
The future of UK EV charge points is rapidly advancing. New charging trends focus on wireless and ultra-fast electric vehicle charging. This innovation is vital for UK EV adoption, as a significant barrier exists for many potential EV owners.
Approximately 40% of UK households lack dedicated off-street parking, making home EV charging a considerable challenge.
Technologically advanced EV charger manufacturers, such as TPSON, are developing smart charging solutions to solve this. This new EV charging infrastructure makes EV charging convenient. It supports the national grid and accelerates the adoption of the electric vehicle. The technology behind each EV Charger and the wider network of EV charging points is reshaping the UK’s entire charging infrastructure for every EV.
Solving On-Street Parking: The Future of UK EV Charge Points
Solving the on-street parking puzzle is central to the future of UK EV charge points. The UK government is targeting a tenfold increase in chargers to 300,000 by 2030. This goal is supported by a £450 million fund for on-street and local EV charging points. Industry bodies like the Society of Motor Manufacturers and Traders (SMMT) are also advocating for a coordinated infrastructure plan. They want binding targets to ensure every region has accessible and affordable public charging. These initiatives directly address the needs of households without private driveways, a critical step for mass EV adoption. Innovative charging solutions are emerging to turn this vision into a reality.
Pop-Up Chargers: Power from the Pavement
Pop-up chargers offer a discreet and effective way to integrate charging infrastructure into the urban landscape. These devices remain hidden until needed, preserving the character of residential streets and public spaces.
How Retractable Bollards Work
Retractable bollards are charging stations that rise from the pavement when activated by a user’s app. After the charging session ends, they retract back into the ground, leaving the pavement clear. This design minimizes street clutter. Installation is surprisingly efficient.
This high deployment rate makes them a viable option for widespread adoption across the UK.
UK City Trials and Early Results
Several UK cities are already testing the viability of pop-up charging technology. These trials provide valuable data on user behavior and system reliability.
- Urban Electric Networks deployed Europe’s first fully retractable EV charger, the UEone, in Dundee. Eighteen of these app-controlled units are now permanently installed across the city.
- Companies like Fastned and Be.EV are also expanding the public charging network with new hubs in Glasgow and Manchester, respectively, signaling strong growth in the sector.
Benefits for Urban Aesthetics
One of the greatest advantages of pop-up chargers is their minimal visual impact. In historic towns and conservation areas, preserving the streetscape is a priority. Retractable charging stations achieve this by disappearing completely when not in use. This approach provides essential EV infrastructure without permanently altering the appearance of a neighborhood, making it a popular choice for local councils.
Lamppost Charging: Leveraging Existing Infrastructure
Lamppost charging is one of the most practical and scalable charging solutions for urban areas. It repurposes existing street furniture to provide widespread access to EV charging, accelerating the transition to electric mobility.
The Technology Behind Lamppost Conversion
The technology involves retrofitting existing street lampposts with integrated EV charging sockets. Companies can add a smart charging unit to the lamppost column, drawing power from its existing electrical connection. This method is ideal for overnight charging, typically providing speeds around 5-7kW. Users simply park their EV, connect with a standard cable, and initiate the charging session through an app.
Cost-Effectiveness and Scalability
Leveraging existing infrastructure dramatically reduces installation costs and time. There is no need for extensive civil engineering works or new grid connections. This makes lamppost charging a highly cost-effective way to rapidly expand the public charging network. The cost for drivers is also competitive compared to other public charging stations.
