Most homes can support a standard Level 2 EV-Ladegerät. The EV market is growing, with EV adoption projected to hit 10% of new car sales by 2025. This makes a reliable EV charger essential for any EV owner. A successful home EV charger installation depends on key requirements. Unlike tragbare EV-Ladegeräte, a permanent charger needs planning. Hersteller von EV-Ladegeräten like TPSON, a provider of technologically advanced EV-Ladelösungen, offer various options. Homeowners can use this quick checklist for their property.
- Sufficient Electrical Capacity: A modern home panel (100A or more) usually has enough capacity for an EV charger.
- Dedicated Off-Street Parking: A driveway or garage is ideal for a charger.
- Property Permission: The property owner must approve the charger installation.
The Key Requirements for a Home EV Charger
Meeting a few essential installation requirements is the first step toward convenient home charging. An EV owner must evaluate their property’s electrical system, parking arrangement, and ownership status. A clear understanding of these areas will streamline the entire Installationsvorgang for an electric car charger.
1. Your Home Electrical System’s Capacity
The home’s electricity supply is the most critical factor for a successful EV charger installation. A powerful electric vehicle charger places a significant and sustained demand on a home’s electrical system. Ensuring the system can handle this new load is a matter of safety and functionality.
Understanding Amps, Volts, and Circuits
Think of your home’s electricity like water in pipes. Voltage (Volts) is the water pressure, while Amperage (Amps) is the flow rate. A Level 2 EV charger is a high-flow appliance. It requires both high pressure (240 Volts) and a high flow rate. For this reason, an EV charger needs its own dedicated circuit. This circuit acts as an exclusive pathway for electricity from the panel to the charger, preventing overload on other circuits in the home.
How to Check Your Electrical Panel’s Amperage
A homeowner can perform a basic check of their main electrical panel. The panel is typically a grey metal box located in a garage, basement, or utility closet.
- Open the panel door.
- Locate the main breaker. It is usually the largest switch at the top or bottom of the panel.
- The amperage capacity is printed on the main breaker switch (e.g., “100”, “150”, “200”).
Sicherheit geht vor! ⚠️ Never touch any wiring inside the electrical panel. Only observe the numbers on the breaker switches. If you are unsure, contact a Elektrofachkraft.
A modern home often has a 200A supply, while many older homes have a 100A or 150A supply. This number represents the total electrical capacity available for the entire property.
When Is a Panel Upgrade Necessary?
A panel upgrade becomes necessary when the existing electricity supply cannot safely support the additional load of an EV charger. A home with a 60A panel will almost certainly require an upgrade. Even a 100A panel might be insufficient if the home already uses numerous high-power appliances like electric heating, a hot tub, or an electric stove.
Most Level 2 EV chargers, which operate at 240 volts, require a dedicated circuit with a minimum of 40 amps for proper installation. A Level 2 EV charger typically necessitates a dedicated circuit of either 40-amp or 50-amp. This circuit is designed to continuously draw power, adding to the existing electrical load from other household appliances. An insufficient electricity supply creates a safety hazard.
The Importance of a Professional Load Calculation
The number on the main breaker provides a starting point, but it does not tell the whole story. A qualified electrician must perform a professional load calculation. This detailed assessment measures the home’s current peak electricity usage and determines if there is enough spare capacity for the new EV charger. This calculation is a non-negotiable step for a safe and compliant installation, ensuring the electricity supply is adequate. Technologically advanced solutions from providers like TPSON often include smart features that can help manage this load, but the fundamental electrical capacity must be present.
2. Your Parking Situation
A dedicated and consistent parking spot is a core requirement for a home EV charger. The location of this spot directly influences the complexity and cost of the installation.
Off-Street Parking: The Easiest Path
The most straightforward installation occurs when the property includes a private driveway or garage. This provides a secure, accessible location to mount the charger and park the EV for extended periods. The charger can be connected directly to the home’s electricity supply without crossing public land.
