requirements for home chargers remain minimal, which helps keep ongoing costs low. By choosing the right type of charger and taking advantage of available incentives, homeowners can maximize the benefits of installing an EV charger. The ev charger installation cost becomes a smart investment for those who drive regularly.
Note: Homeowners who schedule charging during off-peak hours can lower their electricity bills and increase savings.
Impact on Home Value from EV Charger Installation
Recent real estate studies highlight a strong connection between home value and the presence of an electric vehicle charger. Demand for charging solutions continues to rise as more buyers seek properties equipped for EVs. Homes with a charger often sell faster and command higher prices. The following table shows how proximity to a charging station can influence property value:
| Proximity to EV Charging Station | Price Increase (%) | Price Increase ($) |
|---|---|---|
| Within 1 km | 3.3% | $17,212 |
| 0.4-0.5 km | 5.8% | N/A |
- Increasing numbers of homebuyers prefer properties with EV chargers.
- Homes with charging stations tend to sell at higher prices.
- Residential properties with chargers can sell for up to 5% more than those without.
A positive correlation exists between EV charging stations and property values. As the market shifts toward electric vehicles, the benefits of installing an EV charger become even more apparent. The cost of installing an EV charger not only provides immediate convenience but also enhances long-term investment potential.
The average cost to install an EV charger at home depends on equipment, labor, and local permit fees. Key factors such as the type of charger, electrical upgrades, and installation location influence the total investment. Homeowners should gather multiple quotes, ask about incentives, and review eligibility for rebates before starting. Reliable information helps individuals make informed decisions and maximize the value of their EV charging setup.
FAQ
How long does EV charger installation usually take?
Most electricians complete a standard home EV charger installation in two to four hours. Complex projects, such as panel upgrades or outdoor setups, may require a full day.
Can any electrician install an EV charger?
Licensed electricians with experience in EV charger installations handle most residential projects. They follow local codes and manufacturer guidelines to ensure safety and compliance.
Is a permit required for EV charger installation?
Local building departments often require permits for EV charger installations. Homeowners should check with city officials before starting the project to avoid fines or delays.
What maintenance does a home EV charger need?
Routine maintenance includes inspecting cables, cleaning the unit, and checking for damage. Most chargers require minimal upkeep. Professional service may be needed for error codes or hardware issues.
Will installing an EV charger increase my electricity bill?
Charging an electric vehicle at home increases monthly electricity costs. The average homeowner pays about $47 more per month, depending on driving habits and local utility rates.
Can I install a Level 3 charger at home?
Level 3 chargers, also called DC Fast Chargers, require commercial-grade electrical service. Most homes lack the necessary infrastructure. Residential installations typically use Level 1 or Level 2 chargers.
Do EV chargers work during power outages?
EV chargers do not operate during power outages unless connected to a backup power source. Some homeowners install battery systems to maintain charging capability during outages.
Are there incentives for installing an EV charger?
Federal, state, and utility incentives help reduce installation costs. Homeowners should research available programs and confirm eligibility before purchasing equipment or scheduling installation.





