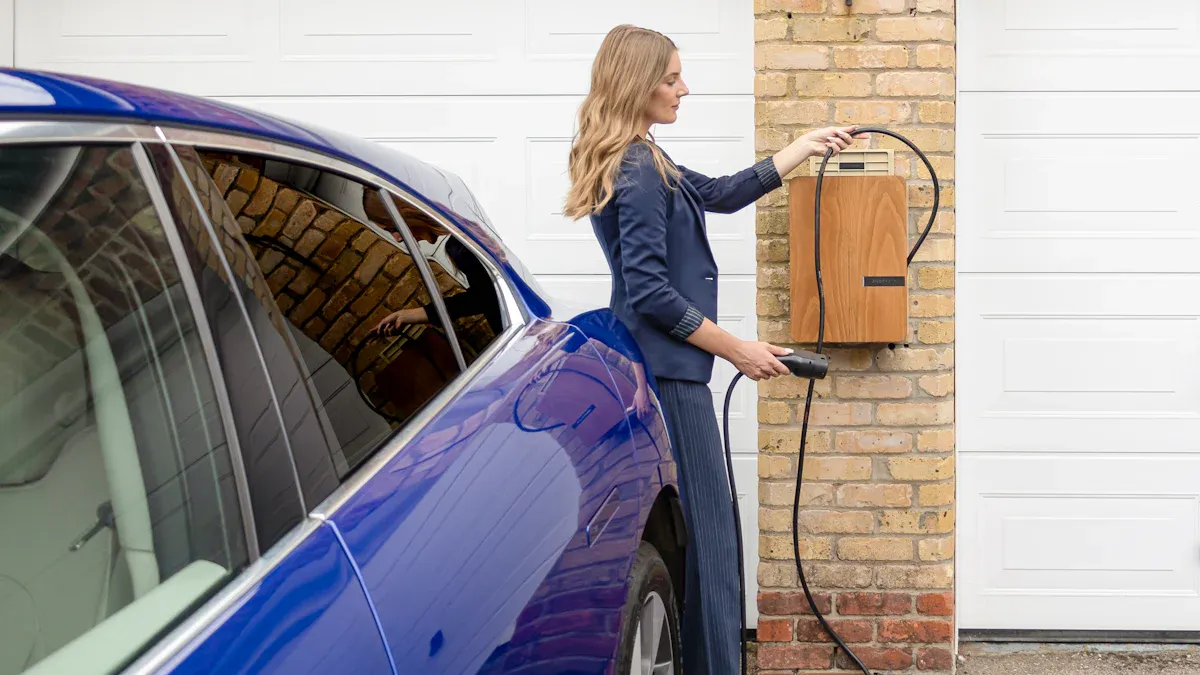
The decision to pick best ev charger requires careful consideration of your charging needs. An owner must choose the right ev charger by evaluating their vehicle, home, and daily driving needs. The best home charger aligns these factors for optimal performance. EV charger manufacturers, such as the technologically advanced TPSON, provide diverse EV charging solutions. These range from a stationary home ev charger to versatile portable ev chargers. Selecting the correct ev charger ensures faster charging and potential long-term savings.
Step 1: Match the EV Charger to Your Car and Home

Selecting the right home ev charger begins with understanding the relationship between your car, your home’s electrical system, and the types of chargers available. This initial step ensures compatibility and sets the foundation for an efficient charging experience.
Understanding Charging Levels
There are several types of electric car chargers, but for home use, the decision primarily comes down to Level 1 and Level 2.
Level 1 Charging (120V): The Slow but Simple Option
Level 1 charging uses a standard 120-volt household outlet. Most electric vehicles include a Level 1 cordset. This method requires no special installation. However, it is extremely slow. It adds only a few miles of range per hour of charging. This makes it a backup option or a solution for plug-in hybrids with small batteries.
