
Efficiently locating an EV charger is essential for seamless electric vehicle ownership. Drivers often search for “ev chargers near me” and rely on a quality ev charge point map. Dedicated apps and a vehicle’s navigation system offer the fastest methods for finding a charger. The availability of electric car charging points varies globally, highlighting the need for reliable search tools.
| Region | Public Charging Stations (as of 2024) |
|---|---|
| United States | Over 168,000 |
| Europe | 632,000 |
Leading EV charger manufacturers like TPSON, a technologically advanced electric vehicle charging solution provider, contribute to this growing infrastructure. This guide begins by exploring the best applications for EV charging.
Top Apps and Tools: Your EV Charge Point Map

Navigating the world of electric vehicle charging is simple with the right digital tools. An effective ev charge point map is an EV driver’s best friend. While many options exist, they fall into three main categories: dedicated charging apps, built-in vehicle navigation, and everyday mapping apps. Each offers unique advantages for finding electric car charging points.
Dedicated Charging Apps
Dedicated EV apps provide the most comprehensive and detailed information. They are purpose-built for EV drivers. These apps allow users to find chargers, check availability, and even monitor charging sessions remotely. They offer powerful filters for connector type and charging speed, making them superior to generic solutions. Technologically advanced providers like TPSON help expand the network these apps catalog.
PlugShare: The Crowd-Sourced Favorite
PlugShare is a global favorite for a reason. It operates as a massive, crowd-sourced ev charge point map. Its strength lies in its active user community.
- User Check-ins: Drivers report on their charging experience, noting if a station is working, broken, or occupied.
- Photos and Tips: Users often upload photos of the charger’s location and provide helpful tips for finding it.
- Comprehensive Filters: Drivers can filter by network, plug type, and charging speed.
A Better Routeplanner (ABRP): For Road Trip Gurus
A Better Routeplanner (ABRP) excels at long-distance journey planning. The driver inputs their EV model, starting battery percentage, and destination. ABRP then creates an optimized route. The route includes all necessary charging stops, estimating charging times and state-of-charge upon arrival at each point. It is an essential tool for eliminating range anxiety on road trips.
Electroverse: One App for Many Networks
The Electroverse app aims to simplify the charging process. It consolidates multiple charging networks into a single platform. This allows a driver to start and pay for charging at thousands of locations with one app and one card. It reduces the need to juggle multiple network-specific applications. Similar apps like Plugsurfing offer real-time data for over 600,000 stations.
Zap-Map: A UK & Europe Option
For drivers in the United Kingdom and parts of Europe, Zap-Map is the go-to interactive ev charge point map. It provides a detailed view of the uk ev charging network and beyond.
- Live Data: The app offers live charger availability from many connected networks.
- Community Reviews: It has access to a large community of user reviews and check-ins.
- Route Planner: A built-in route planner helps drivers plan journeys with charging stops included.
Your Vehicle’s Built-in Navigation
Most modern electric vehicles come equipped with a native navigation system. This system is often integrated directly with the car’s battery management system. It can automatically suggest charging stops when a destination is beyond the current range.
Using Your Car’s Native System
An EV’s native system uses real-time battery data to provide accurate range estimates. When navigating, it can proactively add a charger to the route if it predicts the car will not reach the destination. This integration offers a seamless experience, as the car knows its own energy consumption and needs.
Pros and Cons of In-Car Navigation
While convenient, built-in systems may lack the detailed, real-time user feedback of dedicated apps. The data on charger availability or operational status can sometimes be less current. The following table compares the typical features of a dedicated ev charging map app with more general systems.
| Feature | Dedicated EV Apps | In-Car / General Apps |
|---|---|---|
| Detailed Station Info | Yes | Often Limited |
| Real-time Availability | Yes | Sometimes |
| User-Generated Reviews | Yes | No |
| Route Optimization for EV | Yes | Basic or None |
| Multi-Network Payment | Often | No |
Everyday Mapping Apps
Familiar apps like Google Maps, Apple Maps, and Waze have added features for EV drivers. They are convenient for users who prefer to stay within a single application for all their navigation needs.
