
The EV charging industry is undergoing a significant transformation. Key technological advancements are reshaping the future of EV charging. While a recent survey indicates 30.6% of EV drivers still worry about public charging infrastructure, this concern has notably decreased. The future of EV infrastructure points toward a smart, user-centric ecosystem. EV charger manufacturers, including technologically advanced providers like TPSON, are developing the intelligent EV Charger needed for this shift. This evolution in public charging is crucial for accelerating mass EV adoption and making the charging experience effortless for every EV driver.
The Future of EV Charging: AI and Predictive Analytics

Artificial intelligence (AI) is the engine driving the future of EV charging. It transforms charging from a simple power transaction into a smart, responsive service. This advanced charging technology is making the entire EV ecosystem more reliable, efficient, and user-friendly. Providers like TPSON are developing intelligent charging solutions that integrate these AI capabilities.
Predictive Maintenance to Minimize Downtime
A broken charger is a major frustration for any EV driver. AI-powered predictive maintenance directly addresses this issue, ensuring EV charging points are operational when needed.
How AI Forecasts Hardware Failures
AI algorithms continuously analyze operational data from EV charging points. They monitor variables like voltage fluctuations, internal temperatures, and component usage patterns. The system identifies subtle anomalies that signal a potential hardware failure before it happens.
Real-Time Monitoring and Alerts
When the AI detects a high probability of failure, it automatically generates an alert. This notification is sent directly to maintenance teams with diagnostic details. Technicians arrive with the right parts to fix a problem before a charger ever goes offline.
The Impact on Charger Reliability
This proactive approach significantly boosts the reliability of public charging infrastructure. The key benefits include:
- Reduced charger downtime and improved availability.
- Lower long-term maintenance costs for network operators.
- Increased driver confidence in the public charging network.
Dynamic Load Balancing for Grid Stability
As more EVs hit the road, their collective impact on the power grid becomes a serious concern. AI-driven dynamic load balancing is a critical tool for managing this new demand.
Optimizing Power in Real-Time
At busy charging stations, an AI management system intelligently distributes available power among all connected vehicles. It ensures the site’s total power draw never exceeds its capacity, preventing tripped circuits and local outages.
Preventing Grid Strain During Peak Hours
Unmanaged EV charging could increase peak demand by 40% during evening hours, straining local grids. AI prevents this by automatically reducing charging speeds during peak grid times and increasing them during off-peak hours. This smooths out demand and maintains grid stability.
Prioritizing Urgent Charging Needs
The system can also prioritize charging for specific vehicles. For example, an EV arriving with a very low battery can be allocated more power to ensure the driver can reach their destination, while an EV with a nearly full battery receives a slower charge.
Personalized User Experiences Driven by AI
AI is also making the EV charging experience deeply personal and convenient. It learns driver habits to offer tailored recommendations and automated services.
AI-Powered Route and Charge Planning
Companies like evtonomy are developing AI platforms that deliver personalized route recommendations. The system considers charging cost, speed, and even predicted wait times at charging stations to plan the most efficient journey for the driver.
Smart Station Availability Predictions
AI moves beyond showing if a charger is currently available. It analyzes historical data and real-time traffic to predict the likelihood that a charging spot will be free when a driver arrives, reducing wasted trips.
Automated Schedules and Cost Optimization
AI helps EV drivers save money by automatically scheduling charging sessions. The system can identify the cheapest electricity rates based on time-of-use pricing and initiate charging during those low-cost windows.
Machine Learning’s Role in EV Charging Efficiency
Machine learning (ML) is a cornerstone of the future of ev charging, moving beyond simple power delivery to create a highly efficient and intelligent ecosystem. These advanced algorithms analyze vast datasets to optimize every aspect of the ev charging process. Technologically advanced providers like TPSON are integrating ML to make ev charging smarter, faster, and more cost-effective for every EV driver. This data-driven approach ensures that the charging infrastructure operates at peak performance.
Learning User Behavior Patterns
Machine learning excels at identifying patterns in how people use charging infrastructure. Clustering algorithms analyze historical data to segment users based on their unique charging habits, such as arrival times, duration of charging sessions, and energy needs. This allows charging networks to predict demand with high accuracy. By anticipating user needs, these systems can create optimized charging schedules that lead to significant cost reductions, often between 20-30%, for network operators and consumers alike. This intelligent scheduling ensures an EV is ready when needed without unnecessary expense.