| Charger Type | Average Cost per kWh |
|---|---|
| Connected Kerb | ~45p |
| Ubitricity Lamppost | ~50p |
| Standard Public Charger | ~53p |
| Tesla Supercharger | 55p – 67p |
| IONITY | ~69p |
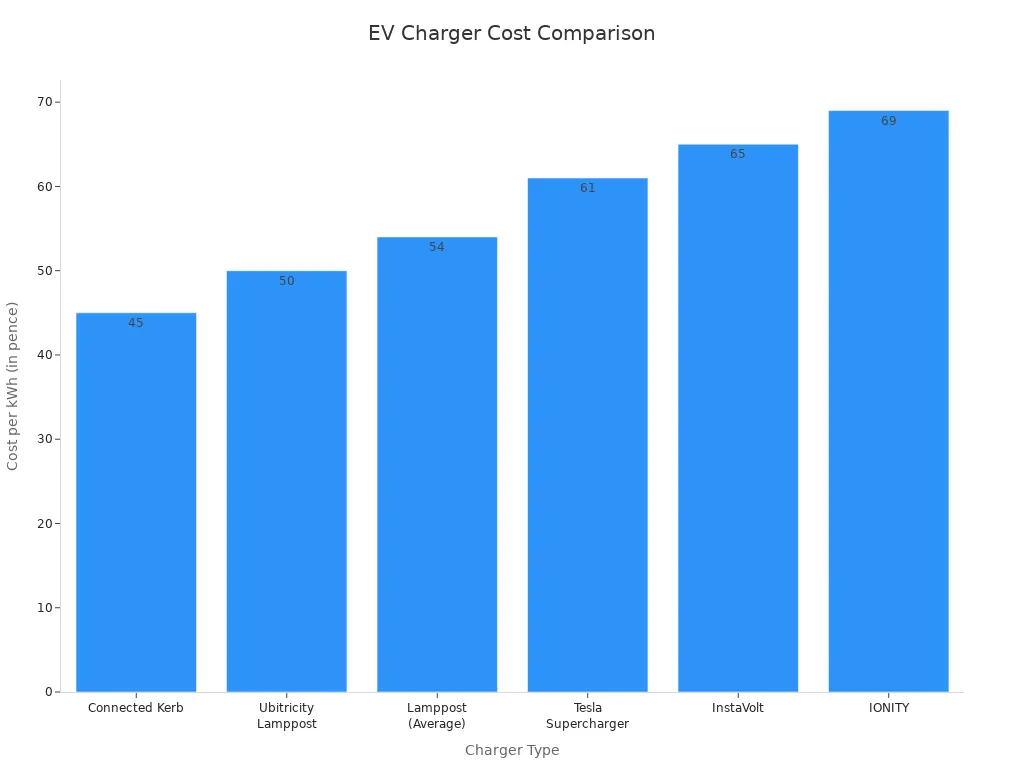
This affordability makes lamppost charging an attractive option for regular use.
Impact on Residential Streets
Lamppost chargers directly tackle the problem of on-street charging for residents. They provide a convenient and accessible option right outside people’s homes. This widespread availability helps build driver confidence and supports the broader adoption of electric vehicles. The presence of these charging stations transforms residential streets into a core part of the UK’s national EV infrastructure.
Pavement-Integrated Charging Solutions
Another innovative approach involves integrating charging technology directly into the pavement. These systems are designed to be almost invisible, providing power without creating obstructions or trip hazards.
Flush-Mounted Pavement Channels
This technology uses a metal channel installed flush with the pavement surface. The channel contains a power line that runs along the curb. EV owners use a special smart cable, often called a “lance,” to connect their vehicle to the channel. The system is designed to be completely safe, with the channel remaining de-energized until a valid connection is made.
User Experience and Accessibility
The user experience is simple and safe. Drivers park their EV, open a small lid on the channel, and insert their smart cable to begin charging. Because the cable plugs directly into the pavement at the curb, it eliminates the hazard of wires trailing across the sidewalk. This design is particularly beneficial for accessibility, ensuring that walkways remain clear for pedestrians, wheelchair users, and people with strollers.
Trojan Energy Case Study
A leading example of this technology in the UK is from Trojan Energy. Their system uses flush-mounted connection points along the street. EV drivers carry a personal “lance” to connect their car to the network. This innovative approach provides charging for multiple parking bays from a single power source. It keeps street furniture to a minimum and offers a clean, scalable solution for terraced streets where lampposts may not be suitably located for charging. This is another key part of the future of UK EV charge points.