Level 2 Charging (240V): The Home Standard
Level 2 is the most common and practical solution for home charging. These units use a 240-volt circuit, similar to an electric dryer. A Level 2 ev charger dramatically reduces charging time compared to Level 1. It makes overnight charging a reliable strategy for daily driving needs.
| Charging Level | Description | Charging Time (for a 60 kWh EV) |
|---|---|---|
| Level 1 | Standard 120V wall outlet | 24 to 40 hours |
| Level 2 | 240V outlet (home/public) | 6 to 12 hours |
| DC Fast Charging | Public high-power stations | ~30 minutes (to 80%) |
Decoding Charging Speed (kW and Amps)
An owner must understand charging speed and power output. Power, measured in kilowatts (kW), is the product of voltage (V) and amperage (A). For Level 2 chargers, higher amperage means faster charging speed.
Common Power Outputs: 16A to 48A
Level 2 chargers come in various amperages. Common options include 16A (3.8 kW), 32A (7.7 kW), 40A (9.6 kW), and 48A (11.5 kW). A higher amperage delivers more power to the car’s battery.
How Amperage Affects Charging Time
A higher power output directly translates to more miles of range added per hour. For example, an 11.5 kW charger can add approximately 44 miles of range in an hour. A 7.7 kW charger adds significantly less in the same amount of time. The optimal charging speed depends on daily mileage and how quickly a driver needs to replenish the battery.
Check Your Car’s Onboard Charger Limit
A crucial, often overlooked factor is the vehicle’s own limitation. The car’s onboard charger dictates the maximum rate of AC power it can accept.
Finding Your EV’s Maximum AC Charging Rate
An owner can find this specification in the vehicle’s manual or on the manufacturer’s website. It is typically listed in kW, such as 7.7 kW or 11.5 kW.
Pro Tip: Matching your charger’s output to your car’s maximum rate is key. A 48A (11.5 kW) charger will not charge a car with a 7.7 kW onboard limit any faster than a 32A (7.7 kW) charger would.
Why Your Car Sets the Speed Limit
Manufacturers limit the onboard charger’s capacity for several reasons. Faster onboard chargers are larger, heavier, and more expensive. These factors can increase the vehicle’s cost and reduce its overall range. Automakers balance charging speed with vehicle efficiency and price, which is why this internal limit exists.
Step 2: Assess Your Home’s Electrical System
After an owner understands the car’s limits, the next step is to evaluate the home’s electrical infrastructure. A home’s electrical system determines the maximum power available for home charging. This assessment is critical for a safe and effective installation.
The Need for a 240V Circuit
A Level 2 charger requires a 240-volt circuit to deliver power efficiently. This is the same voltage used by large appliances like electric stoves and clothes dryers.
Identifying Existing 240V Outlets
Some garages or utility rooms may already have a 240V outlet. These outlets are larger than standard 120V outlets and have a unique plug configuration. While using an existing circuit is possible, an electrician must first confirm it can safely support the continuous load of an EV charger.
Assessing Your Electrical Panel Capacity
The home’s main electrical panel, or breaker box, must have enough capacity to support a new, high-draw circuit. An owner should check if there are open slots in the panel. More importantly, the panel’s total service rating (e.g., 100A, 150A, or 200A) must be sufficient to handle the home’s existing electrical load plus the new home charge point.
Circuit Amperage Explained
The amperage of the circuit directly impacts charging speed. A higher amperage allows for a more powerful charger. Technologically advanced providers like TPSON offer solutions compatible with various circuit capacities.
30-Amp vs. 40-Amp vs. 50-Amp Circuits
Most Level 2 chargers are installed on dedicated circuits of 30, 40, or 50 amps. A 50-amp circuit, for instance, can support a 40-amp charger, delivering significantly faster speeds than a 24-amp charger on a 30-amp circuit. The choice depends on the home’s panel capacity and the driver’s charging speed requirements.
The National Electrical Code’s 80% Rule
Safety regulations require that a continuous load, like an EV charger, not exceed 80% of the circuit’s maximum rating. This rule prevents overheating and ensures system stability.
Safety First: This 80% rule is a critical safety standard. A charger must be rated for a lower amperage than the circuit it is on.
| Circuit Amperage | Maximum EV Charger Amperage (80% Rule) |
|---|---|
| 30-amp | 24 amps |
| 40-amp | 32 amps |
| 50-amp | 40 amps |
The Importance of a Professional Home Assessment
Attempting a DIY installation is extremely risky. A professional assessment guarantees safety, compliance, and optimal performance for your home ev charger.