Adapting to Battery Health
An EV battery is a complex and valuable component. Machine learning plays a crucial role in preserving its lifespan. Reinforcement learning models continuously analyze the battery’s state of health, temperature, and current charge level. The system then recommends optimal charging speeds and patterns to minimize stress on the battery cells.
This adaptive approach to charging is highly effective. It can reduce battery degradation by up to 15% compared to conventional charging methods. This directly translates to a longer and more reliable battery life for the EV.
Improving Energy Transfer Rates
Maximizing the efficiency of power transfer is another key area for ML. Neural networks process complex variables in real-time, including grid stability, ambient temperature, and the specific EV model connected. This allows the charging system to fine-tune the energy flow, minimizing power loss during the charging session. The benefits of this optimization are substantial:
- Energy transfer efficiency can improve by as much as 25%.
- Real-time AI systems can adjust charging parameters within milliseconds to protect the grid.
- The overall ev charging experience becomes quicker and more reliable for the user.
Seamless Integration: The Charger, Car, and Grid
The future of EV charging lies in a deeply connected ecosystem where the vehicle, the charger, and the power grid communicate seamlessly. This grid integration creates a more resilient, efficient, and sustainable energy landscape. It transforms the EV from a simple mode of transport into an active participant in the energy network.
Vehicle-to-Grid (V2G) Goes Mainstream
Vehicle-to-Grid (V2G) technology is moving from pilot programs to practical application. It enables a two-way flow of energy between an EV and the grid, unlocking significant benefits for both EV owners and utility providers.
How Bidirectional Charging Works
Bidirectional charging allows an EV to not only draw power from the grid but also to send stored energy back. This process requires a special V2G-enabled charger and a compatible vehicle. The EV’s battery effectively becomes a mobile energy storage unit, ready to support the grid when needed.
Stabilizing the Power Grid with V2G
V2G technology offers a powerful solution for grid stability. During times of high energy demand, a network of connected EVs can discharge power back to the grid, acting as a virtual power plant. This helps prevent blackouts and reduces the need for expensive, fossil-fuel-powered peaker plants. Several key pilot programs have demonstrated this potential:
- Electric Nation (UK): This residential trial showed that V2G charging could reduce grid strain and save costs for participants.
- NI Intelligent Electric Vehicle (NIEV) (Northern Ireland): The project proved that public parking lots with V2G-equipped EVs can serve as temporary batteries to manage grid congestion.
- Parker Project (Denmark): This initiative tested V2G with commercial fleets, highlighting major advantages in energy management.
Monetizing Your EV’s Battery
V2G participation creates a new revenue stream for EV owners. By selling excess energy back to the grid during peak hours, drivers can offset their charging costs.
A UK-based trial found that an average EV owner could save up to £840 annually through V2G participation compared to unmanaged charging. This represents a significant financial incentive for adopting the technology.
Overcoming V2G Adoption Hurdles
Widespread V2G adoption faces challenges, including the need for standardized communication protocols, regulatory frameworks, and broader vehicle compatibility. However, ongoing innovation and collaboration between automakers, charging solution providers, and utility companies are steadily breaking down these barriers.
The Rise of Integrated Charging Hubs
Modern charging stations are evolving into comprehensive, sustainable energy hubs. These advanced charging hubs integrate on-site renewable energy generation and storage to create a self-sufficient and user-friendly experience.
Integrating Solar Canopies for On-Site Power
Solar canopies are becoming a common feature at public charging hubs. They generate clean, renewable electricity directly on-site, reducing the facility’s reliance on the grid. 3ti’s Papilio3 hubs, for example, are modular solar EV charging hubs that can generate around 18 MWh of renewable energy per year, powering up to 12 EV charging points.
Using Battery Storage for Off-Peak Energy
Integrated charging hubs often include large-scale battery storage systems. These batteries store excess renewable energy generated during the day or cheap electricity drawn from the grid during off-peak hours. The stored energy is then used to power EV charging during peak times, lowering operational costs and ensuring a consistent power supply.
Combining Charging with Retail and Amenities
The most successful charging hubs enhance the customer experience by offering more than just power. The InstaVolt Superhub in Winchester combines solar and wind-powered charging with a Starbucks café and a children’s play area. This model transforms charging time into a productive and pleasant break, making the EV lifestyle more convenient.