Using Google Maps to Find Chargers
Google Maps allows users to search for “ev charging stations.” The results appear on the map, and users can filter by plug type (like J1772, CCS, CHAdeMO, and NACS). The platform often shows the number of available ports and charging speeds, pulling data directly from charging network operators.
Using Apple Maps for EV Charging
Apple Maps provides similar functionality. Users can search for EV charging stations and see details about the charger type and availability. For some vehicle models, Apple Maps can integrate with the car to track its charge and plan routes that include charging stops, offering a more connected experience. This creates a useful live ev charging map within the Apple ecosystem.
Waze’s EV Charging Features
Waze, known for its community-based traffic alerts, has also enhanced its EV features. The platform now provides a more personalized interactive ev charge point map. Drivers can configure their specific EV and plug type for tailored results.
Waze’s EV features include:
- Users can input their EV model and plug type in the app settings.
- The app uses this information to show relevant charging stations along a route.
- Community map editors help keep the charging station information accurate.
- After setting a route, a user can search for “EV charging” to see compatible options and add one as a stop.
How to Filter Your Search to Find Public Chargers
An EV driver’s ability to find public chargers quickly depends on effective search filtering. Using an app’s filters for connector type, charging speed, and live availability transforms a frustrating search into a simple task. Mastering these tools ensures that every search for electric car charging points yields a compatible and working station.
Filtering by Connector Type
Why Connector Type is Crucial
Not all chargers fit all EVs. An EV has a specific charging port, much like a phone has a specific charging cable. Attempting to use an incompatible connector is like trying to fit a square peg in a round hole—it simply will not work. Filtering by connector type is the first and most critical step to ensure a driver arrives at a charger they can actually use. This saves time and prevents the disappointment of finding an unusable station.
CCS (Combined Charging System)
The Combined Charging System, or CCS, is a widely adopted standard for DC fast charging. Most new non-Tesla EVs in North America and Europe use this connector.
- CCS1: The standard in North America, combining a J1772 connector with two large DC pins below it.
- CCS2: The standard in Europe, which integrates the Type 2 connector with the same DC pins.
Its widespread adoption makes it a common and reliable choice for many EV drivers seeking fast charging.
NACS (North American Charging Standard)
Originally developed by Tesla, the North American Charging Standard (NACS) is a compact and powerful connector that handles both AC and DC charging. Following Tesla’s decision to open its standard, a significant number of automakers have committed to adopting NACS for their future vehicles.
Note: Many major automotive brands will begin equipping their North American models with NACS ports starting in 2025. This includes:
- Kia, Lucid Motors, and Mercedes-Benz
- Nissan, Polestar, and Rivian
- Stellantis (Chrysler, Jeep, Dodge)
- Toyota (including Lexus) and the Volkswagen Group (Audi, Porsche)
This shift signals a major consolidation in the North American public EV charging landscape.
CHAdeMO
CHAdeMO is a DC fast-charging standard developed in Japan. It was an early leader in the EV market and is primarily found on older models from Japanese manufacturers, such as the Nissan LEAF and Mitsubishi Outlander PHEV. While still available, the network is no longer expanding in North America as the industry moves toward CCS and NACS. Drivers of vehicles with CHAdeMO ports must be diligent in filtering for these specific chargers.
Type 2 / J1772 for AC Charging
These connectors are the universal standards for Level 1 and Level 2 AC charging.
- J1772 (Type 1): The standard AC connector for all non-Tesla EVs in North America.
- Type 2: The standard AC connector in Europe, which can support single-phase and three-phase power.
Nearly every public Level 2 charging station uses one of these connectors, making them essential for everyday top-ups at workplaces, shopping centers, and public parking lots.
Filtering by Charging Speed
After selecting the correct connector, the next filter to apply is charging speed. The speed determines how long a driver will spend at the station. Charging speeds are categorized into three main levels.
Level 1: Slow Overnight Charging
Level 1 charging uses a standard household outlet (120V in North America). It is the slowest method, adding only about 3-5 miles of range per hour. This option is best suited for overnight charging at home or for plug-in hybrids with smaller batteries. It is rarely a practical choice for public charging unless it is a multi-day stop.