Why You Should Hire a Licensed Electrician
A licensed electrician possesses the training to handle high-voltage wiring safely. Hiring a professional mitigates severe risks.
- Safety Hazards: Incorrect wiring can lead to electrical shocks, overheating, and accidental fires.
- Voided Warranties: Most manufacturers will void the charger’s warranty if it is not installed by a certified professional.
- Insurance Complications: A non-certified installation may void a home insurance policy in the event of an electrical fire.
- Regulatory Fines: DIY work often violates local building codes, which can result in significant fines.
What to Expect During an Installation Quote
During a home assessment, a licensed electrician will perform a load calculation on your electrical panel. They will identify the safest and most efficient path for running new wiring. The professional will also discuss the best location for the dedicated ev charger and provide a comprehensive quote covering all labor and materials.
Step 3: Choose Between Plug-In and Hardwired Installation
An owner’s next decision involves selecting the installation method for their home ev charger. This choice between a plug-in unit and a hardwired station impacts cost, power, and flexibility. The best option depends on the owner’s specific circumstances, including their housing situation and where to install your ev charging point.
Plug-In EV Chargers
Plug-in chargers connect to a high-voltage 240V outlet, much like a large appliance. They offer a balance of performance and convenience.
Pros: Portability and Simpler Installation
The primary advantage of a plug-in ev charger is its portability. An owner can easily unplug the unit and take it with them if they move. Installation is also simpler and often less expensive. An electrician only needs to install a compatible 240V outlet, not wire the charger directly.
Cons: Lower Maximum Power and Outlet Wear
Plug-in chargers have some limitations. They are typically capped at 40 amps of output to comply with electrical codes. This is because the outlet itself is a potential point of failure under higher, continuous loads. Repeatedly plugging and unplugging the unit can also cause wear on the outlet, potentially leading to a loose connection and overheating.
Common Plug Types: NEMA 14-50 and NEMA 6-50
Two outlet types are common for plug-in chargers:
- NEMA 14-50: This is the most popular choice. It has four prongs (two hot wires, one neutral, one ground) and is often used for electric ranges. It supports up to a 50-amp circuit, allowing for a 40-amp charger.
- NEMA 6-50: This outlet has three prongs (two hot wires, one ground) and is common for welders or other high-power tools. It also supports a 50-amp circuit.
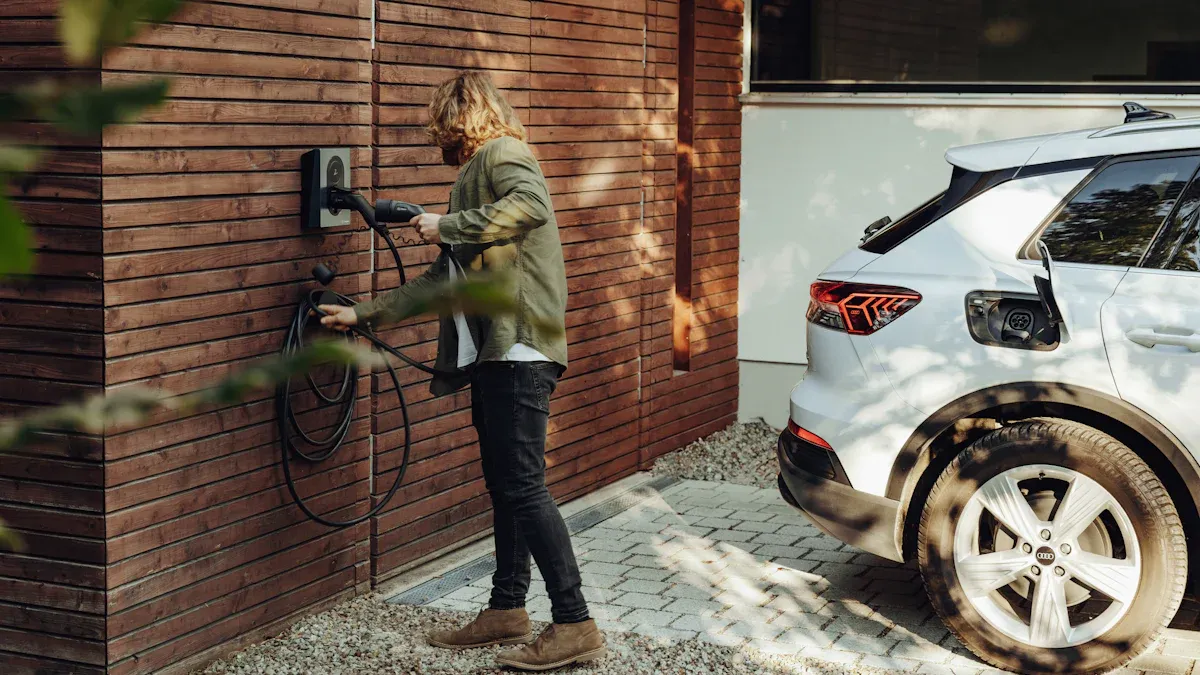
Hardwired EV Chargers
A hardwired charger is wired directly into the home’s electrical system by an electrician. This creates a permanent and dedicated connection.