Garage vs. Driveway Installation Considerations
Choosing between a garage and a driveway for the charger location involves a few trade-offs.
| Merkmal | Garage Installation | Driveway Installation |
|---|---|---|
| Schutz | Excellent protection from weather and potential vandalism. | Charger must be outdoor-rated (e.g., NEMA 4) to withstand rain, snow, and sun. |
| Kosten | Often cheaper if the electrical panel is in the garage, requiring less wiring. | Can be more expensive if long wiring runs or trenching are needed to reach the spot. |
| Bequemlichkeit | Ideal for overnight charging, keeping the EV and charger secure. | Very convenient for quick plug-ins without needing to open the garage. |
The Challenge of On-Street Parking
On-street parking presents a significant barrier to a home EV charger installation. Running a charging cable across a public sidewalk is a safety hazard and is illegal in most municipalities. Installing a curbside charger requires extensive permits and cooperation with local utility companies and city planners, a process that is often complex and costly.
Shared Parking in Condos and Apartments
Installing an EV charger in a multi-unit dwelling with shared parking is more complex than in a single-family home. Residents face several unique challenges that require careful planning and coordination. Key hurdles include:
- Infrastructure and Costs: Installation is often considered a structural change. It can be expensive due to the need for electrical upgrades, long wiring runs to a deeded parking space, and potential load management systems to balance the electricity supply for multiple chargers.
- Logistical Complexities: Many residents lack dedicated parking spots, making a personal charger impossible. Even with an assigned spot, getting the necessary electricity supply to that location is a major project.
- Building Approvals: Navigating the approval process with property managers, building owners, and other tenants is a primary obstacle. Drivers frequently face rejections from landlords when requesting chargepoint installations.
3. Property Ownership and Permissions
Securing the proper authorization is a critical installation requirement. The path to approval depends on whether you own, rent, or live within a homeowners’ association (HOA).
For Homeowners: You Are in Control
For owners of single-family homes, the process is simplest. The homeowner has the authority to approve modifications to their property. The primary requirements are to ensure the installation meets local electrical and building codes. An electrician will handle the necessary permits as part of the installation project.
For Renters: How to Get Landlord Approval
Renters must obtain explicit, written permission from their landlord before installing an electric car charger. A landlord may be hesitant due to concerns about liability or modifications to their property. To improve the chances of approval, a renter should present a professional proposal that outlines the plan, uses a licensed and insured electrician, and highlights the benefit of adding a desirable amenity to the property.
For Condo Owners: Navigating HOA Rules
Condo owners must consult with their homeowners’ association. Residents in shared buildings must check with building management or the HOA, as they may have their own specific requirements or restrictions concerning EV charger installations.
Before proceeding with an EV charger installation, homeowners should review their HOA’s specific rules or consult directly with the association to avoid potential conflicts or violations. Common HOA rules include:
- Location Restrictions: The HOA may dictate exactly where on the property an electric car charger can be installed.
- Aesthetic Requirements: Rules might exist to ensure the charger’s appearance, including any visible wiring or conduit, aligns with the community’s standards.
4. A Suitable Location for the EV Charger
Choosing the right location for an EV charger is a decision that balances cost, convenience, and durability. The physical placement of the charger on the property directly impacts the installation budget and the daily user experience for an EV owner.
Why Proximity to Your Panel Reduces Cost
The distance between the electrical panel and the EV charger is the single biggest factor influencing installation costs. A shorter distance means less expense.
- Material Costs: An electrician must run heavy-gauge wiring inside a protective conduit from the panel to the charger location. Longer distances require more of these expensive materials.
- Arbeitskosten: The installation process becomes more complex and time-consuming with distance. An electrician may need to navigate finished walls, ceilings, or even trench underground for an outdoor location, all of which increases labor hours.
A location close to the panel simplifies the wiring run, making the installation faster and more affordable.