Open-Source Solutions and Interoperability
Open-source standards are fundamental to creating a flexible, competitive, and future-proof EV charging network. They prevent vendor lock-in and foster rapid innovation.
The Open Charge Point Protocol (OCPP)
The Open Charge Point Protocol (OCPP) is a universal standard that allows charging stations from any manufacturer to communicate with any central management system. This interoperability is crucial for network operators.
Future-Proofing with Open Standards
Adopting open standards ensures that today’s charging infrastructure will remain compatible with tomorrow’s technology. It creates a stable foundation upon which new features and services can be built, protecting investments and promoting a sustainable growth model for the entire industry.
Fostering Innovation Through Collaboration
Open protocols encourage collaboration and innovation. When hardware and software are interoperable, developers can focus on creating new value-added services, such as advanced energy management, dynamic pricing, and seamless payment systems. This collaborative environment accelerates the evolution of EV charging technology.
Smart Grid Communication Protocols
Effective communication between the vehicle, charger, and grid is essential for an intelligent energy network. Smart grid protocols create the digital language that enables this sophisticated dialogue, making the entire system more responsive and efficient. Technologically advanced providers like TPSON build their solutions around these standards to deliver next-generation features.
ISO 15118: The Digital Handshake
ISO 15118 is a leading international standard that governs communication between an electric vehicle (EV) and the charging station. It acts as a secure “digital handshake,” allowing the two to exchange complex information automatically. This protocol is the foundation for many advanced ev charging functionalities. It moves beyond simple power delivery to enable a rich, data-driven interaction. The standard ensures that any compatible EV can communicate seamlessly with any compliant charging point.
Enabling Advanced Charging Features
The implementation of ISO 15118 unlocks a host of user-centric features that redefine the public charging experience. This protocol is the key enabler for a smarter and more convenient EV ecosystem. Its capabilities include:
- Plug & Charge Functionality: This feature automates the entire authentication and payment process. A driver simply plugs in their EV, and the charger automatically identifies the vehicle and handles billing without needing an app or card.
- Vehicle-to-Grid (V2G) Support: The protocol facilitates bidirectional charging, allowing an EV to send power back to the grid. This helps stabilize energy supply and creates opportunities for vehicle owners to earn revenue.
- Dynamic Pricing: The standard allows for real-time price adjustments based on grid demand. This enables the system to offer lower charging costs during off-peak hours.
- Optimized Charging: The protocol lets the vehicle share its specific charging profile and battery status. The station then adjusts the power delivery for maximum efficiency and battery health.
Ensuring Secure Data Exchange
Security is a paramount concern in a connected ev charging network. ISO 15118 addresses this by establishing a highly secure communication channel for every charging session. It protects sensitive information from potential cyber threats.
The protocol uses Transport Layer Security (TLS) encryption, the same technology that protects online banking and e-commerce. This ensures that all data exchanged between the EV and the charger, including payment credentials and user identity, remains private and secure.
This robust security framework builds driver trust. It provides peace of mind that personal and financial data is safe during every transaction, which is critical for the widespread adoption of advanced charging technologies.
Frictionless Experience: Key Electric Vehicle Trends for 2025

The next wave of electric vehicle trends focuses on removing friction from the user experience. In 2025, the process of public charging will become dramatically simpler and more intuitive. Key emerging trends in automation, standardization, and hardware innovation are making the EV lifestyle more convenient than ever. These advancements are central to the future of ev charging.
The Plug & Charge Revolution
The cumbersome process of using apps and payment cards at charging stations is becoming a thing of the past. The Plug & Charge revolution, built on the ISO 15118 protocol, is creating a truly seamless ev charging experience.
Automating Authentication and Payment
Plug & Charge automates the entire transaction. An EV driver simply connects their vehicle to a compatible charger. The system handles authentication and billing automatically without any user input. This technology transforms the car into a digital wallet.
- It eliminates the need for RFID cards, mobile apps, or credit card readers.
- The EV securely stores payment details linked to a personal or corporate account.
- The power socket establishes a unique, secure connection with the car for authentication.
Simplifying the User Journey
This innovation drastically simplifies the public charging journey. Experts like Abigail Burrell-Rann and Matt Penny from Octopus Electroverse believe Plug & Charge will become the primary method for ev charging. While apps will remain as secondary options, the sheer ease of use makes this one of the most important electric vehicle trends.