Level 2: The All-Rounder
Level 2 chargers are the most common type found in public locations like workplaces, shopping centers, and parking garages. They use a 240V connection (similar to an electric dryer) and can add 15-35 miles of range per hour. This makes them perfect for topping up an EV battery while the driver is at work, shopping, or dining. Technologically advanced providers like TPSON manufacture reliable Level 2 solutions that form the backbone of this public infrastructure.
Level 3: DC Fast Charging
Level 3 charging, also known as DC Fast Charging, provides the quickest charging experience. These powerful stations can add hundreds of miles of range in under an hour, with some capable of charging an EV from 10% to 80% in just 20-30 minutes. They are essential for long-distance travel and for drivers needing a significant charge quickly.
| Level | Voltage | Charging Speed (Range per Hour) | Best Use Case |
|---|---|---|---|
| Level 1 | 120V | 3-5 miles | Overnight home charging |
| Level 2 | 240V | 15-35 miles | Workplace, shopping, public lots |
| Level 3 | 480V+ | 100-300+ miles | Long-distance trips, quick top-ups |
Choosing the Right Speed for Your Needs
The right speed depends on the situation. For a quick stop on a road trip, a Level 3 DC fast charger is necessary. For a day at the office or a few hours at the mall, a Level 2 charger is more than sufficient and often more cost-effective. Filtering by speed ensures the charging stop aligns with the driver’s schedule.
Checking Live Availability and Status
Finding a compatible charger is only half the battle. The final, crucial step is to verify its current status. Arriving at a station only to find it occupied or out of service is a common frustration for EV drivers.
Why Live Data is a Game-Changer
Live data transforms an EV charge point map into a dynamic, reliable tool. Real-time availability information tells a driver not just where a charger is, but whether it is currently in use, available, or out of order. This is critical because public charger reliability can be inconsistent.
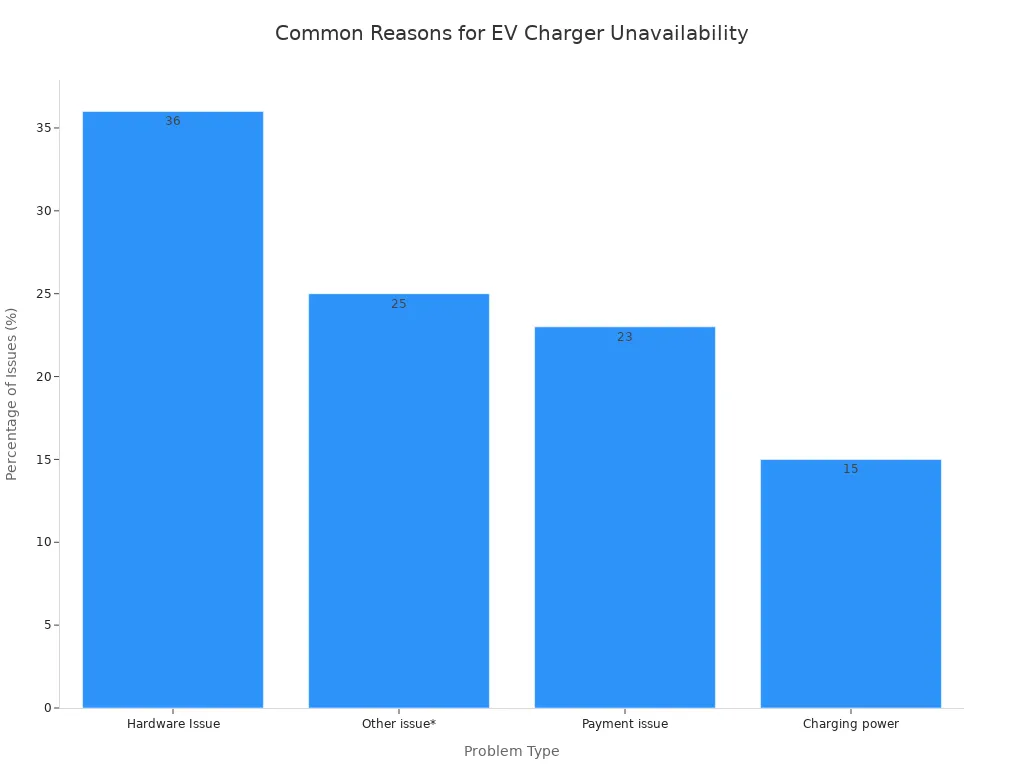
Studies show that a significant percentage of public chargers are non-operational at any given time. Issues range from broken screens and payment system failures to software glitches. Checking the live status before driving to a station saves time and eliminates range anxiety.