Choosing an Indoor vs. Outdoor Location
The choice between installing the charger indoors (like in a garage) or outdoors (on a driveway) depends on the home layout and parking habits. Each location has distinct advantages. An indoor location in a garage offers the best protection for the EV charger from weather, extreme temperatures, and potential damage. An outdoor location provides convenience, allowing an EV driver to plug in without entering the home. However, any charger installed outdoors must be specifically rated for weather resistance (e.g., NEMA 4) to withstand rain, snow, and sun exposure.
Wall-Mounting vs. Pedestal Chargers
Most home EV charger installations involve mounting the unit to a wall. In situations where a wall is not available near the parking spot, a pedestal-mounted charger is an alternative. The choice between them involves trade-offs in cost and placement flexibility.
| Merkmal | Wall-Mounted Charger | Pedestal-Style Charger |
|---|---|---|
| Installationskosten | More affordable installation | Higher installation costs due to the pedestal and foundation work. |
| Placement | Limited to existing walls in a garage or on the side of the home. | Offers versatile placement in parking lots or driveways away from the home. |
| Dauerhaftigkeit | Less risk of damage from passing cars. | Sturdy construction designed for outdoor environments, but at higher risk of impact. |
| Ideale Verwendung | Space-saving and effective for most residential garages and carports. | Ideal for locations without a nearby wall or for serving multiple parking spots. |
5. Connectivity for Smart Charging Features
Modern EV chargers are more than just power outlets; they are sophisticated smart devices. These advanced features rely on a stable internet connection, which has become one of the key requirements for a modern home EV charger setup.
Why Modern Chargers Need a Wi-Fi Signal
A Wi-Fi connection unlocks the full potential of a smart EV charger. It allows the charger to communicate with a mobile app and the manufacturer’s network. Technologically advanced solutions from providers like TPSON use this connectivity for a range of powerful functions. An EV owner can manage their charger remotely and optimize their charging routine.
Key features that require Wi-Fi include:
- Over-the-Air (OTA)-Updates: The charger can automatically receive software updates to improve performance and add new features without a technician visit.
- Fernverwaltung: An EV owner can start, stop, and monitor charging sessions from anywhere using a smartphone app.
- Ladungsterminierung: This allows the EV to charge during off-peak hours when electricity rates are lowest, saving money on utility bills.
- Ferndiagnose: Technicians can diagnose issues with the charger based on real-time data, often resolving problems without a site visit.
How to Test Signal Strength at Your Parking Spot
Before installation, it is crucial to verify the Wi-Fi signal at the proposed charger location. A weak or nonexistent signal will prevent smart features from working correctly. An owner can perform a simple test.
- Take a smartphone to the exact spot where the EV charger will be installed.
- Connect the phone to the home’s Wi-Fi network.
- Check the Wi-Fi icon. Two or three bars usually indicate a stable enough connection.
- Try browsing a website or streaming a short video to confirm the connection is reliable.
Solutions for Poor Wi-Fi Coverage
If the signal at the desired location is weak, several solutions can extend the home network to reach the charger. The best method depends on the distance and any obstacles between the router and the parking spot.
“I just use a mesh and it reaches the EV charger good enough. It’s just on the edge of my WiFi range. After years of powerline adapters and boosters and running cables the mesh made all the wifi problems go away.”
This experience highlights how modern solutions can solve connectivity challenges. For many properties, a mesh Wi-Fi system is a highly effective, future-proof option. These systems use multiple units placed around the home to create a single, seamless network with excellent coverage. Other options include Wi-Fi extenders, which are affordable for shorter distances, or powerline adapters that use the home’s electrical wiring to transmit the internet signal. An electrician or a networking professional can recommend the best solution based on the specific requirements of the property.
What If My Home Doesn’t Meet a Requirement?
Discovering that a home does not immediately meet the requirements for an EV-Ladegerät is not a dead end. Solutions exist for nearly every obstacle, from low electrical capacity to parking challenges. Understanding these options helps an EV owner navigate the path to a successful installation.
Solution for Low Electrical Capacity
A home with an older or maxed-out electrical panel can still support an EV. The solution often involves either a service upgrade or smarter technology.