The Technology Behind Seamless Connections
The technology works by creating a secure digital certificate inside the EV. When plugged in, the vehicle and the charger exchange this certificate to verify the user’s identity and billing information. This “digital handshake” initiates the charging session instantly.
Current Adoption and Future Rollout
Major charging networks and automakers are rapidly adopting this standard. As more compatible vehicles and ev charging points come online, Plug & Charge is set to become the default experience, making range anxiety a distant memory.
Standardization Takes Hold: The NACS Effect
Widespread adoption of the North American Charging Standard (NACS) is a pivotal moment for the industry. This move toward a single plug design promises to resolve long-standing interoperability issues.
The Impact of NACS Adoption
The shift to NACS simplifies the manufacturing process for automakers and reduces confusion for drivers. It creates a more unified ecosystem where an EV can access a wider range of charging stations without needing cumbersome adapters.
Enhancing Interoperability and Accessibility
Major networks like Blink, ChargePoint, and Electrify America plan to include both CCS and NACS plugs in new installations. This ensures broad compatibility during the transition period. Tesla is also building new Superchargers that are accessible to other vehicle brands from the start, rather than retrofitting older stations.
The Future of CCS and Other Standards
While NACS is gaining dominance, the Combined Charging System (CCS) will remain relevant for years. The transition will be gradual, with dual-plug chargers becoming the norm. This ensures that no EV driver is left behind during this important industry shift.
Innovations in Physical Charger Design
Hardware innovation is keeping pace with software advancements. The physical design of charging solutions is evolving to be smarter, more accessible, and more durable. Technologically advanced providers like TPSON are at the forefront of developing these next-generation charging systems.
Automated and Robotic Charging Arms
For ultimate convenience, companies are developing robotic charging arms that handle the entire plugging-in process. This technology is especially beneficial for autonomous vehicles and drivers with mobility challenges.
| Company | Development |
|---|---|
| Bosch & Cariad | Testing an automated valet charging system for driverless EV charging. |
| Volterio | Developing a robotic arm solution for automatic charging in home or fleet settings. |
The Status of Wireless Inductive Charging
Wireless charging is moving from concept to reality. While high costs and a lack of mature standards have slowed commercial adoption, progress is accelerating. Companies like InductEV and HEVO are advancing the technology, and international projects in Sweden and Italy are testing inductive charging roads. This technology promises effortless charging by simply parking over a pad.
More Compact and Weather-Resistant Hardware
Finally, the hardware of ev charging points is becoming more robust. New designs are more compact to fit into tight urban spaces. They also feature enhanced weather resistance to ensure reliability in harsh climates, boosting the overall uptime of the public charging network.
Rethinking the Payment and App Ecosystem
The digital ecosystem surrounding public charging is undergoing a much-needed overhaul. A fragmented landscape of proprietary apps and payment methods has long been a source of frustration for EV drivers. The industry is now actively working to streamline this experience. This shift is one of the most practical electric vehicle trends, focusing on universal access and user convenience. The goal is to make the payment process as simple as any other daily transaction.
The Move Towards Tap-to-Pay Credit Card Readers
The integration of tap-to-pay credit card readers on charging stations marks a significant step toward simplicity. This feature eliminates the need for drivers to download a specific app or subscribe to a network just for a single charging session. It provides a universally understood payment method.
- Universal Access: Anyone with a credit or debit card can initiate a charge.
- Reduced Friction: It removes the hassle of app installation and account creation.
- Increased Confidence: A familiar payment process makes public EV charging less intimidating for new users.
This simple hardware addition directly addresses a major barrier to EV adoption, making the entire process more inclusive.
Consolidating Multiple Charging Apps
Drivers today often juggle multiple apps on their smartphones, one for each charging network they might encounter. This “app fatigue” complicates route planning and creates a cluttered user experience. The industry is responding with a strong push toward consolidation. Some companies are developing “super-apps” that aggregate various networks into a single interface. This allows an EV driver to find, use, and pay for charging across different brands without switching applications.
Roaming Agreements Between Networks
Roaming agreements are the technical backbone that makes app consolidation possible. Similar to how mobile phone users can make calls on different carrier networks when traveling, EV roaming allows members of one charging network to use another network’s stations seamlessly. Technologically advanced providers like TPSON develop hardware that supports these interoperable standards, facilitating a connected ecosystem.