How to Check Charger Status in Apps
Most dedicated EV charging apps provide real-time status updates. This information comes directly from the charging network operators.
Apps like PlugShare and Electroverse connect with network partners to refresh data every minute. This provides a highly accurate live EV charging map, showing if a station’s status is ‘Available’, ‘Busy’, or ‘Out of Service’. This direct data feed is the most reliable source for charger availability.
Within an app, stations are typically color-coded on the map (e.g., green for available, blue for in use, gray for out of service), allowing for a quick visual assessment of charging options in an area.
Using User Check-ins and Comments
Community feedback provides an extra layer of verification. While direct network data reports on a charger’s electronic status, user check-ins offer on-the-ground context. A driver might report:
- A station marked “Available” is blocked by a non-EV.
- A specific charging stall is functioning while others are not.
- A payment terminal is malfunctioning despite the charger being online.
Reading the most recent user comments in apps like PlugShare can provide invaluable details that automated systems miss, offering a complete picture of a station’s true availability and condition.
Understanding Costs and Payments
The cost of public charging can vary significantly between networks and locations. An EV driver must understand the different pricing models and payment methods to manage expenses effectively. Fortunately, modern apps and payment systems make this process straightforward.
Finding Pricing in Your App
The most reliable way to determine the cost of a charging session is to check a dedicated EV app before arriving. Apps like PlugShare, Electroverse, or Zap-Map display pricing information directly on the station’s profile page. Drivers can see the cost per kilowatt-hour (kWh), per minute, or any applicable session fees. This transparency allows for informed decisions, helping a driver choose the most cost-effective option in their vicinity.
Common Payment Methods
Charging networks use several pricing models. A driver’s final bill depends on which model the station operator employs. Understanding these is key to avoiding surprises.
- Energy-based (per kWh): This is the most transparent model. Drivers pay for the exact amount of electricity their vehicle consumes. It is fair because the cost directly relates to the energy received, regardless of how fast the EV can charge.
- Time-based (per minute): Drivers pay for the duration of the charging session. This model can penalize owners of vehicles that charge more slowly, as they pay more for the same amount of energy.
- Fixed-rate: Some networks offer a flat fee for a charging session or a monthly subscription for unlimited use. This can be attractive but may not be economical for infrequent users.
- Hybrid Pricing: This model combines energy and time-based billing. For example, a network might charge per kWh plus a small per-minute fee to encourage drivers to move their vehicles after charging is complete.
- Advanced Models: Some operators use dynamic pricing. Costs may be higher during peak hours to manage grid load or lower during off-peak times. Premium rates often apply for the fastest DC chargers.
Network Subscriptions vs. Pay-As-You-Go
For drivers who frequently need to find public chargers, a network subscription can offer substantial savings. Most networks provide a standard pay-as-you-go (PAYG) rate, but also offer a monthly membership plan that unlocks lower charging costs. The hardware from technologically advanced providers like TPSON is designed to seamlessly support these different payment integrations across networks.
The decision depends on an EV driver’s charging habits. For those who charge at home most of the time, PAYG is sufficient. However, for drivers who rely on public infrastructure, the benefits of a subscription are clear.
A subscription plan can dramatically reduce costs. For example, IONITY’s Passport subscription lowers the per-kWh price from 74p to 43p. For a frequent user, these savings quickly offset the monthly fee.
Generally, a subscription pays for itself after just two or three rapid charging sessions per month. The table below illustrates the potential savings on major UK networks.
| Network | Standard Rate (PAYG) | Subscription Rate | Monthly Fee |
|---|---|---|---|
| BP Pulse | 55p-69p per kWh | 27p-45p per kWh | £7.85 |
| IONITY | 69p per kWh | 35p per kWh | £17.99 |
| Shell Recharge | 79p per kWh | 55p per kWh | £7.99 |
By evaluating their monthly usage, a driver can easily determine if a subscription plan is a financially sound choice for their public charging needs.