Pros: Higher Power Capability and Weather Resistance
Hardwiring allows for higher power delivery. These chargers can support up to 48 amps (on a 60-amp circuit), enabling the fastest possible Level 2 charging speeds for compatible vehicles. The direct connection is also more robust and secure. Many hardwired units offer better weatherproofing, making them an ideal choice for outdoor installations.
Cons: Fixed Location and Professional Install Required
The main drawback is that a hardwired charger is a permanent fixture. It cannot be easily moved. The installation is also more involved and typically more expensive, as it requires an electrician to run conduit and connect the unit directly to the circuit.
How to Decide
The right choice depends on an owner’s living situation and installation location.
Considerations for Renters vs. Homeowners
- Renters: A plug-in charger is almost always the better option. It allows them to take their investment with them when they move. Getting a landlord’s permission to install a 240V outlet is often easier than getting approval for a permanent, hardwired fixture.
- Homeowners: Homeowners have more flexibility. If they plan to stay in their home long-term and want the fastest possible charging, a hardwired unit is an excellent investment.
Choosing for an Indoor Garage vs. Outdoor Driveway
Installation Tip: For outdoor installations, a hardwired charger is generally recommended. The direct electrical connection is better sealed against moisture, dust, and temperature changes, providing greater durability and safety compared to an exposed plug and outlet. An indoor garage can safely accommodate either type.
Step 4: Decide on Smart Features vs. Basic Functionality

An owner’s next decision is whether to invest in a “smart” charger or opt for a basic, “dumb” model. This choice balances upfront cost against long-term convenience and potential savings. Technologically advanced providers like TPSON offer a range of options to suit different user needs.
“Dumb” Chargers: The Simple Choice
A “dumb” or non-smart charger provides the essential function of charging an electric vehicle without any extra connectivity or features.
Core Function: Just Plug In and Charge
These chargers are straightforward. An owner plugs the connector into their vehicle, and charging begins immediately. The unit stops charging only when the car’s battery is full. There are no apps, Wi-Fi connections, or schedules to manage.
When Simplicity is the Best Option
A basic charger is an excellent choice for drivers who prioritize simplicity and a lower initial cost. If an owner’s utility company offers a flat electricity rate without time-of-use variations, the primary financial benefit of a smart charger is lost. Similarly, if a driver’s EV already has robust built-in charging controls, a simple home ev charger may be all that is needed.
The Advantages of a Smart EV Charger
Smart chargers connect to a home’s Wi-Fi network, unlocking a suite of advanced features accessible through a smartphone app.
Wi-Fi Connectivity and Mobile App Control
This connectivity is the gateway to a smart charger’s power. It allows an owner to remotely monitor and control their charging sessions from anywhere. Key functions available through an app include:
- Starting or stopping a charging session.
- Monitoring the vehicle’s current battery level.
- Receiving notifications when charging is complete.
- Adjusting charging preferences and schedules on the fly.
Scheduled Charging for Off-Peak Electricity Rates
One of the most significant benefits is the ability to schedule charging. Many utility providers offer time-of-use (TOU) tariffs with cheaper electricity rates during off-peak hours, typically overnight. A smart ev charger can be programmed to start charging only when these lower rates kick in, significantly reducing costs.