These partnerships are crucial for creating a truly unified EV charging network. They break down the digital walls between providers, ensuring that a driver can access reliable charging wherever they go, using a single account.
This collaborative approach is essential for building a frictionless and dependable public charging infrastructure for every EV.
Market Dynamics and Charging Infrastructure Reliability
The commercial landscape of EV charging is evolving rapidly, driven by market consolidation, a strong push for reliability, and innovative business models. These dynamics are shaping the future of the charging infrastructure and are critical for supporting mass EV adoption. The goal is to build a robust and profitable ecosystem that provides reliable EV charging for every driver.
Market Consolidation and Its Impact
The EV charging industry is experiencing a significant wave of mergers and acquisitions. Larger energy and infrastructure firms are acquiring promising charging networks and technology providers to secure a foothold in this growing market.
How Mergers and Acquisitions Affect Users
This consolidation can lead to more integrated and expansive networks for EV drivers. When a large utility like EDF acquires a provider such as Pod Point, it can inject capital and resources to accelerate the deployment of new EV charging points. This often results in improved service and wider accessibility for users.
The Battle for Market Share
Companies are aggressively pursuing market share through strategic acquisitions. This trend is visible across Europe.
- EQT Infrastructure acquired the UK’s InstaVolt network.
- Mer bought Elmtronics to expand its UK presence.
- DIF Capital Partners purchased Plugit, a Finnish infrastructure company.
These moves highlight a competitive race to build regional and national dominance in the EV charging space.
The Future of Smaller Charging Networks
While consolidation continues, smaller, independent networks face a challenging future. They may struggle to compete with the scale and resources of larger players. Many will likely be acquired or form consortiums, like Germany’s Ladenetz.de, to survive and maintain a competitive edge.
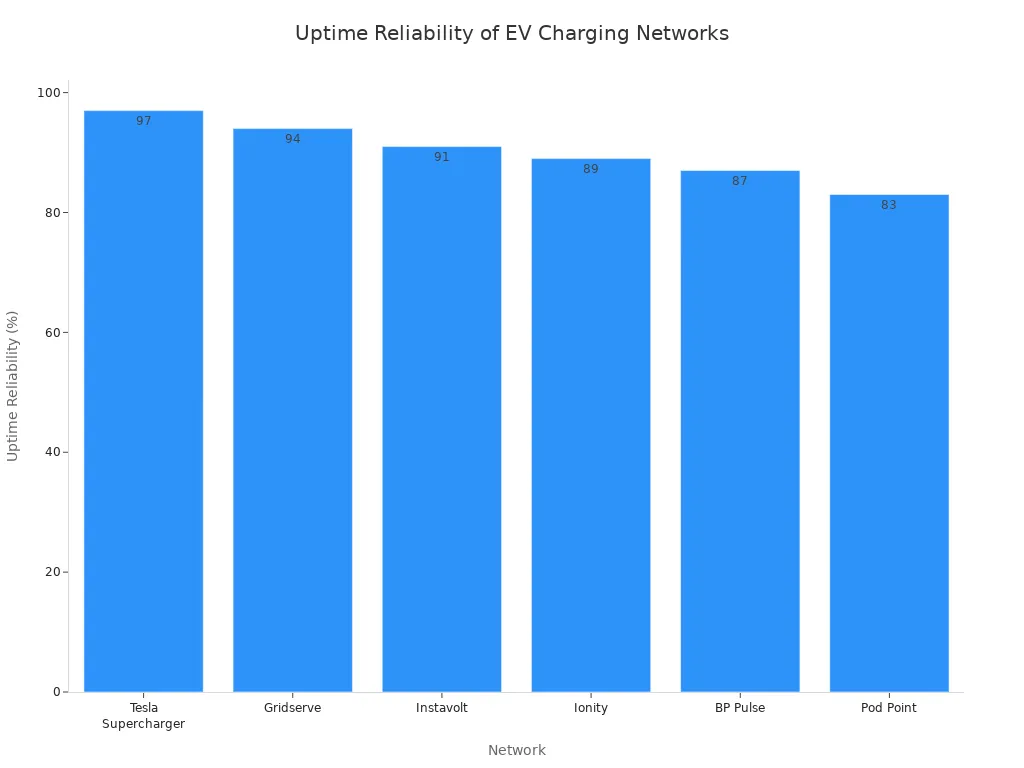
The Push for 99% Uptime
A functional charger is the cornerstone of driver confidence. As a result, the industry is intensely focused on achieving near-perfect operational uptime.