Emerging Trends in Automated and Wireless Electric Vehicle Charging
The next wave of EV charging innovation is moving beyond the cable. New charging trends focus on automation and wireless power to make refueling an EV a seamless background activity. These emerging trends promise to remove friction from the user experience, preparing the UK for a future of even greater EV adoption. Technologically advanced providers like TPSON are key players in developing the smart solutions that underpin these advancements.
Inductive Wireless Charging Pads
Imagine parking your EV and having it start charging automatically. This is the promise of inductive wireless charging, a technology that transfers power through the air from a pad on the ground to a receiver on the vehicle.
The Science of Wireless Power Transfer
Wireless power transfer for an EV works much like a wireless phone charger, but on a much larger scale. It uses magnetic resonance to send electricity across a short distance between two induction coils. Current systems are highly efficient. They can achieve power transfer rates between 90-94%, which is very close to the efficiency of a traditional cable. This makes wireless charging a viable and practical technology.
Public Trials in UK Taxi Ranks
The UK is actively testing this technology in real-world scenarios. Nottingham is a leading example, where the city council has launched a trial for wireless charging at taxi ranks.
In this government-backed project, electric taxis park over 11 kW inductive pads embedded in the road. The system automatically begins charging, providing a convenient way for drivers to top up between fares. This public trial provides valuable data for future large-scale rollouts.
The Future of Wireless Home Charging
Wireless technology stands to revolutionize at-home EV charging. It eliminates the need to handle cables, a significant convenience for daily use. A driver would simply park in their designated spot, and the charging process would begin. While the installation cost of induction coils is currently a hurdle, the long-term benefit of effortless at-home EV charging is a powerful driver for this innovation.
Integration in Supermarket Parking Lots
The convenience of wireless charging extends to public spaces. Supermarkets and retail centers are ideal locations for this technology. Shoppers could park their EV, and the vehicle would gain range while they are in the store. This form of public charging turns dwell time into charging time, making EV ownership even more practical for everyday life.
Robotic Charging Arms
Another key trend in automated charging involves robotics. Automated systems can physically plug an EV in without any human intervention, offering unique benefits for accessibility and future vehicle fleets.
How Automated Charging Works
Companies like Hyundai and Li Auto are developing robotic charging arms for their electric vehicle models. Using 3D cameras, the robot identifies the EV’s charging port, retrieves the connector from the charging station, and precisely plugs it in. Once charging is complete, the arm retracts the cable. This entire process is fully automated.
Enhancing Accessibility for All Drivers
Robotic charging offers a major advantage for drivers with mobility challenges. It removes the physical effort of handling heavy charging cables, making EV charging stations more accessible to everyone. This inclusivity is a critical component of designing a fair and equitable public charging network.
Preparing for Autonomous Vehicle Fleets
This technology is also essential for the future of autonomous vehicles. Self-driving cars will need to navigate to charging stations and refuel themselves. Robotic charging arms provide the missing link, enabling an autonomous EV fleet to operate and recharge without human assistance.
The Standardization Challenge
For any new technology to succeed, it needs a common standard. Universal standards ensure that hardware from different manufacturers can work together seamlessly, which is vital for building a reliable national network of EV charging points.
Creating a Universal Wireless Standard
The lack of a single standard previously slowed the adoption of wireless EV charging. To solve this, the Society of Automotive Engineers (SAE) published the J2954 standard. This guideline establishes a technical specification for wireless power transfer, defining power levels up to 11 kW and ensuring interoperability. It also incorporates critical safety protocols based on standards like IEC 61851 and ISO 15118.
Cross-Manufacturer Compatibility
A universal standard means any compliant EV can use any compliant wireless charging station. This cross-manufacturer compatibility is crucial for driver confidence. It prevents a fragmented market where drivers have to search for specific brands of charging stations. This unified approach accelerates the rollout of public wireless charging infrastructure across the UK.