Energy Monitoring and Cost Tracking
Smart chargers provide detailed data on energy consumption. An owner can track exactly how much electricity their vehicle uses per session, week, or month. This data helps in calculating the precise cost of charging and understanding the vehicle’s energy efficiency.
Voice Control via Alexa and Google Assistant
For added convenience, many smart chargers integrate with popular voice assistants. An owner can use simple voice commands to start, stop, or check the status of their charging session without needing to open an app.
Is a Smart Charger Worth the Extra Cost?
The higher price of a smart charger is an investment in savings, convenience, and future technology.
Calculating Your Potential Energy Savings
The financial case for a smart charger is compelling for those on a time-of-use electricity plan. By shifting charging to off-peak periods, many EV owners can save hundreds of dollars annually compared to charging on a standard variable tariff.
Cost Savings Example: An EV owner who drives an average amount could see annual savings of around $195 just by using a smart charger to schedule charging during off-peak hours. For households with higher overall electricity use, the savings could be even greater.
Future-Proofing for Utility Programs and Updates
A smart charger prepares an owner for the future of energy management. Utilities are increasingly developing demand response programs that offer financial incentives to customers who allow their charging to be paused or slowed during periods of high grid stress. Smart chargers can automatically participate in these programs. They are also ready for advanced integrations like:
- Vehicle-to-Grid (V2G): Using the EV’s battery to supply power back to the grid.
- Dynamic Load Balancing: Adjusting charging speed based on the home’s total energy use to prevent overloading the electrical panel.
- AI-Powered Forecasting: Using algorithms to predict peak demand and optimize charging schedules automatically.
Step 5: Evaluate Key Physical Features and Durability
An owner must carefully consider the physical attributes of an EV charger. These features directly impact daily usability, long-term reliability, and safety. A well-built charger from a provider like TPSON ensures a seamless ownership experience.
Connector and Cable Type
The connector is the physical interface between the charger and the vehicle. In North America, two primary standards exist, creating a choice between a tethered or untethered ev charger setup.
The Universal J1772 Connector
The J1772 connector has long been the standard for most electric cars and plug-in hybrids in North America, with the notable exception of Tesla. Its universal adoption means a charger with this connector can power a wide range of vehicles, making it a versatile choice for households with multiple EV brands.
Tesla’s NACS Connector and Adapters
Tesla developed its own connector, now known as the North American Charging Standard (NACS). While originally exclusive to Tesla vehicles, NACS is becoming the dominant standard. Major automakers like Ford and General Motors have announced plans to adopt it for their EVs starting in 2025.
- For Tesla Owners: A charger with a native NACS plug offers the most convenience.
- For Non-Tesla Owners: A J1772 charger is standard. However, an adapter allows a J1772 charger to power a Tesla, and vice-versa.
This evolving landscape makes the choice between a tethered or untethered ev charger more relevant, as an untethered unit could allow for swapping cables if standards change.
Cable Length and Management
The charging cable is a component an owner will handle every day. Its length and how it is stored are crucial for convenience and safety.
Choosing the Right Cable Length (18-25 feet)
Most home chargers come with cables ranging from 18 to 25 feet. The ideal length depends on the garage layout and parking habits.
Measurement Tip: An owner should measure the distance from the planned charger location to the vehicle’s charge port. They should account for different parking scenarios, like backing in versus pulling in straight. A longer cable provides more flexibility, but a cable that is too long can be cumbersome and a trip hazard.
The Importance of Holsters and Cable Holders
Proper cable management is essential. A holster protects the connector plug from dust, moisture, and damage when not in use. A cable holder or hook keeps the cord neatly wrapped and off the garage floor, preventing trips and protecting the cable from being run over.
Durability and Weatherproofing
A home charger is a significant investment. Its construction quality determines its lifespan, especially if installed outdoors.
Understanding NEMA Enclosure Ratings (NEMA 3R vs. NEMA 4)
The National Electrical Manufacturers Association (NEMA) rating indicates a charger’s resistance to environmental elements.
- NEMA 3R: Rated for outdoor use. It protects against falling rain, sleet, and external ice formation.