NEVI Program Reliability Mandates
Government incentives and programs are increasingly tying funding to strict reliability standards. Mandates often require networks to achieve and maintain at least 97% uptime for their charging equipment. This pressure ensures that public funds contribute to a dependable and sustainable charging infrastructure.
How Networks Are Fixing Broken Chargers
Networks are moving from reactive repairs to proactive maintenance powered by AI and real-time monitoring. Technologically advanced charging solutions from providers like TPSON incorporate self-diagnostics to alert technicians before a failure occurs. This approach is key to boosting the reliability of charging hubs.
The Role of Third-Party Audits
Independent audits provide transparent data on network performance. While many operators report high uptime, third-party data reveals a more varied picture. Achieving true 99% uptime remains a significant challenge for the industry.
Evolving Business Models in EV Charging
Sustainable business models are essential for the long-term growth of public EV charging. Companies are exploring diverse revenue streams beyond simple energy sales.
Subscription vs. Pay-As-You-Go
Providers offer flexible payment options to cater to different user needs. Pay-as-you-go models appeal to occasional users, while subscription plans provide lower rates for frequent drivers. This flexibility is crucial for making EV charging accessible to a broader audience.
Dynamic and Time-of-Use Pricing
Smart charging with dynamic pricing is becoming a powerful tool. It offers financial incentives for drivers to charge their EV during off-peak hours.
UK-based trials have shown that even small financial incentives can shift up to 95% of charging sessions away from peak grid times. This behavior helps balance energy demand and supports a more sustainable grid powered by renewable sources.
Advertising and Data Monetization
Modern charging hubs are becoming multi-purpose destinations. Operators are leveraging large digital screens on charging stations for advertising. They also explore data monetization strategies, using anonymized usage data to provide insights for urban planning and retail partners, creating new, sustainable revenue streams.
The future of ev charging is defined by its intelligence, integration, and convenience. The convergence of AI, Vehicle-to-Grid (V2G) technology, and universal standards transforms public charging from a simple utility into a dynamic, user-centric service. This evolution in ev charging makes the EV lifestyle more practical, paving the way for mass ev adoption. Key developments in ev charging include:
- NACS: Standardizes connectors, simplifying the public charging experience for every EV.
- V2G: Allows an EV to support the grid, boosting ev adoption and offering financial benefits.
This advanced charging infrastructure is ready to support significant market growth.
| Metric | Value |
|---|---|
| Market Revenue in 2024 | USD 396.4 billion |
| Estimated Value by 2030 | USD 620.3 billion |
FAQ
What is Vehicle-to-Grid (V2G) technology?
Vehicle-to-Grid (V2G) technology enables bidirectional energy flow. An electric vehicle can send stored battery power back to the grid. This capability helps stabilize energy supply during peak demand and creates potential revenue for the EV owner.
How does AI improve charger reliability?
Artificial intelligence improves reliability through predictive maintenance. AI algorithms analyze operational data to forecast hardware failures before they happen. This proactive approach allows for timely repairs, significantly reducing charger downtime and enhancing the user experience.
What is the Plug & Charge feature?
Plug & Charge automates the entire charging process. A driver simply connects their EV to a compatible charger. The system automatically handles authentication and payment without needing an app or card, creating a seamless and convenient experience.
Why are open standards like OCPP important?
Open standards like the Open Charge Point Protocol (OCPP) ensure interoperability. They allow charging stations from any manufacturer to work with any management system. Technologically advanced providers like TPSON use these standards to create flexible, future-proof solutions.
What is the NACS effect on EV charging?
The NACS effect refers to the industry’s widespread adoption of the North American Charging Standard. This shift simplifies the charging experience by creating a unified plug design. It enhances interoperability and reduces the need for drivers to carry multiple adapters.
How do integrated charging hubs enhance the user experience?
Integrated charging hubs offer more than just power. They often include amenities like cafes and retail stores.
Many also integrate on-site renewable energy generation, such as solar canopies, and battery storage. This model transforms charging time into a productive and pleasant break for drivers.
What is dynamic load balancing?
Dynamic load balancing is an AI-driven feature that intelligently manages power distribution at a charging site. It optimizes energy flow to multiple vehicles in real-time. This prevents overloading the local grid and ensures efficient charging for all connected EVs.