Finding Electric Car Charging Points in Different Scenarios
An EV driver’s charging needs vary greatly depending on the context. A daily commute requires a different strategy than a cross-country road trip. Understanding how to find electric car charging points in various scenarios is key to a smooth ownership experience. Whether searching for “ev chargers near me” for a quick top-up or planning stops for a long journey, the right approach makes all the difference.
For Your Daily Commute
Daily driving routines rely on convenient and predictable charging. Most EV owners handle this at home, but public options play a vital role.
Locating Chargers Near Home
For drivers without home charging, finding reliable local stations is essential. An ev charge point map app like PlugShare helps identify nearby Level 2 chargers at public car parks or on-street locations. Some drivers establish a routine, charging their EV once or twice a week, similar to visiting a petrol station.
Workplace Charging Solutions
Charging an EV at the workplace is an increasingly popular and convenient option. It allows drivers to arrive with a full battery each evening. While not universally available, the infrastructure is growing.
- ChargePoint data shows active workplace charging ports increased by 22% in 2023.
- The number of unique drivers using these chargers grew by 57% in the same period.
- Charging sessions saw a 64% increase, indicating much higher use of existing stations.
This trend shows that while only about half of employees report having access to workplace charging, those who do are using it more than ever.
Charging While Running Errands
Many retail locations now offer EV charging, turning shopping time into charging time. Supermarkets and shopping centres are common places to find these facilities.
- Fast chargers (7-22kW) are the most common type found at supermarkets and public car parks.
- Rapid chargers (50kW+) are also appearing at major retail destinations for quicker top-ups.
These are often Level 2 chargers, perfect for adding significant range during a one or two-hour shopping trip. Some retailers even offer this service for free to attract customers.
For Long-Distance Road Trips
Road trips require more planning than daily commutes. An EV driver must map out charging stops to avoid range anxiety and delays.
Planning Your Route with Charging Stops
Apps like A Better Routeplanner (ABRP) are indispensable for long journeys. A driver enters their vehicle model, starting charge, and destination. The app then calculates an optimal route, including necessary charging stops, estimated charging times, and battery levels at each point. This proactive planning is crucial for a stress-free trip.
Navigating “Charging Deserts”
Some areas have fewer charging options, often called “charging deserts.” Navigating them requires careful strategy.
- Use apps like PlugShare to identify all available chargers, including slower Level 2 options.
- Always start the day with at least an 80% charge.
- Check user comments to confirm a charger is operational before driving to it.
- Have multiple charging network apps downloaded and funded to avoid payment issues.
Hotel and Destination Charging
Many hotels now attract EV drivers by offering destination chargers, often for free. These are typically Level 2 chargers, allowing for a full charge overnight. Filtering for hotels with EV charging on booking sites or in apps like PlugShare is a smart way to ensure a driver starts each day of their trip with a full battery.
In Urban vs. Rural Areas
Charger availability differs dramatically between city and country environments.
High Charger Density in Cities
Major metropolitan areas boast a high density of EV chargers. Competition and government initiatives mean drivers can often find multiple charging options within a short distance. This abundance makes owning an EV in a city straightforward, with plenty of opportunities for charging.
Finding Chargers in the Countryside
In contrast, rural areas have significantly less infrastructure. While the network is expanding, finding a charger can be more challenging.
- Only 45% of rural counties have at least one fast charging port, compared to 76.5% of metropolitan counties.
- This disparity means drivers in rural areas must plan their journeys more carefully, often relying on slower chargers or traveling further to find a fast charger.
Using a comprehensive ev charge point map and planning ahead are essential for navigating areas with lower charger density.
How to Find Free EV Charging Points
Locating free EV charging points can significantly reduce an EV driver’s running costs. While not as common as paid stations, a surprising number of free public charging opportunities exist. Drivers who know where to look and how to use their apps can easily find free EV charging points. This makes the EV ownership experience even more economical.
Using App Filters to Find Free Chargers
The most efficient way to find free EV charging points is by using the filter functions within dedicated EV apps. These tools turn a hopeful search into a targeted and successful one.
Filtering for “Free” in PlugShare
PlugShare and similar apps offer powerful filtering tools. A driver can simply select a “free” or “no cost” filter to instantly update the map. This action removes all paid stations from view, showing only the free chargers in the vicinity. It is the quickest method to find free chargers by area.