- NEMA 4: Offers a higher level of protection. It is watertight, protecting against hose-directed water, making it ideal for uncovered driveways or areas with harsh weather.
Build Quality, Materials, and Certifications (UL Listed)
An owner should look for chargers made from robust, high-quality materials. More importantly, they must ensure the charger is certified by a Nationally Recognized Testing Laboratory. UL certification is a critical safety benchmark. It confirms the product has undergone rigorous testing and meets accepted safety standards for electrical equipment. This certification is often a legal requirement for sale and provides peace of mind that the device is safe for home use.
Step 6: How to Pick the Best EV Charger Based on Total Cost and Value
An owner’s final step to pick the best EV charger involves a comprehensive analysis of total cost and long-term value. This evaluation goes beyond the sticker price to include installation expenses, potential savings from incentives, and the charger’s overall quality. Making an informed decision requires balancing these financial elements to find the best home charger for one’s budget and needs.
Upfront Charger Costs
The initial purchase price of a home EV charger varies significantly based on its features and capabilities. Understanding these price considerations helps an owner align their budget with their desired functionality.
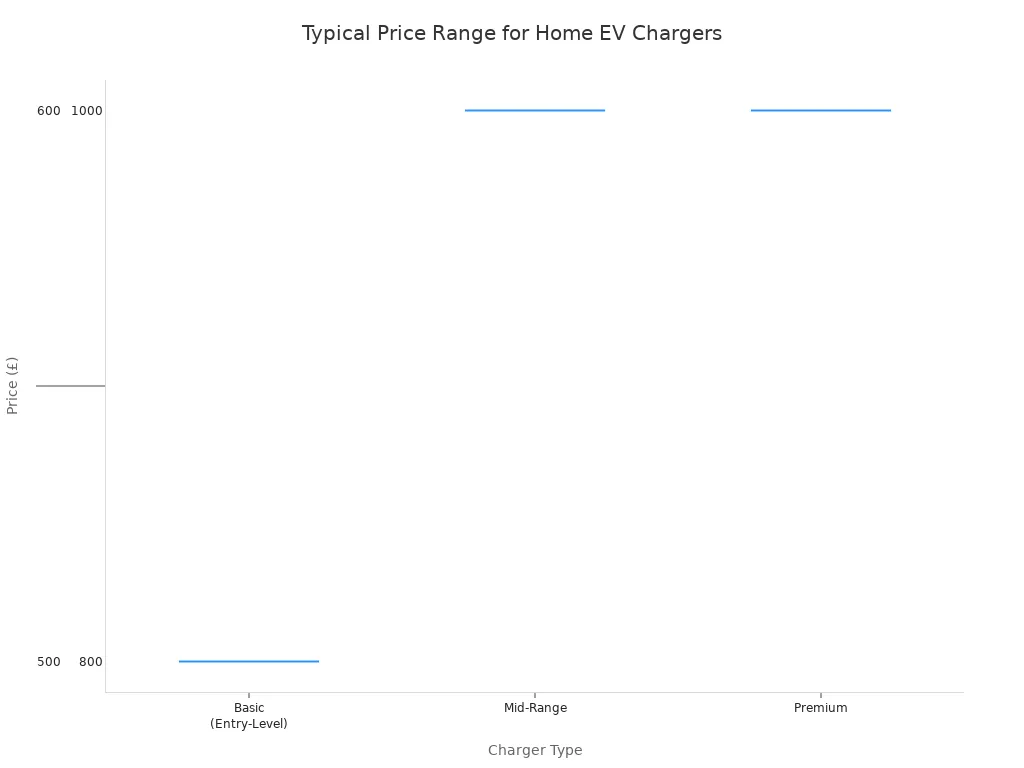
Price Ranges for Level 2 Chargers
Level 2 chargers fall into distinct price brackets. Basic models offer core functionality, while premium units provide advanced smart features and higher power outputs.
| Charger Type | Typical Price Range |
|---|---|
| Basic (Entry-Level) | $500–$700 |
| Mid-Range | £800–£1,200 |
| Premium | $1,500+ |
What Features You Get at Different Price Points
The price of a charger directly correlates with its feature set.