What Is an Electrical Panel Upgrade?
An electrical panel upgrade involves replacing the home’s main breaker box with a new one that has a higher amperage capacity. This increases the total electrical capacity available for the entire property, creating room for a new, high-power EV charger circuit.
The Process of Upgrading Your Service
Upgrading a panel is a major electrical project. An electrician will coordinate with the local utility company to temporarily disconnect power. They then replace the old panel and breakers. The process requires permits and inspections to comply with local regulations.
Costs and Timelines for Panel Upgrades
The cost and timeline for a panel upgrade vary significantly. Factors include the complexity of the job and local labor rates. The process can take anywhere from a few days to several weeks, depending on utility company schedules and inspection availability.
Using Smart Chargers with Load Management
A panel upgrade is not always necessary. Technologically advanced EV charging solution providers like TPSON offer an EV charger with dynamic load management. This technology avoids overloading a circuit.
A smart charger with load management works by:
- Monitoring the home’s total electrical demand in real time.
- Calculating the available spare capacity after accounting for other appliances.
- Adjusting the EV charging power automatically to stay within safe limits, preventing tripped breakers and ensuring compliance with safety regulations.
This feature makes an EV charger installation possible even when the panel’s capacity is limited.
Solution for No Off-Street Parking
For residents without a private driveway or garage, installing a personal EV charger is challenging but not impossible. Success depends on local regulations and available public infrastructure.
Researching Local City Ordinances
The first step is to research local city regulations. Many municipalities have specific rules about running cables across public sidewalks or installing equipment at the curbside. These regulations are in place for public safety.
Exploring Curbside Charging Solutions
Some cities are pioneering innovative solutions. Programs like those in Westminster and Oxfordshire show what is possible. These initiatives use lamppost conversions or partnerships with commercial operators to install on-street chargers for residents. Exploring these local regulations can reveal opportunities.
Using Public Charging as Your Main Method
If a home installation is not feasible, using the public charging network becomes the primary strategy. This approach requires planning an EV charging routine around chargers located at workplaces, shopping centers, or dedicated charging hubs.
Solution for Landlord or HOA Denials
Navigating denials from landlords or Homeowners’ Associations (HOAs) requires persistence and a clear strategy. Understanding legal rights and local regulations is key.
Verständnis der “Right-to-Charge”-Gesetze
Some regions have “Right-to-Charge” laws or similar regulations. These regulations may prevent landlords or HOAs from unreasonably restricting an EV charger installation. An EV owner should research these specific regulations.
How to Present Your Case Effectively
A professional proposal increases the chance of approval. It should detail the installation plan, confirm the use of a licensed electrician, and highlight how the charger adds value to the property. Following all HOA regulations is crucial.
Negotiating a Compromise for Installation
If an initial request is denied, negotiation may be possible. A renter or owner could offer to cover all costs, assume liability through insurance, and agree to restore the property to its original condition upon moving. This addresses common concerns and shows a commitment to following all regulations for the charger installation.
Choosing the Right EV Charger for Your Home
Ein EV-Besitzer muss das richtige Ladegerät auswählen for their home and lifestyle. The choice between a basic Level 1 charger and a more powerful Level 2 charger depends on daily driving habits, vehicle battery size, and budget. Understanding the differences is key to a satisfying EV ownership experience.
Level 1 Charging: The Plug-and-Play Option
Level 1 charging is the most basic method for powering an EV. It offers simplicity but comes with significant limitations.
What Is a Level 1 Charger?
A Level 1 charger is essentially a portable cord that plugs into a standard 120-volt household outlet. Most electric vehicles include one of these chargers from the manufacturer. It requires no special installation, making it a true plug-and-play solution for any home with a standard electrical outlet near the parking spot.
Pros: No Installation, Low Initial Cost
The primary advantage of a Level 1 charger is its convenience and low cost. There are no installation expenses since it uses an existing wall socket. This makes it an excellent temporary or backup charging option for an EV owner.