Identifying No-Cost Options
Once filtered, the app displays all available free charging options. Drivers can then tap on individual station icons to get more details. This helps them confirm the charger is indeed free and check recent user comments for any issues. This simple process makes it easy to find free chargers.
Common Locations for Free Charging
Many businesses and public entities offer free charging as an amenity to attract visitors. These free chargers are often Level 2, providing a useful top-up while the driver is otherwise occupied.
Retail and Grocery Stores
Several large retail chains provide free charging for their customers. This is a popular perk that encourages shoppers to visit.
- Sainsbury’s: Offers free charging stations at many locations.
- Lidl: Provides free chargers, though policies can vary.
- Ikea: Often has free chargers, including some free rapid chargers, available for customers.
Note: The availability of free charging can change. Some retailers that previously offered free chargers are transitioning to paid models, so it is always best to verify in an app before visiting.
Public Libraries and Municipal Buildings
Local governments sometimes install free chargers at public facilities like libraries, town halls, and community centers. These stations are intended as a public service to encourage EV adoption. These free chargers are a great resource for residents.
Hotels and Destination Chargers
Hotels frequently offer free charging as a perk for overnight guests. These are typically Level 2 chargers, allowing a full charging session overnight. This is a convenient way for travelers to start their day with a full battery.
Understanding the “Free” Charging Catch
The term “free” often comes with conditions. Drivers should be aware of the rules associated with free EV charging points to avoid unexpected fines or issues.
Time Limits and Customer-Only Rules
Most free chargers have rules to ensure fair access.
- Time Limits: Many locations impose a time limit (e.g., 1-2 hours) on free charging sessions. Overstaying can result in penalty fees.
- Customer-Only: Charging at retail stores is usually intended for paying customers only.
These rules prevent a single EV from blocking a charger all day.
Is It Truly Free?
While the electricity is free, there can be indirect costs. The primary rule is to be considerate. A driver should move their vehicle once it has enough charge, allowing others to use the station. The hardware at these sites, sometimes from technologically advanced providers like TPSON, is designed for high turnover. Ultimately, these free chargers are a shared community resource.
A Deep Dive into Major Charging Networks

While many companies operate public chargers, a few major networks dominate the landscape. Understanding the strengths and characteristics of each helps drivers choose the best option for their needs. These networks provide the backbone of public EV infrastructure.
Electrify America
Network Overview and Locations
Electrify America focuses on providing high-speed DC fast charging along major highways and cross-country routes. This makes it a top choice for long-distance travel. The network manages over 4,400 individual chargers, providing extensive coverage for road trips. Its stations are strategically placed in retail parking lots just off major travel corridors.
Pricing and Membership Plans
Electrify America offers two main pricing tiers.
- Electrify America Pass: This is the standard, pay-as-you-go option with no monthly fee.
- Electrify America Pass+: A subscription plan that offers lower per-kWh rates for a small monthly fee, ideal for frequent users.
Many automakers partner with Electrify America to provide new EV owners with a complimentary amount of free charging, making the first year of ownership even more affordable.
EVgo
Network Strengths and Locations
EVgo’s strength lies in its extensive urban and suburban coverage. With over 2,850 fast chargers, the network partners with grocery stores, retail centers, and other convenient locations. This focus makes it an excellent option for drivers who need to charge while running errands around town. While not typically free, the convenience is a major draw.
Using EVgo Autocharge+
EVgo simplifies the charging experience with its Autocharge+ feature. After a one-time setup in the EVgo app, drivers can simply plug in their vehicle at a compatible station to start a session automatically. The system recognizes the vehicle and handles billing without needing an app or card, making the process seamless.
ChargePoint
How the ChargePoint Network Operates
ChargePoint operates differently from other networks. It functions more like an open platform, providing the hardware and software for businesses and individuals to own and operate their own stations. This model has created a massive network with over 200,000 active ports. The overall ev charging station coverage is vast, though the experience can vary. Technologically advanced providers like TPSON supply hardware that integrates smoothly into this type of open network.
Finding and Using Their Stations
Drivers use the ChargePoint app to locate and pay for charging. A key difference is that individual station owners set their own prices. This means a driver might find a charger that is completely free right next to one that is not.