- Basic ($500–$700): These are typically non-smart, “dumb” chargers. They provide safe, reliable charging without Wi-Fi connectivity or app control.
- Mid-Range (£800–£1,200): This category includes most smart chargers. An owner gets Wi-Fi connectivity, app-based scheduling for off-peak rates, and energy monitoring. Technologically advanced providers like TPSON offer excellent value in this range.
- Premium ($1,500+): Premium models often feature higher power outputs (up to 48A), premium build materials like metal casings, advanced load management, and sometimes even integrated payment systems for commercial use.
Factoring in Installation Costs
Installation is a significant part of the total cost. These expenses depend on the installation type and the home’s existing electrical setup.
Typical Cost to Install a 240V Outlet
For a plug-in charger, an electrician must install a 240V outlet. The cost for this service is generally lower than a full hardwiring job, as it involves less labor and materials.
Estimated Costs for Hardwiring a Charger
Hardwiring a Level 2 EV charger typically costs between £500 and £2,500. This wide range reflects several factors:
- The condition of the electrical panel.
- The distance from the panel to the charger location.
- The need for any panel upgrades or trenching.
- Local permit fees.
Labor costs for a professional electrician can range from £500 to £2,000, depending on the installation’s complexity.
Finding Rebates, Credits, and Long-Term Value
An owner can significantly reduce the total cost by taking advantage of available incentives and focusing on long-term value.
Federal, State, and Local Incentives
Governments often provide incentives to encourage EV adoption. Federal tax credits are sometimes available for the purchase and installation of a home charging station, effectively lowering the net cost. An owner should research current federal, state, and local programs.
Utility Company Rebate Programs
Many electricity providers offer their own rebates for purchasing a qualified smart charger. These programs help offset the upfront cost and encourage charging during off-peak hours to stabilize the grid.
Evaluating Warranty, Customer Support, and Brand Reputation
Long-term value extends beyond the initial price. An owner should evaluate:
- Warranty: A strong warranty (typically 3 years) protects the investment.
- Customer Support: Responsive support is crucial if issues arise.
- Brand Reputation: A reputable brand ensures a quality, certified product.
An owner’s final decision to pick best ev charger rests on a few key steps. An owner must first confirm their car’s maximum AC charging rate and their home’s electrical capacity. Then, they select an installation type and decide if smart features meet their needs. Finally, they pick best ev charger by choosing a durable, certified unit with a strong warranty that fits their total budget.
The journey to pick best ev charger begins with one action: looking up the EV’s maximum AC charging rate. This anchors all other choices.
FAQ
What is the difference between Level 1 and Level 2 charging?
Level 1 charging uses a standard household outlet. It is very slow. Level 2 charging requires a 240V circuit, similar to a large appliance. It charges an EV much faster, making it the practical choice for most home charging needs.
Do I really need a smart charger?
A smart charger is valuable for owners with time-of-use electricity plans. It allows scheduled charging during cheaper, off-peak hours to reduce costs. Technologically advanced providers like TPSON offer smart chargers with robust energy management features. A basic charger is sufficient for those with flat electricity rates.
How do I find my car’s maximum charging speed?
An owner can find the vehicle’s maximum AC charging rate in the owner’s manual or on the manufacturer’s official website. This specification is typically listed in kilowatts (kW) and determines the fastest speed the car can accept from a Level 2 charger.
Is a plug-in or hardwired charger better for me?
The best installation type depends on an owner’s situation.
Plug-in chargers offer portability, making them ideal for renters. Hardwired chargers deliver higher power and better weather resistance, suiting homeowners who want the fastest charge or need an outdoor installation.
Why is professional installation so important?
A licensed electrician ensures a safe and compliant installation.
- It prevents serious safety hazards like electrical fires.
- It guarantees the work meets local electrical codes.
- It protects the charger’s warranty, which DIY installations often void.
What does the NEMA rating on a charger mean?
The NEMA rating indicates a charger’s durability against environmental elements. A NEMA 3R rating means the unit is protected from rain and suitable for most outdoor locations. A NEMA 4 rating offers superior, watertight protection against hose-directed water and harsh weather.