Cons: Extremely Slow Charging Speeds
The major drawback of Level 1 charging is its extremely slow speed. This type of charger adds only about 3 to 5 miles of range per hour of charging. For an EV with a large battery, a full charge could take several days, making it impractical for drivers who cover long distances daily.
Level 2 Charging: The Gold Standard for Home Use
A Level 2 EV charger represents the ideal balance of speed and cost for most home charging needs. It is the most common type of dedicated home electric car charger.
What Is a Level 2 Charger?
A Level 2 EV charger operates on a 240-volt circuit, similar to a large appliance like an electric dryer. This higher voltage allows it to charge an EV significantly faster than a Level 1 charger. A EV-Schnellladegerät of this type can fully charge most EVs overnight.
Pros: Fast, Convenient Overnight Charging
The speed of a Level 2 charger is its main benefit. It provides fast, reliable charging that easily replenishes a battery overnight, even after a long day of driving. This makes it the perfect solution for the daily needs of most EV drivers. A fast EV charger ensures the vehicle is always ready to go each morning.
Cons: Requires Professional Installation
Unlike a Level 1 charger, a Level 2 EV charger requires professional installation. An electrician must install a dedicated 240-volt circuit from the home’s electrical panel to the charger’s location. The average cost for this installation is around $1,000, though it can vary.
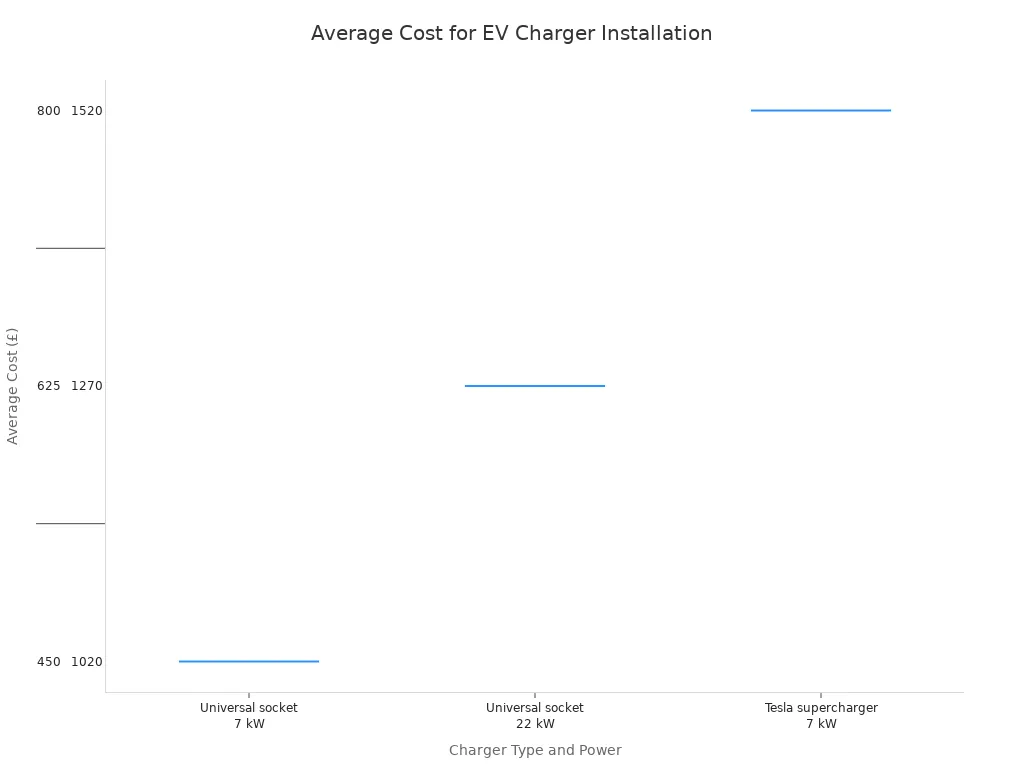
How to Decide Which Charger Level Is for You
Choosing the right EV charger involves assessing personal needs and vehicle specifications.