Speed and Stability: The UK EV Charging Infrastructure Evolution

The evolution of the UK EV charging infrastructure is not just about adding more chargers; it is about making them faster, smarter, and more integrated with the national grid. This next phase focuses on two critical goals: reducing charging times to rival gasoline refueling and ensuring the grid can handle the rising demand. These advancements are crucial for making the electric vehicle a practical choice for every driver in the UK.
Ultra-Rapid Charging Hubs (350kW+)
For drivers on long journeys, speed is essential. Ultra-rapid charging hubs, delivering 350kW of power or more, represent the pinnacle of high-speed EV charging technology. They are transforming the public charging experience.
The 350kW Power Benchmark
A 350kW charger is a game-changer for EV drivers. This power level can add over 200 miles of range in approximately 15 minutes to a compatible EV. This speed dramatically reduces waiting times and makes long-distance travel seamless. However, deploying these powerful charging stations requires significant planning. Site selection depends on several technical factors.
- Grid Connection: Securing an efficient connection to the high-voltage grid is essential. Planners must engage with the local Distribution Network Operator (DNO) early to identify available capacity.
- Electrical Capacity: A site must have sufficient electrical capacity to handle the increased load. A load balancer may be necessary to support the additional power demands of 350kW charging.
- Future-Proofing: The infrastructure design should account for future expansion, including additional chargers, battery storage, and even potential hydrogen refueling.
Liquid-Cooled Cable Technology Explained
Delivering 350kW of power generates immense heat. Standard charging cables would overheat and fail under such a load. The solution is liquid-cooled cable technology. A cooling fluid circulates through the cable and connector, actively drawing heat away from the components. This innovation allows the cables to remain relatively thin and lightweight while safely handling the high electrical current needed for ultra-rapid charging.
Expanding the UK’s Motorway Network
Major companies are rapidly expanding the UK’s network of ultra-rapid charging hubs along motorways. Moto is transforming service areas across England, Scotland, and Wales, aiming to install over 1,600 ultra-rapid chargers by 2030. Similarly, bp pulse plans to invest £1 billion in EV charging infrastructure, rolling out its Gigahubs™ in high-demand locations. These efforts are supported by specialist firms like The EV Network (EVN), which has raised £400 million to develop property and infrastructure for these advanced charging networks.
The “Gas Station” Experience Reimagined
Modern charging hubs are designed to be more than just a place to plug in. They are reimagining the traditional gas station experience for the EV era.
These new sites often feature multiple charging bays covered by canopies, along with amenities like coffee shops, lounges, and Wi-Fi. This creates a comfortable and convenient environment where drivers can relax while their EV gets a high-speed charge.
Vehicle-to-Grid (V2G) Technology
Vehicle-to-Grid (V2G) technology turns every EV into a small, mobile power station. This smart charging system allows an electric vehicle to not only draw power from the grid but also export it back, creating a two-way energy flow that offers powerful benefits.
How V2G Balances the National Grid
The UK national grid must constantly balance electricity supply and demand. V2G technology helps achieve this balance. During periods of high demand, parked and connected EVs can collectively discharge a small amount of their battery power back to the grid. During periods of low demand or high renewable energy generation, they can resume charging. This process helps prevent grid overload and reduces the need for fossil fuel power plants.
Creating a Revenue Stream for EV Owners
V2G participation creates powerful financial incentives for EV owners. By allowing their vehicle’s battery to be used for grid services, drivers can generate a significant income.
An EV owner in the UK could earn over £1,500 annually through V2G schemes. For households with high energy usage, such as those with solar panels, the savings could be even greater, potentially reaching up to £2,400 per year. This revenue stream, supported by government incentives, helps offset the cost of EV ownership.
Current V2G Trials and Participants
The UK is a global leader in V2G research and deployment. Numerous trials are underway involving energy suppliers, car manufacturers, and technology providers like TPSON, who develop the smart charging hardware. These projects test the real-world performance of V2G systems, gathering data on user behavior and grid impact. The results are paving the way for a commercial rollout of the technology.