- The app’s filters are essential for finding a station that meets a driver’s needs.
- Many workplace and retail chargers on the ChargePoint network are set to be free for employees or customers.
- A driver can easily filter for these free options within the app.
- Finding a free charger is a significant benefit of this network’s model.
- These free chargers serve as a great amenity for businesses.
- It is often easy to find a free top-up while shopping.
- The network includes thousands of these free ports.
The Tesla Supercharger Network
The Tesla Supercharger network has long been considered the gold standard for public fast charging. Its reputation is built on reliability, speed, and expansive coverage. Historically an exclusive perk for Tesla owners, the network is now gradually opening to other electric vehicles, significantly enhancing the public charging landscape.
Access for Tesla Drivers
For Tesla drivers, using the Supercharger network is a seamless and hassle-free experience. The vehicle’s navigation system integrates directly with the network, automatically planning routes with necessary charging stops.
- Upon arrival, a driver simply plugs in the connector.
- The station authenticates the vehicle and begins the session automatically.
- Billing is handled through the owner’s Tesla account.
New Tesla owners sometimes receive a number of free Supercharging credits. This promotional offer provides a period of free travel, making the initial ownership experience even more attractive. These free credits are a significant benefit. While not a permanent free pass, this initial free period is highly valued. The convenience is a key part of the brand’s appeal, offering a worry-free and free-from-complexity process.
Using Magic Dock for Non-Tesla EVs
Tesla is expanding access to its network for drivers of other EV brands. This is made possible through a technology called the “Magic Dock.” This integrated adapter allows vehicles with a CCS port to connect to a Tesla Supercharger. This expansion greatly improves the overall charging coverage available to all drivers.
Drivers of compatible non-Tesla vehicles can use the Tesla mobile app to find and activate these stations. The process is straightforward:
- Locate a Magic Dock-equipped Supercharger in the Tesla app.
- Select the specific stall and unlock the adapter through the app.
- Plug the Magic Dock connector into the vehicle to begin a session.
This access is not free for non-Tesla drivers; they pay per session through the app. The initiative significantly boosts fast charging availability and improves route coverage across many regions. However, not all Supercharger locations are equipped with Magic Dock technology. Drivers should always consult the Tesla app to verify site compatibility and availability. This growing coverage makes road trips easier for everyone. The goal is a future of free and open access, though for now, payment is required. This is not a free service. The network’s excellent coverage is a major advantage.
A driver’s most powerful tools are a quality ev charge point map and the car’s navigation. Finding electric car charging points becomes simple with a few key practices.
- Utilize a live ev charging map to check real-time charger status, saving time.
- Always filter searches by connector type and speed for compatible results.
- Explore the ev charge point map for free ev charging points. Many free locations offer a free top-up, making this a great free benefit. Finding free ev charging points is a smart strategy.
FAQ
What should a driver do if a charger is broken?
A driver should use their app to report the station as out of service. This action alerts the network operator and other users. They can then use the app’s map to navigate to the next nearest available station.
How do drivers pay for public charging?
Payment methods vary by network. Common options include:
- A dedicated network app
- Contactless card payment
- An RFID card
Some networks offer subscriptions for lower rates, while others are pay-as-you-go.
What is the difference between AC and DC charging?
AC chargers (Level 2) are slower and best for topping up over several hours at a workplace or shopping center. DC fast chargers (Level 3) are much quicker, making them ideal for long-distance travel when time is limited.
Can any EV use any public charger?
No. Vehicles have specific connector types, such as CCS or CHAdeMO. Drivers must use an app to filter for a compatible connector. This ensures they arrive at a station their car can use.
How can a driver find free charging stations?
Drivers can use the filter function in an app to display only free stations. Retailers, hotels, and public libraries often provide this service as an amenity to attract visitors and customers.
What is a “destination charger”?
A destination charger is typically a Level 2 unit found at locations like hotels or shopping centers. It allows a driver to fully charge their vehicle over several hours while they are parked for an extended period.
Why do some networks require a subscription?
Subscriptions are optional but offer lower per-kWh rates. This model is cost-effective for drivers who rely heavily on public infrastructure. The hardware from technologically advanced providers like TPSON supports these varied payment systems.