Bewertung Ihrer täglichen Fahrbedürfnisse
An EV owner should consider their daily commute. If they drive less than 30-40 miles per day, a Level 1 charger might suffice for overnight replenishment. Drivers with longer commutes or less predictable schedules will find a Level 2 fast EV charger essential for their home.
Factoring in Your Vehicle’s Battery Size
The size of the EV’s battery also plays a role. Vehicles with larger batteries take much longer to charge. A Level 2 charger is almost a necessity for these vehicles to ensure a full charge in a reasonable timeframe.
Hardwired vs. Plug-In Level 2 Chargers
Level 2 chargers come in two main types: hardwired and plug-in. A hardwired electric car charger is connected directly to the circuit, while a plug-in model connects to a 240-volt outlet. Technologically advanced providers like TPSON offer both types of this electric car charger.
| Merkmal | Festverdrahtetes Level-2-Ladegerät | Plug-in Level 2 Charger (NEMA 14-50) |
|---|---|---|
| Safety (GFCI) | Avoids nuisance tripping because internal GFCI is sufficient. | Often requires an external GFCI breaker, which can lead to nuisance tripping if the charger also has an internal GFCI. |
| Leistung | Generally charges faster. | Typically charges slower. |
| Elektrische Probleme | Less prone to electrical issues. | Can cause electrical issues. |
| Genehmigungen | May require less permitting related to GFCI. | Requires more permitting, especially for GFCI. |
A hardwired installation is often preferred for its reliability and slightly better performance, making it a robust choice for a permanent home EV charger.
The Home EV Charger Installation Process Explained
Die home EV charger installation process involves several clear steps, from finding an expert to the final checks. Understanding this installation process ensures a safe and efficient setup for any EV owner. Following a structured approach guarantees that the new charger meets all technical requirements and safety standards.
Step 1: Finding a Qualified Electrician
Selecting the right professional is the most important decision in the entire installation process. This is not a standard electrical job; it requires specific expertise.
Why a Certified Installer Is Essential
An EV charger installation must be performed by a Elektrofachkraft to ensure it adheres to strict safety standards. A qualified installer possesses specialized training for EV charging equipment. Homeowners should look for professionals with credentials demonstrating their expertise.
Key qualifications to look for include:
- A formal, advanced award (e.g., Level 3) specifically for the installation and commissioning of EV charging equipment.
- Verifiable knowledge of the national code of practice for EV charger installation.
- Membership in a government-approved Competent Person Scheme, which confirms their work meets required safety standards.
This level of certification ensures the electrician can safely handle the high-power requirements of an EV charger.
Where to Find Reputable Installers
Reputable installers can be found through several reliable channels. Technologically advanced EV charging solution providers like TPSON often maintain a network of approved installers. Additionally, professional electrical trade organizations list certified members on their websites. These sources help an EV owner connect with electricians experienced in EV charger installation.
Die Bedeutung des Einholens mehrerer Kostenvoranschläge
An EV owner should obtain at least three quotes before choosing an installer. This allows for a comparison of not just price, but also the scope of work, proposed materials, and timelines. A detailed quote provides insight into the electrician’s professionalism and understanding of the project.
Step 2: The Site Survey and Quote
A thorough site survey is a critical part of the installation process. It allows the electrician to create an accurate and comprehensive quote for the home EV charger installation.
What Happens During a Site Survey?
During a site survey, the electrician inspects the home’s electrical system. They will check the main panel’s capacity, identify a suitable location for the new circuit breaker, and plan the wiring route to the desired charger location. This assessment determines the full scope of the installation.
How to Read Your Installation Quote
A proper quote breaks down all costs. It should clearly list the price for the charger unit, labor charges, and materials like wiring and conduit. This transparency helps the EV owner understand exactly what they are paying for.
Identifying Potential Hidden Costs
A site survey helps identify factors that can increase the cost of an installation. Long wiring runs, the need to trench underground for a driveway charger, or repairs to finished walls can add to the final bill. A good electrician will discuss these potential costs upfront.