The Role of Smart Energy Tariffs
Smart energy tariffs are the key that unlocks the financial benefits of V2G. These tariffs offer different electricity prices throughout the day, encouraging EV owners to charge when power is cheap and sell it back when it is expensive. Octopus Energy has pioneered this in the UK, launching the country’s first publicly available V2G tariff, known as ‘Octopus Power Pack’. This bundle provides a framework for drivers to easily participate in V2G and earn money from their EV.
Kinetic and Solar-Powered Charging
The future of charging infrastructure also involves harnessing renewable and ambient energy sources. Innovations in kinetic and solar power are creating new possibilities for sustainable and even off-grid charging solutions.
Capturing Energy from Braking Vehicles
Kinetic energy capture is an emerging technology that generates electricity from the movement of traffic. Special pads or ramps installed in the road surface compress as vehicles drive over them, converting the kinetic energy from braking or deceleration into usable electricity. This power can then be stored and used to supply nearby EV charging stations.
Solar Canopies in Charging Hubs
Many new public charging hubs feature large solar canopies. These structures serve a dual purpose: they protect drivers and their vehicles from the elements and generate clean electricity. The solar panels feed power directly to the charging stations or to an onsite battery storage system. This reduces the hub’s reliance on the grid and lowers the carbon footprint of every charging session.
Off-Grid Charging Possibilities
Combining solar power with battery storage opens the door to off-grid charging stations. These self-sufficient installations are ideal for remote or rural locations where grid connections are difficult or expensive. Government grants, including the EV chargepoint grant, can help fund these innovative projects. They ensure that a robust charging infrastructure is available across the entire UK, supporting the transition to electric mobility for everyone.
The Digital Backbone of Future Charging
The physical hardware of EV chargers is only one part of the equation. A sophisticated digital backbone powers the entire ecosystem, managing energy flow, payments, and user experience. These digital charging trends are making the UK network smarter and more efficient for every EV driver.
Smart Charging and Grid Management
Smart charging technology is the brain behind the brawn of the charging infrastructure. It intelligently manages how and when an EV draws power, providing critical benefits for grid stability and cost savings.
How Smart Charging Prevents Grid Overload
Smart charging directly addresses the challenge of increased electricity demand from the growing number of EV models. UK regulations mandate that new chargers avoid charging during peak hours by default. This shifts energy consumption to off-peak times when demand is lower and renewable energy is more plentiful. Trials like ‘Project Shift’ have shown that smart charging can reduce peak demand from EV charging by 80%, helping utility companies use existing infrastructure more efficiently and defer costly upgrades.
The Role of AI and Machine Learning
Artificial intelligence and machine learning are elevating smart charging capabilities. These technologies analyze vast datasets, including driver behavior, energy prices, and grid conditions. Based on this analysis, AI can predict future demand and automatically schedule charging for the most optimal times. Technologically advanced providers like TPSON are developing these solutions to create a responsive and predictive charging network.
Optimizing Charging for Cost and Carbon
Smart charging offers powerful financial incentives for EV owners. By automatically charging when electricity is cheapest, drivers can significantly lower their running costs.
A study by EY and Eurelectric indicates that smart charging solutions can save an EV owner over £10,000 over seven years. This optimization also aligns charging with periods of high renewable energy generation, reducing the carbon footprint of every journey. Government grants further support the adoption of this technology.
Interoperability and Roaming Networks
A seamless charging experience requires different networks to communicate effectively. Interoperability ensures that an EV driver can easily find, use, and pay for charging regardless of the provider.
The Push for a Single Payment System
One of the biggest frustrations for EV drivers is the fragmented payment landscape. Many public charging networks require their own app or membership card. This creates a significant barrier, especially for the 88% of UK adults who own a smartphone but may not want to manage dozens of apps. The industry is pushing toward a unified system where a single contactless payment method works across all chargers.
Seamless Cross-Network Charging
True interoperability allows for “roaming,” similar to a mobile phone network. This means a driver can use one account to access multiple different charging networks. This simplifies the public charging experience, removing the need to sign up for numerous services. Achieving this requires deep technical and commercial agreements between operators.