Step 3: Permitting and Utility Approvals
Navigating the required approvals is a key step in the installation process. A qualified electrician manages this aspect to ensure full compliance.
Does Your EV Charger Installation Need a Permit?
Whether an installation requires a permit often depends on the parking situation.
- An installation at a home with off-street parking, like a garage or driveway, generally does not require extensive planning permissions from local councils.
- An installation for on-street parking, however, requires permission from local planning and highway authorities for any solution that crosses a public pavement.
Even with rule changes, on-street solutions for an EV charger demand formal approval.
The Electrician’s Role in the Permitting Process
The certified electrician is responsible for the permitting part of the installation process. They will determine which permits are necessary, submit the required applications, and ensure the final installation passes inspection. This service guarantees the home EV charger project complies with all local regulations and safety standards.
Step 4: The Installation Day
With the planning complete, the installation day is the final step toward convenient home charging. A professional installation ensures the EV charger operates safely and efficiently for years to come.
How Long Does the Installation Take?
A standard EV charger installation is surprisingly quick, often taking just two to four hours on the day. The total time from the initial quote to the final installation, however, can vary. Homeowners should plan for a process that may span several weeks.
From quote to installation, the majority of installations go ahead within 4 weeks. If you live in Scotland or south west England, it may take a little longer. Wait times can differ depending on whether there is any extra work required before your installation. This may include any necessary DNO work, site preparation, electrical work or gathering relevant permissions.
For straightforward jobs, the timeline can be much shorter. Some providers can complete an EV charger installation in the same week, provided the homeowner completes all pre-installation forms promptly and engineer availability allows. In general, EV owners can expect a timeline of a few weeks.
- Trusted engineers can get you charging in as little as a few weeks.
- You could be charging in as little as 3 weeks by following their steps.
What to Expect on the Day of Installation
On the day of the installation, the electrician will first confirm the plan with the homeowner. They will review the agreed-upon location for the charger and the planned wiring route. For safety, the electrician will need to shut off the main power to the house for a portion of the installation. The homeowner should prepare for a temporary power outage. The electrician will then mount the EV charger, run the necessary wiring from the panel, and install the new dedicated circuit.
Final Inspection and System Walkthrough
After the physical installation is complete, the electrician will restore power and test the new charger to ensure it is functioning correctly. They will conduct a final inspection of their work, verifying that every connection is secure and compliant with all safety codes. The final, crucial part of the installation is the system walkthrough. The installer will demonstrate how to use the charger, including how to handle the cable and plug in the EV. For a smart charger, this walkthrough is especially important. TPSON is a technologically advanced electric vehicle charging solution provider, and their installers will guide the EV owner through connecting the charger to Wi-Fi and using the mobile app to manage charging schedules and monitor the EV. This ensures the owner can take full advantage of their new charger from day one.
Understanding the Costs of an EV Charger Installation
Budgeting for a home EV charger installation requires understanding several cost components. The total price is more than just the charger unit; it includes labor, materials, and potential electrical upgrades. An EV owner can create an accurate budget by breaking down these expenses.
Breaking Down the Total Cost
The final cost of an EV charger installation depends on the specific needs of the home and the chosen equipment. A clear breakdown helps manage expectations.
The Price of the Charger Unit
The EV charger itself is the first major expense. Prices for Level 2 chargers vary by brand, features, and power output. Technologically advanced providers like TPSON offer a range of models to suit different EV needs. The cost for popular units typically falls between $500 and $700.
| Marke | Preis |
|---|---|
| ChargePoint | Around $700 |
| JuiceBox | Around $600 |
| Wallbox | Around $500 |
Standard Installation Labor Costs
Professional installation is essential for a safe and compliant setup. Standard labor costs cover the electrician’s time to mount the charger, run wiring from the panel, and install a new dedicated circuit. This part of the installation ensures the home’s electrical supply can safely power the new EV charger.
Additional Costs: Trenching, Conduit, and Wiring
The complexity of the installation can add to the cost. A long distance between the electrical panel and the charger requires more wiring and conduit, increasing material and labor expenses. If the charger is located away from the home, trenching may be necessary to bury the electrical supply line.
The Cost of an Electrical Panel Upgrade
If a home’s existing electrical supply is insufficient, a panel upgrade is the largest potential cost. This major project increases the home’s total electrical capacity, ensuring the supply can handle the sustained load of an EV. An upgrade guarantees the electrical supply is robust enough for the charger.
Finding Savings: Rebates, Tax Credits, and Incentives
An EV owner can significantly lower the cost of an EV charger installation by taking advantage of various financial incentives. These programs make home charging more accessible.
Federal Tax Credits for EV Chargers
The federal government offers a tax credit to help offset the cost of purchasing and installing a home EV charger. This incentive, renewed under the Inflation Reduction Act, can provide substantial savings.
Key details of the Alternative Fuel Refueling Property Tax Credit include:
- It covers 30% of the equipment and installation costs.
- The maximum credit is capped at $1,000 for individuals.
- Eligibility is often tied to living in specific low-income or rural census areas.
- Taxpayers must file Form 8911 with their tax return to claim the credit.
Rabatte für staatliche und lokale Behörden
Many state and local governments offer their own rebates for an EV charger installation. These programs vary widely by location. An EV owner should research incentives available in their specific area to maximize savings on their new charger.
Anreizprogramme der Versorgungsunternehmen
Local utility companies are another excellent source of savings. Many offer rebates or special rates for EV owners who install a home charger. These programs help manage the new demand on the electrical supply and encourage charging during off-peak hours, benefiting both the EV owner and the power grid. The utility’s electrical supply is a key part of the EV ecosystem.
Most single-family homes are ready for a Level 2 EV charger. An EV owner’s first step involves checking their home’s electrical panel and parking situation. Securing permission is the next critical task for renters or those in an HOA. The final step for any EV owner is contacting a certified electrician for their EV. A professional provides a quote to begin the home EV charger installation. This installation ensures a safe and reliable charger. This EV charger will power their EV for years, making this charger a key asset for the home.
FAQ
How long does a home EV charger installation take?
A standard installation typically takes two to four hours on the scheduled day. The entire process, from getting a quote to the final installation, often spans a few weeks. This timeline allows for site surveys, potential utility work, and any necessary permitting.
Can an EV owner install a charger themselves?
No, a DIY installation is not recommended. An EV charger is a high-power device that requires a dedicated circuit. A certified electrician must perform the installation to ensure it meets all safety codes and operates correctly, preventing electrical hazards.
What if a home has an old electrical panel?
An older panel may require an upgrade to support an EV charger. Alternatively, an EV owner can choose a smart charger with load management. Technologically advanced providers like TPSON offer chargers that automatically adjust charging power to prevent overloading the home’s electrical system.
What is the main difference between Level 1 and Level 2 charging?
The key difference is speed.
- Stufe 1: Plugs into a standard outlet, adding only 3-5 miles of range per hour.
- Stufe 2: Uses a 240-volt circuit to charge much faster, making it possible to fully charge an EV overnight.
Is a Wi-Fi connection necessary for an EV charger?
A Wi-Fi connection is not required for basic charging. However, it is essential for unlocking smart features. Connectivity enables remote management, charge scheduling to save on electricity costs, and over-the-air software updates for improved performance and new features.
What is the first step for a condo owner wanting a charger?
A condo owner’s first step is to contact their homeowners’ association (HOA) or building management. They must review the community’s rules and get formal approval before proceeding. The HOA may have specific requirements for location, appearance, and installation.
How much does a Level 2 charger installation cost?
The total cost varies. It includes the charger unit (typically $500-$700), plus labor. Additional expenses can arise from long wiring runs, trenching for outdoor placement, or a necessary electrical panel upgrade. Getting multiple quotes from qualified electricians is recommended.