The Role of Open Charge Point Protocol (OCPP)
The Open Charge Point Protocol (OCPP) is the key to technical interoperability. It acts as a universal language that allows chargers and management systems from different manufacturers to communicate.
- It enables remote management of chargers.
- It supports smart charging features required by UK regulations.
- It ensures chargers from various brands can work together.
- It prevents operators from being locked into a single hardware supplier. This standard is fundamental to building a unified and future-proof national charging infrastructure.
The EV Charging App Ecosystem
Mobile apps have become the primary interface for EV drivers to interact with the public charging network. These apps are evolving from simple maps into comprehensive management tools.
From Finding a Charger to Paying
Modern EV apps guide drivers through the entire charging process. Users can locate nearby chargers, see real-time availability, check pricing, and initiate payment all within a single application. Apps like Zap-Map have become essential tools for navigating the UK’s charging landscape.
| App Name | Key Features |
|---|---|
| Zap-Map | Comprehensive UK map, real-time availability, journey planner, and in-app payment with Zap-Pay. |
| PlugShare | Global map with a large community providing user-generated reviews, photos, and real-time check-ins. |
| ChargePoint | Virtual waiting lists, charging status notifications, and integration for home and public charging. |
Integrating Charging with Vehicle Infotainment
The next evolution in charging trends sees app functionality moving directly into the car’s dashboard. Through Apple CarPlay and Android Auto, drivers can access charging maps and start sessions without touching their phones. This integration creates a safer and more seamless user experience for the EV driver.
Forecasting Demand with Data Analytics
The data collected by charging apps is invaluable. By analyzing usage patterns, operators can forecast demand with high accuracy. This allows them to identify high-traffic areas where new grants-supported chargers are needed and manage energy loads more effectively, ensuring the network grows in line with the number of EV drivers on the road.
The future of UK EV charge points is defined by innovation. Integrated on-street, automated, and ultra-fast charging solutions are making EV adoption more practical. These advancements eliminate key barriers, turning charging into a seamless background activity for every EV driver. The convergence of these technologies is creating intelligent and resilient charging networks across the UK. To accelerate this future of UK EV charge points, targeted policies are essential for expanding the network of EV charging points.
- Direct policies for charging stations show immediate positive effects.
- Subsidies for EV prices are less effective than infrastructure support.
This strategic approach supports the UK’s push for widespread EV adoption and ensures the growth of advanced charging solutions.
FAQ
What is smart charging?
Smart charging technology intelligently manages when an electric vehicle draws power. It automatically schedules charging sessions for off-peak hours. This process helps prevent grid overload, lowers costs for drivers, and maximizes the use of renewable energy.
How does Vehicle-to-Grid (V2G) work?
Vehicle-to-Grid (V2G) technology enables a two-way energy flow. An EV can not only draw power from the grid but also export it back during peak demand. This helps stabilize the national grid and can create a revenue stream for the EV owner.
What are the main on-street charging solutions in the UK?
Key on-street solutions include:
- Pop-up bollards that rise from the pavement.
- Lamppost chargers that leverage existing street furniture.
- Pavement-integrated channels that keep walkways clear.
These innovations provide convenient charging for residents without private driveways.
How fast is ultra-rapid charging?
Ultra-rapid chargers (350kW+) can add over 200 miles of range in about 15 minutes to a compatible vehicle. This technology uses liquid-cooled cables to handle the high power, making long-distance EV travel much more convenient.
Why is a single payment system important for EV drivers?
A single payment system eliminates the need for multiple apps and membership cards. It allows drivers to use any public charger with a simple contactless payment. This creates a seamless and user-friendly public charging experience for everyone.
What is the role of companies like TPSON in this evolution?
Technologically advanced providers like TPSON develop the smart hardware and software that power these new systems. They create the intelligent chargers and management platforms that enable features like smart charging, V2G, and seamless network integration.





